Polypeptide amino acid sequence De novo sequencing method based on chemical modification and isotope labeling
A technology of isotope labeling and chemical modification, applied in the field of de novo sequencing of protein amino acid sequences to identify fragment ions, can solve the problems of affecting the accuracy of de novo sequencing, complex peptide fragmentation mechanism, and reduced probability and intensity, so as to improve specificity, improve Accuracy and efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] 1. Peptide N-terminal labeling and C-terminal labeling based on arginine labeling
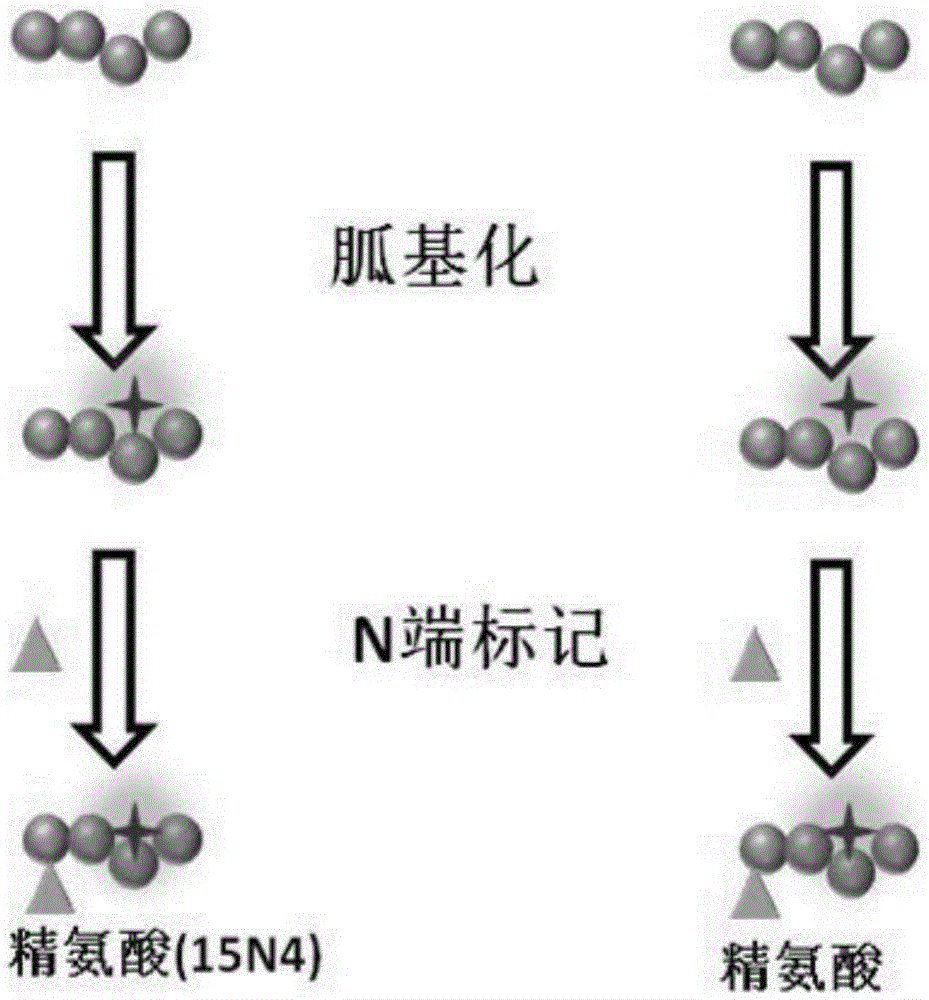
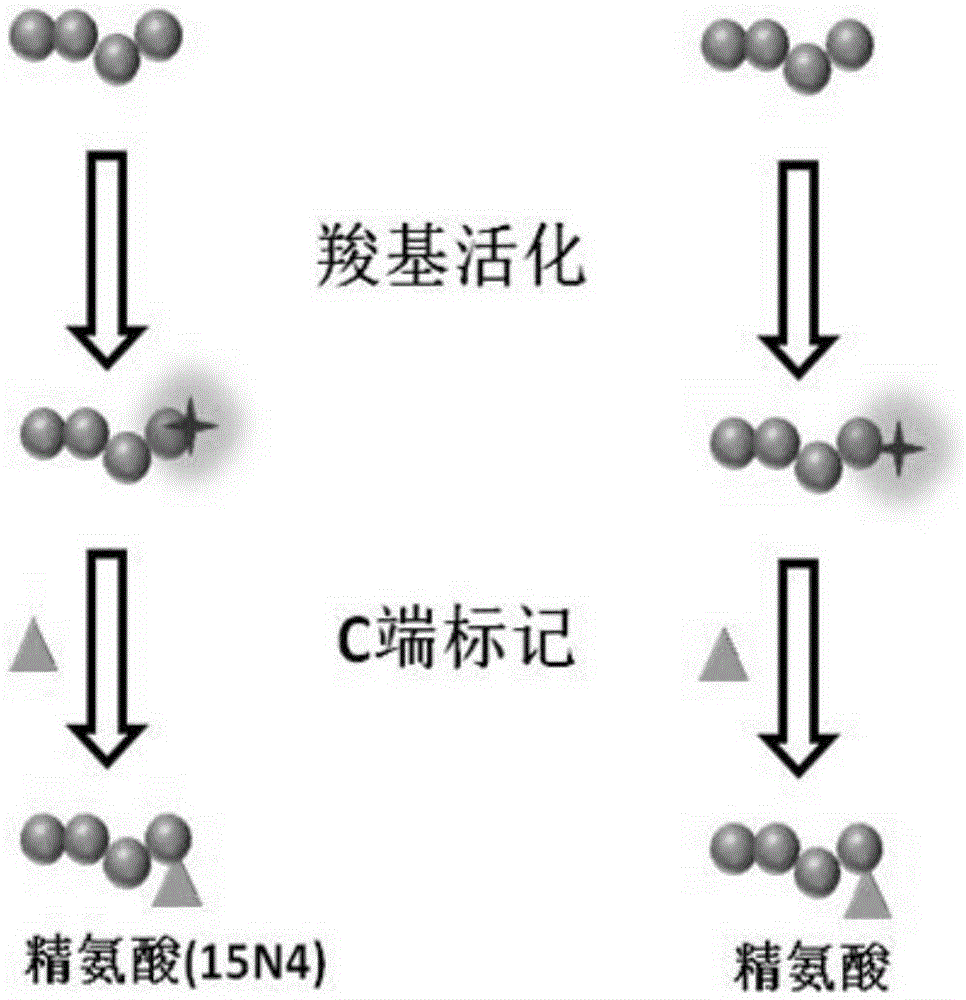
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, mark according to the following process:
[0026] 1) Guanylation of polypeptide lysine amino groups: Add 40 μL of 100 mM sodium bicarbonate solution containing 2M O-methylisourea to 1 ml of polypeptide solution, adjust the pH value to 11 with 2M sodium hydroxide solution, and incubate at 37 °C React for 2 hours. The reaction was then terminated by adding 10% trifluoroacetic acid and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 8.0.
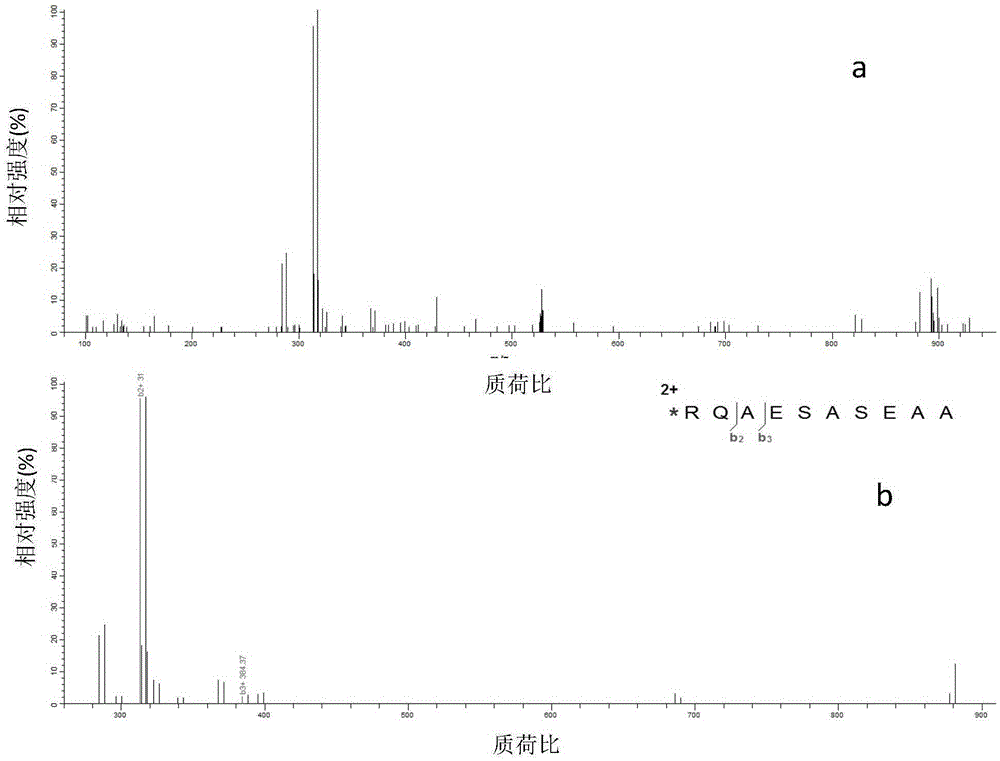
[0027] 2) Polypeptide N-terminal arginine labeling: 1) the amino group of arginine is blocked with 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.5) containing 4% formaldehyde and 60 mM sodium cyanoborohydride; use 1-(3- Dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) activate the carboxyl group of arginine; 2) The obtained peptide samples are divided into two equal In the first batch,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com