A kind of inorganic cementitious material with fly ash and waste glass as raw materials and preparation method thereof
An inorganic cementitious material and waste glass technology, applied in cement production and other directions, can solve the problems of potential safety hazards, low recycling of waste glass, occupation of land resources, etc., and achieve good resistance to sulfate corrosion, fuel consumption and greenhouse gas. The effect of low emission and high curing strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
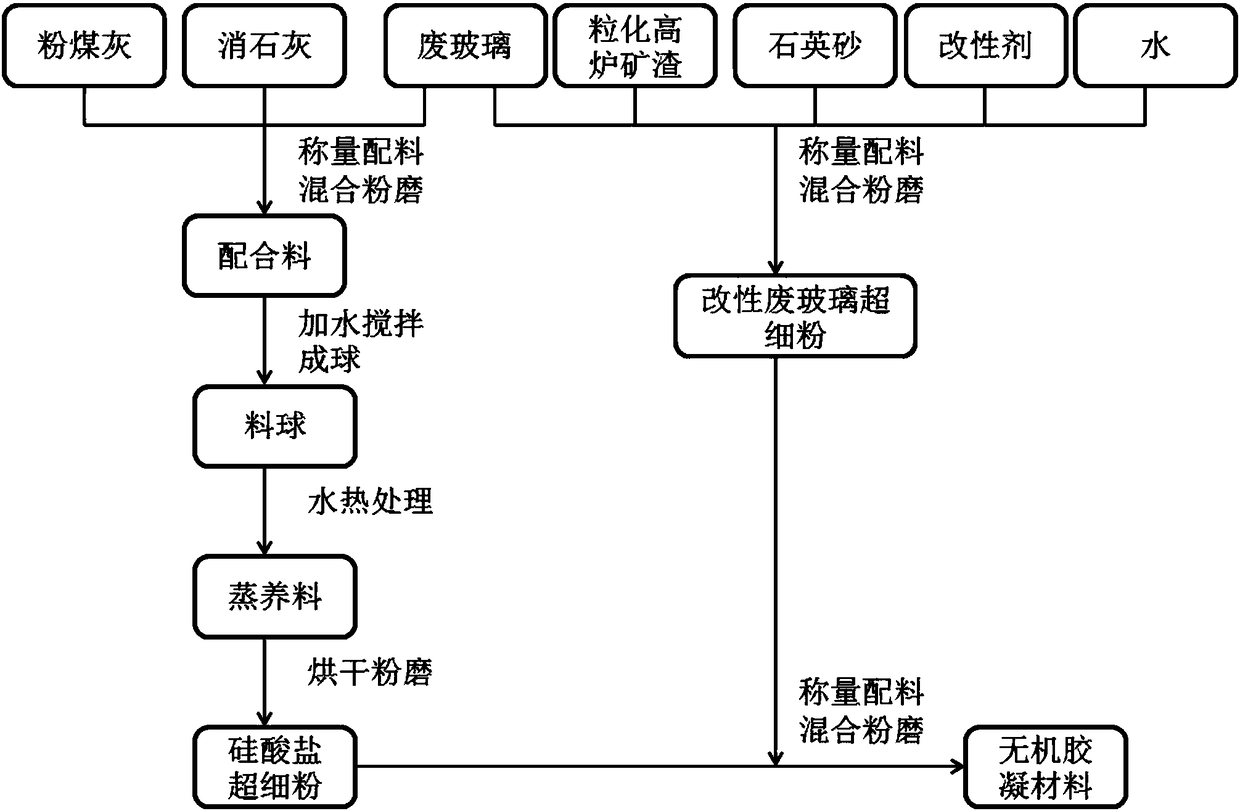
[0020] The waste glass was washed, dried, crushed and passed through a 5 mm square hole sieve. Weigh 40 parts of fly ash, 40 parts of slaked lime and 20 parts of waste glass, mix and grind to get 0.92% of the 80μm sieve; mix and mix the batch with water to make a ball with a diameter of 8~12mm ; Steam the pellets at 90°C for 16 hours to obtain steamed nutrients; dry the steamed nutrients at 80°C, cool and grind until 2.5% of the 45μm sieve is obtained, and obtain superfine silicate powder;
[0021] Respectively weigh 50 parts of waste glass, 30 parts of granulated blast furnace slag, 20 parts of quartz sand, 4 parts of sodium hydroxide, and 1 part of water, mix and grind to 45 μm sieve residue 2.8%, to obtain superfine powder of modified waste glass;
[0022] Mix and grind 65 parts of silicate superfine powder and 35 parts of modified waste glass superfine powder for 30 minutes to prepare an inorganic gelling material.
[0023] It is measured that the initial setting time of ...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The waste glass was washed, dried, crushed and passed through a 5 mm square hole sieve. Weigh 65 parts of fly ash, 30 parts of slaked lime and 5 parts of waste glass, mix and grind to get 0.84% of the 80μm sieve; mix and mix the batch with water to make a ball with a diameter of 8~12mm ; Steam the pellets at 95°C for 14 hours to obtain steamed nutrients; dry the steamed nutrients at 120°C, cool and grind to 4.3% of the 45μm sieve, and obtain superfine silicate powder;
[0026] Weigh 70 parts of waste glass, 15 parts of granulated blast furnace slag, 15 parts of quartz sand, 5 parts of sodium carbonate, and 1 part of water, mix and grind until the sieve residue of 45 μm is less than 1.6%, and obtain superfine powder of modified waste glass;
[0027] Mix and grind 75 parts of silicate superfine powder and 25 parts of modified waste glass superfine powder for 30 minutes to prepare inorganic gelling material.
[0028] The measured initial setting time of the inorganic ge...
Embodiment 3
[0030] The waste glass was washed, dried, crushed and passed through a 5 mm square hole sieve. Weigh 55 parts of fly ash, 35 parts of slaked lime and 10 parts of waste glass, mix and grind to get 0.70% of the 80μm sieve; mix the batch with water and stir evenly, and make a ball with a diameter of 8~12mm ; Steam the pellets at 98°C for 14 hours to obtain steamed nutrients; dry the steamed nutrients at 100°C, cool and grind to a 45 μm sieve with a residue of 3.1%, and obtain superfine silicate powder;
[0031] Weigh 60 parts of waste glass, 25 parts of granulated blast furnace slag, 15 parts of quartz sand, 3.5 parts of potassium hydroxide, and 1 part of water, mix and grind until the sieve residue of 45 μm is less than 2.4%, and obtain superfine powder of modified waste glass;
[0032] Mix and grind 70 parts of silicate superfine powder and 30 parts of modified waste glass superfine powder for 30 minutes to prepare inorganic gelling material.
[0033] The initial curing time o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com