Method for improving mechanical properties of steel plate through thermal forming-subcritical quenching-partitioning technology
A sub-temperature quenching and hot forming technology, applied in the field of improving the mechanical properties of steel plates, can solve the problems of lack of large-scale application of aluminum and magnesium alloys, complex forming processes, poor welding performance, etc., to save fuel, improve the environment, improve The effect of mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
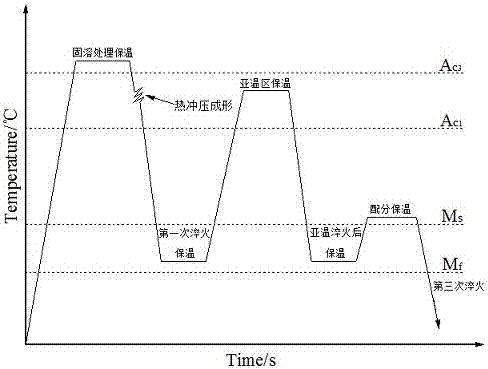
[0012] Example 1 The material used in actual production is C-Si-Mn steel plate, and its production process includes the following steps: (1) Solution treatment: first heat the steel plate at a certain heating rate to Ac 3 Above 150°C, and keep warm for 5min.
[0013] (2) The first quenching: Then the steel plate is transferred to the die for hot stamping, then quenched, and quenched to Q T1 =Ms-170℃, keep warm for 15s.
[0014] (3) Insulation in sub-temperature zone: then quench to Q T1 The steel plate was reheated to Ac 3 -10°C, and keep warm for 3 minutes.
[0015] (4) Sub-temperature quenching: Then immediately quench the steel plate Q T2 = Ms - 180°C, and keep warm for 15s.
[0016] (5) Partitioning and heat preservation: Then heat the steel plate to Ms+10°C and keep it warm for 90s.
[0017] (6) The third quenching: finally quench the steel plate to room temperature.
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2 The material used in actual production is C-Si-Mn steel plate, and its production process includes the following steps: (1) Solution treatment: first heat the steel plate at a certain heating rate to Ac 3 Above 120°C, and keep warm for 8min.
[0019] (2) The first quenching: Then the steel plate is transferred to the die for hot stamping, then quenched, and quenched to Q T1 = Ms - 190°C, keep warm for 15s.
[0020] (3) Insulation in sub-temperature zone: then quench to Q T1 The steel plate was reheated to Ac 3 -20°C, and keep warm for 3 minutes.
[0021] (4) Sub-temperature quenching: Then immediately quench the steel plate Q T2 = Ms - 200°C, and keep warm for 15s.
[0022] (5) Partitioning and heat preservation: Then heat the steel plate to Ms+20°C and keep it warm for 60s.
[0023] (6) The third quenching: finally quench the steel plate to room temperature.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3 The material used in actual production is C-Si-Mn steel plate, and its production process includes the following steps: (1) Solution treatment: firstly, the steel plate is heated to Ac 3 Above 100°C, and keep warm for 10min.
[0025] (2) The first quenching: Then the steel plate is transferred to the die for hot stamping, then quenched, and quenched to Q T1 = Ms - 200°C, keep warm for 15s.
[0026] (3) Insulation in sub-temperature zone: then quench to Q T1 The steel plate was reheated to Ac 3 -10°C, and keep warm for 3 minutes.
[0027] (4) Sub-temperature quenching: Then immediately quench the steel plate Q T2 =Ms-210°C, and keep warm for 15s.
[0028] (5) Partitioning and heat preservation: Then heat the steel plate to Ms+20°C and keep it warm for 45s.
[0029] (6) The third quenching: finally quench the steel plate to room temperature.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com