Unequal power divider based on microstrip ridge-type gap waveguide
A technology of power divider and gap waveguide, which is applied in the field of electronics, can solve the problem of unequal power distribution and phase adjustment of gap waveguide, and the method of power distribution ratio adjustment and phase matching of microstrip gap waveguide, which is not mentioned. Issues such as unequal power distribution and phase matching method of microstrip ridge-shaped gap waveguide achieve the effects of easy processing and integration, excellent transmission performance, and low insertion loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
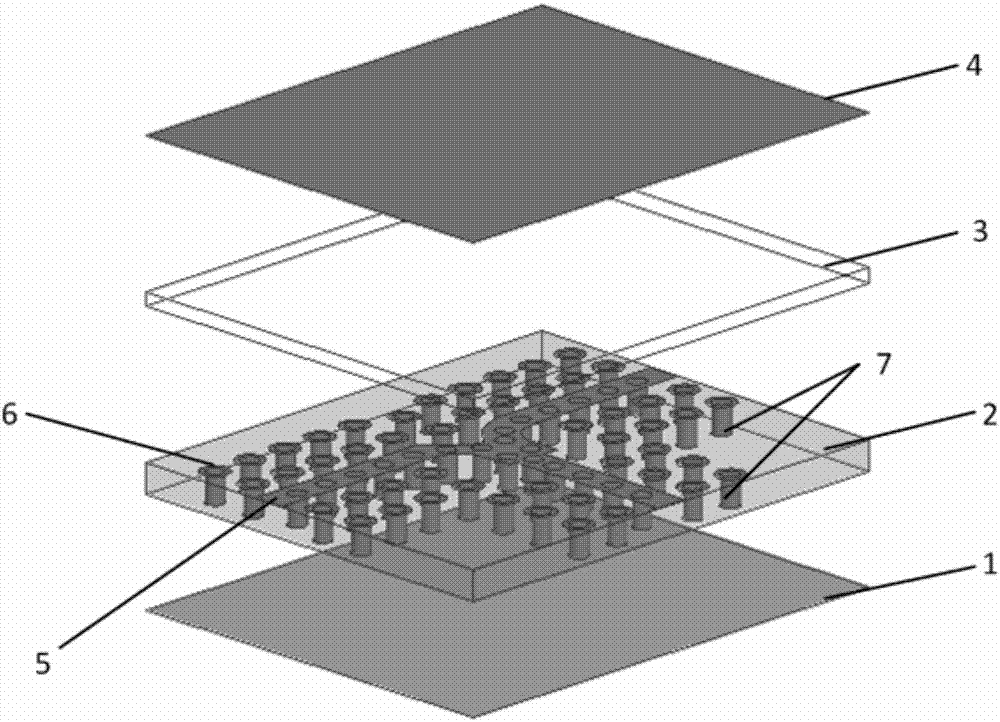
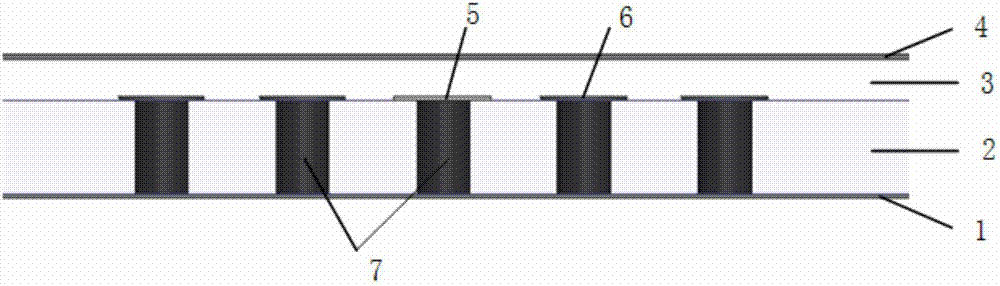
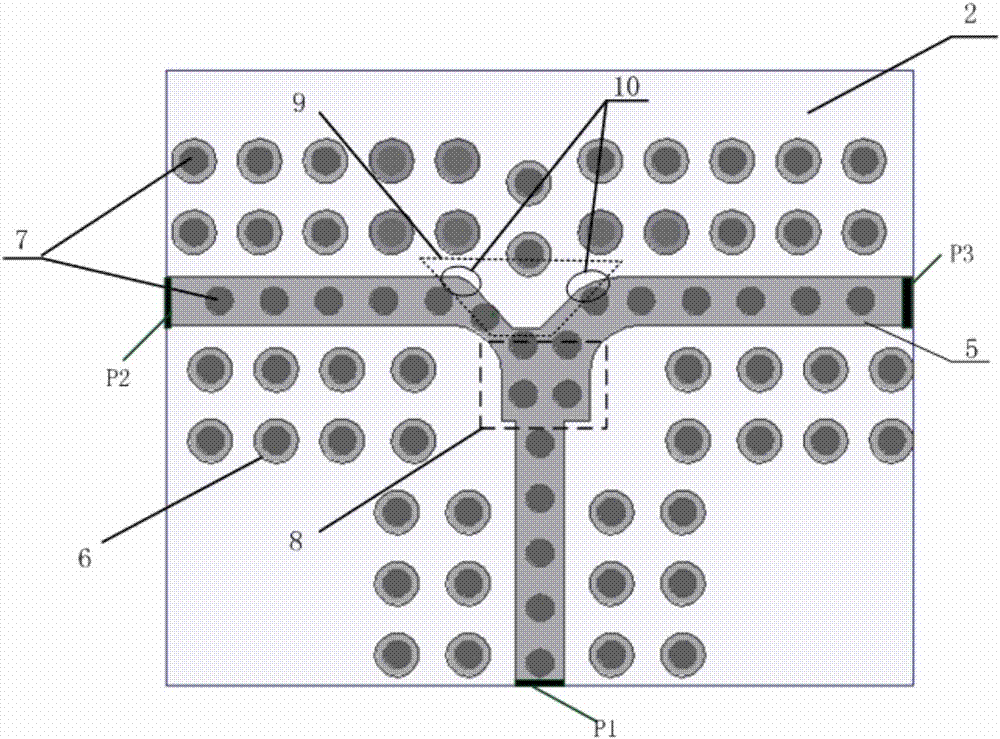
[0037] The three-dimensional structure of the unequal power divider based on the microstrip ridge gap waveguide is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the cross-sectional view is shown in figure 2 As shown, the top view is as image 3 As shown, the relevant dimensions and specifications are as follows Figure 4 shown. The dielectric plate 2 used is Rogers RO4003 dielectric material with a relative permittivity of 3.55 and a loss tangent of 0.0027, with a size of 5.6mm×6.8mm×0.406mm. The gap layer 3 is filled with air, and the thickness is 0.2mm. The size parameters of the microstrip ridge gap waveguide unequal power divider are as follows: W=0.8mm, L=1.1mm, l1=0.45mm, w1=0.25mm, w2=0.5 mm, R=0.45mm, r1=0.2mm, r2=0.75mm, a=0.125mm, b=0.2mm.
[0038] This example is based on the microstrip ridge gap waveguide unequal power divider is modeled and simulated in the electromagnetic simulation software HFSS.13. Figure 5 It is the S-parameter simulation diagram of the unequal power ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com