Copolymer with electric storage characteristics and preparation method thereof, and application of copolymer in electric storage
A copolymer and electric storage technology, applied in the field of copolymers, can solve the problems of few types of materials, incapable of large-scale industrial production, and unguaranteed storage stability, achieving excellent stability and unsatisfactory results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] In this Example 1, a preparation method of the above-mentioned copolymer with electrical storage properties, 0.5 g of monomer X, 0.8 g of monomer Y, 0.02 g of azobisisobutyronitrile and 2 mL of cyclohexanone were added to In the polymerization tube, react in an oxygen-free environment at 80°C for 12 h to 20 h, then pour the reaction product into methanol to precipitate a solid, and dry it to obtain the copolymer. Wherein, azobisisobutyronitrile is used as a catalyst for the polymerization reaction; cyclohexanone is used as a solvent, and any one or more of cyclohexanone, toluene, dimethylformamide or dichloroethane can also be used to replace; none The oxygen environment can be realized by introducing an inert gas into the reaction vessel, and the inert gas that can be used includes any one or more of nitrogen, argon, and helium.
[0036] In this example 1, monomer X can be purchased from the market, and can also be prepared by the following method: the parts mentioned ...
Embodiment 2
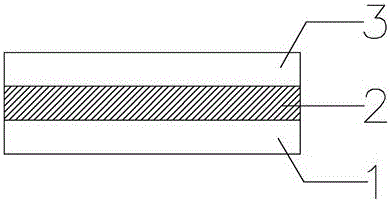
[0040] An electric storage device with a copolymer having electric storage properties obtained in Example 1, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a first electrode layer 1, an active layer 2 and a second electrode layer 3 from bottom to top, wherein the active layer 2 is the copolymer obtained in Example 1 with electrical storage properties. In this embodiment 2, the thickness of the active layer 2 is 100 nm to 200 nm; the first electrode layer 1 and the second electrode layer 3 are conductive glass or metal electrodes, further, the first electrode layer 1 and the second electrode layer 3 is a magnesium electrode, a silver electrode, a calcium electrode or an aluminum electrode.
Embodiment 3
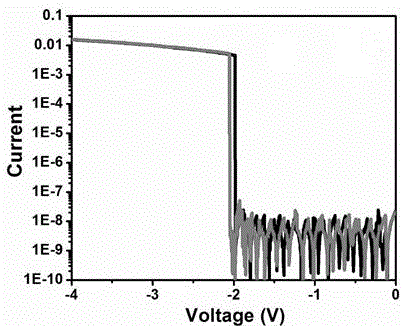
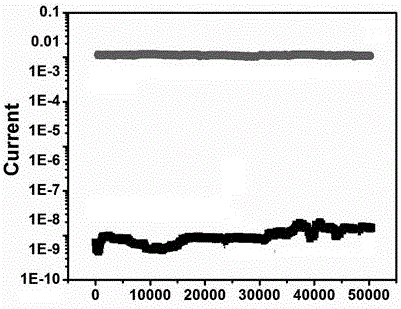
[0042] A method for preparing the electrical storage device of Example 2, using ITO glass as the first electrode layer 1, using an organic solvent to ultrasonically clean the ITO glass, and drying to remove the organic solvent. In this Example 3, chloroform, Acetone and isopropanol were used to ultrasonically clean the ITO glass in sequence; at room temperature, the copolymer with electrical storage properties prepared in Example 1 was dissolved in chloroform to form a solution of 10 mg / mL to 20 mg / mL , the solution was stirred at a stirring speed of 200 rpm to 1200 rpm for 6 h to 10 h to ensure that the copolymer with electrical storage properties was fully dissolved; the prepared solution was spin-coated on ITO at a speed of 600 rpm to 4000 rpm On one side of the glass, an active layer 2 with a thickness of 150 nm is formed. In the present embodiment 3, the spin coating speed is preferably 1500 rpm; -4 A 100 nm aluminum electrode is plated on the other side of the active la...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com