A method for electrochemical denitrification and dephosphorization of sewage
A sewage electricity and chemical technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of electrode surface scaling and passivation, low removal rate of ammonia nitrogen, etc., to slow down plate passivation, high Nitrogen and phosphorus removal rate, beneficial to the effect of waste resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
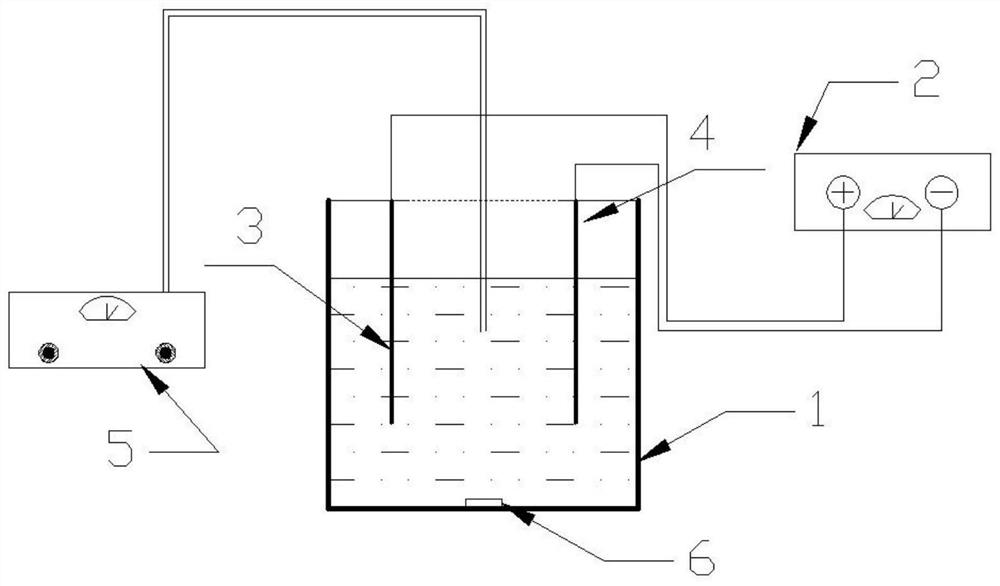
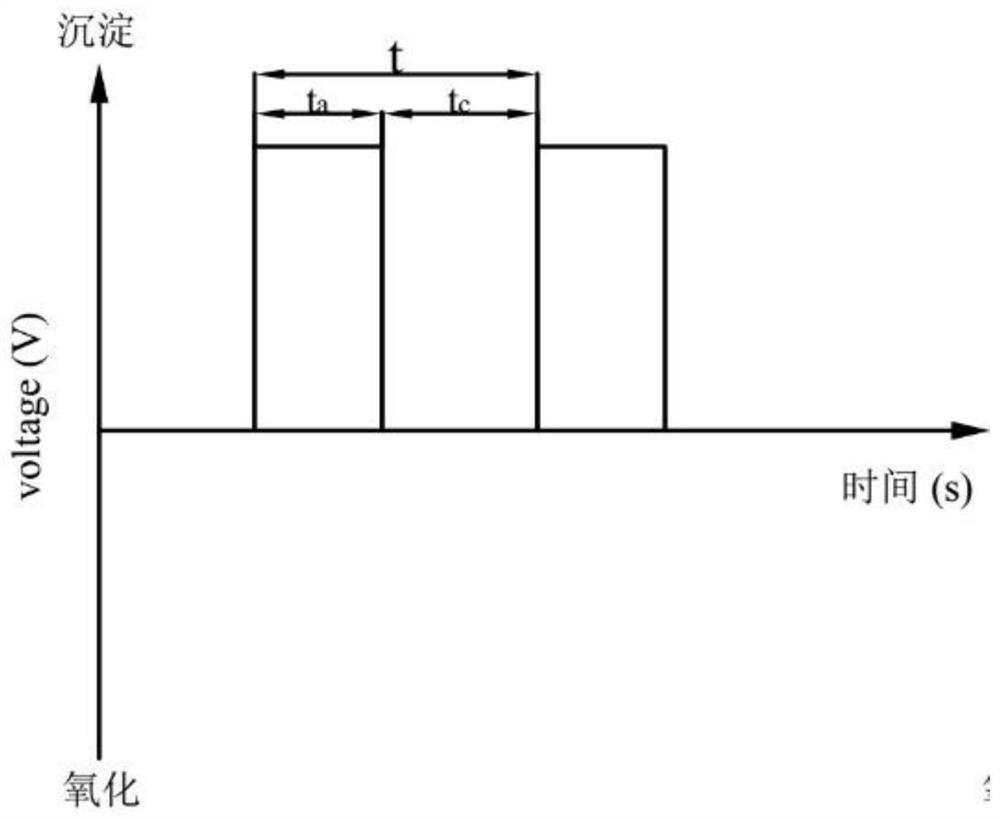
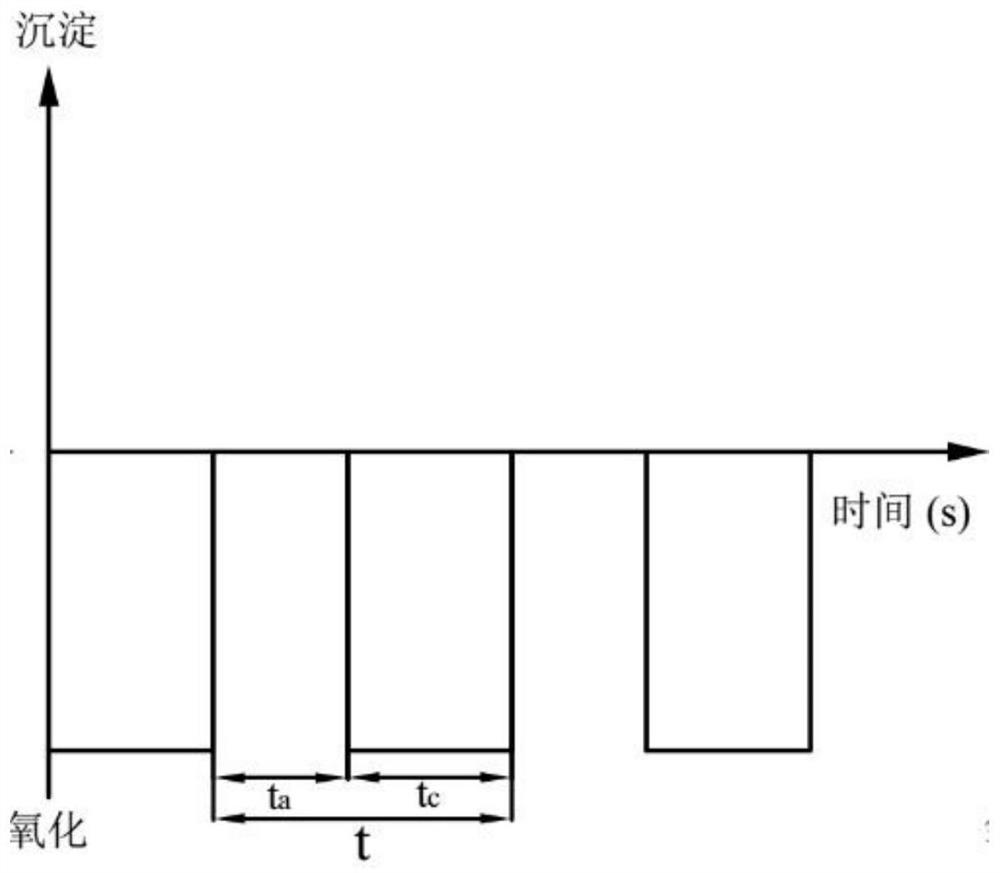
[0054] At a concentration of 0.010molL -1 In the simulated wastewater of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, NaCl was added as a supporting electrolyte to make the concentration reach 0.020molL -1 , adjust the pH of the solution to 7.0, the stirring rate is 200rpm, the pulse power supply voltage is +10V, -10V, ±10V respectively, the frequency is 0.04hz, the bias is 0.0%, and the electrolysis time is 180min respectively. A Mg / Pt electrode reactor is used. The experiment uses three waveforms: A (﹢10V), B (-10V), and C (±10V) (such as Figure 2a -c shown).
[0055] When the voltage is positive, the first electrode made of magnesium is at a high potential, and a precipitation reaction occurs in the solution. When the voltage is negative, when the second electrode made of platinum is at a low potential, an oxidation reaction occurs in the solution. During the experiment, samples were taken every 30 minutes to detect the concentration of ammonia nitrogen and phosphate to calculate th...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Set three gradients of ammonium ion to phosphate ion molar ratio 1:0.2, 1:0.5 and 1:1, where the concentration of ammonia nitrogen is 0.010molL -1 , the concentration of phosphate ion is 0.002molL respectively -1 , 0.005molL -1 , 0.010molL -1 . NaCl is used as a supporting electrolyte, so that the concentration is 0.020molL -1 , adjust the pH of the solution to 7.0, the stirring rate is 200rpm, the pulse power supply voltage is ±10V, the frequency is 0.02hz, the bias is 0.0%, and the electrolysis time is 180min. Such as Figure 5a As shown, under the conditions of N:P 1:0.2, 1:0.5 and 1:1, after 180 min of reaction, the final removal rates of ammonia nitrogen were 32.2%, 49.5% and 70.8%, respectively. Such as Figure 5b As shown, under the conditions of N:P being 1:0.2 and 1:0.5 respectively, the final removal rates of phosphate were 96.8% and 98.2% respectively when reacting for 60 minutes. When N:P was 1:1, phosphoric acid was The root removal rate was 38%, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com