Method for extracting rare earth from precipitation sludge of rare earth wastewater pool
A sedimentation slag and wastewater tank technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of organic phase emulsification, fine sedimentation particles, and difficulties in sedimentation enrichment, and achieve the effects of low cost, efficient recovery, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
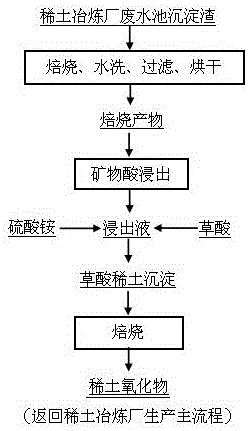
[0022] Take 10g of the sediment residue from the rare earth wastewater pool, in which the content of REO is 30.66 wt.%, and the content of CaO is 29.72 wt.%. It is roasted at 850°C for 1.5h and taken out. The roasted product is further ground, water-soluble, filtered and dried. The dried roasted product was leached for 1.0 h under the conditions of hydrochloric acid concentration of 3 mol / L, liquid-solid ratio of 6:1 mL / g, and reaction temperature of 80°C, and filtered to obtain 130 ml of a leaching solution containing 23.03 g / L of rare earths, of which The leaching rate is 97.65%. At 30°C, add 10.4g of ammonium sulfate to the rare earth leaching solution, stir well to dissolve, stop stirring, then add 1.2 times the theoretical amount of oxalic acid, adjust the pH of the solution to 1.5~2, stand at 80°C for 6h, filter and wash 7.07g of precipitated slag was obtained by drying. The rare earth content in the precipitated slag was 41.97wt.%, and the calcium content was 0.2 wt.%. ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Take 50g of the sediment residue from the rare earth wastewater pool, in which the content of REO is 27.55 wt.%, and the content of CaO is 26.54 wt.%. After roasting at 900°C for 2 hours, the roasted product is further ground, dissolved in water, filtered and dried, and dried The final roasted product was leached for 1.0 h under the conditions of nitric acid concentration of 4 mol / L, liquid-solid ratio of 7:1 mL / g, and reaction temperature of 70°C to obtain 580 ml of leaching solution containing 23.70 g / L of rare earth, and the leaching rate of rare earth was 99.79% %. At 50°C, add 17.4g of ammonium sulfate to the leaching solution, stir to dissolve, stop stirring, then add 1.5 times the theoretical amount of oxalic acid, adjust the pH of the solution to 1.5~2, let stand at 90°C for 4 hours, filter, wash, After drying, 37.81g of precipitated slag was obtained. The rare earth content in the precipitated slag was 28.77wt.%, and the calcium content was 5.23wt.%. The recove...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Take 25g of the sediment residue from the rare earth wastewater pool, in which the content of REO is 31.68 wt.%, and the content of CaO is 28.53 wt.%. After roasting at 800°C for 2 hours, the roasted product is further ground, dissolved in water, filtered and dried, and dried The final roasted product was leached for 1.5h under the conditions of sulfuric acid concentration of 3mol / L, liquid-solid ratio of 8:1mL / g, and reaction temperature of 60°C to obtain 310ml of leaching solution containing 23.10g / L of rare earth, wherein the leaching rate of rare earth was 90.33 %. Add 26.35g of ammonium sulfate to the leaching solution, stir well to dissolve, stop stirring, then add 1.3 times the theoretical amount of oxalic acid, adjust the pH of the solution to 1.5~2, stand at 50°C for 8 hours, filter, wash, and dry to obtain 17.58g of precipitate The rare earth content in the precipitated slag is 41.10 wt.%, and the calcium content is 0.18 wt.%. The recovery rate of rare earth i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com