Downfield-driven oriented Mn-Ni-Sn magnetic refrigeration alloy material, and production method of ribbon thereof
A technology of alloy materials and magnetic refrigeration, which is applied in the direction of magnetic materials, heat exchange materials, inorganic materials, etc., can solve unclear problems, achieve good cooling capacity, reduce the effect of hysteresis loss, and large cooling capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
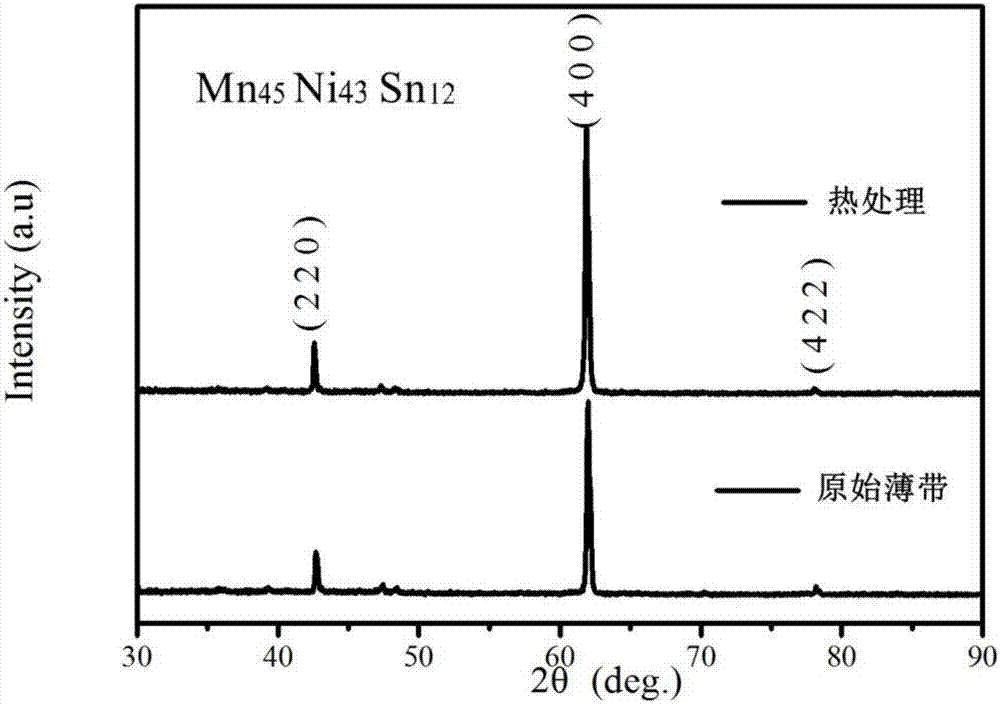
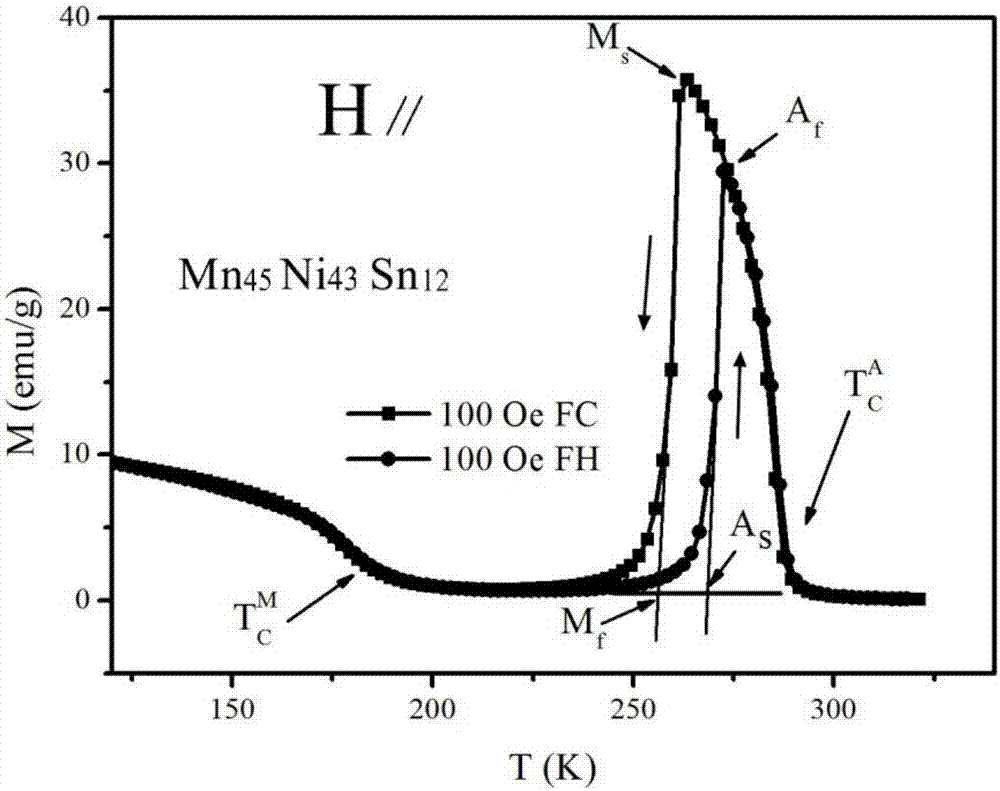
[0053] The first embodiment provides a low magnetic field driven orientation Mn 45 Ni 43 Sn 12 The preparation method of the magnetic refrigeration alloy material thin strip specifically comprises the following steps:
[0054] (1) According to Mn 45 Ni 43 Sn 12 Chemical formula ingredients, respectively weighing Ni, Mn, Sn metal raw materials with a purity of 99.9%; the molar ratio of each element in the alloy is: Ni is 43%, Sn is 12%, Mn is 45%;
[0055] (2) Put the weighed raw materials into a water-cooled crucible, and extract the vacuum to reach 1×10 -3 When the Pa is below, argon gas is introduced to generate an electric arc, and the melting current is 200A. Each sample is turned over 3 times, and smelted 4 times in total to ensure uniform composition;
[0056] (3) Put the obtained polycrystalline ingot into a quartz tube with a small hole at the bottom, then place the quartz tube with the open end up in the furnace cavity of the belt thrower, and vacuumize until th...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The second embodiment provides a low magnetic field driven orientation Mn 42.7 Ni 44.1 Sn 13.2 The preparation method of the magnetic refrigeration alloy material thin strip specifically comprises the following steps:
[0063] (1) According to Mn 42.7 Ni 44.1 Sn 13.2 Chemical formula ingredients, respectively weighing Ni, Mn, Sn metal raw materials with a purity of 99.9%; the atomic percentages are: Ni is 44.1%, Mn is 42.7%, Sn is 13.2%;
[0064] (2) Put the weighed raw materials into a water-cooled crucible, and extract the vacuum to reach 1×10 -3 When the Pa is below, argon gas is introduced to generate an arc, and the melting current is 300A. Each sample is turned over 3 times, and smelted 4 times in total to ensure uniform composition;
[0065] (3) Put the obtained polycrystalline ingot into a quartz tube with a small hole at the bottom, then place the quartz tube with the open end up in the furnace cavity of the belt thrower, and vacuumize until the degree of v...
Embodiment 3
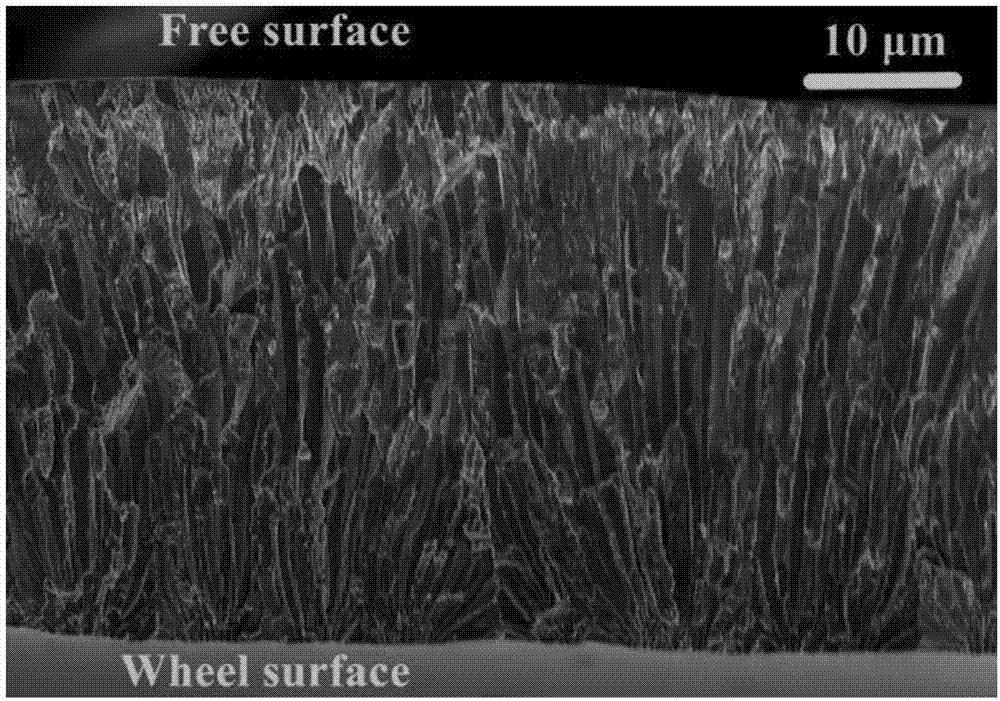
[0069] The preparation component is Mn 44.1 Ni 44.5 Sn 11.4 The alloy quick-quenched strip: except that the composition of the sample is Mn 44.1 Ni 44.5 Sn 11.4 , the atomic percentages are: Ni is 44.5%, Mn is 44.4%, Sn is 11.4%; and the annealing temperature is 1023K, the rest of the steps are the same as those in the first embodiment. In the preparation of oriented ribbon samples, it is obvious that large whole grains can be seen running through the ribbon direction. The martensitic transformation temperature is 295K under the magnetic field strength of 10kOe, ΔS M 8.9J / kg K(H ⊥ , 10kOe). Effectively suppressing the reduction of actual magnetic cooling capacity due to hysteresis loss, the cooling capacity reduction caused by hysteresis is approximately 11.4% (vertical to the stripe direction) and 28% (parallel stripe direction).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com