A low-defect mutation buffer layer with chirped digitally graded structure
A buffer layer, low-defect technology, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as insignificant effects, and achieve the effects of improving crystal quality, reducing residual strain and defect density, and simplifying the growth process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
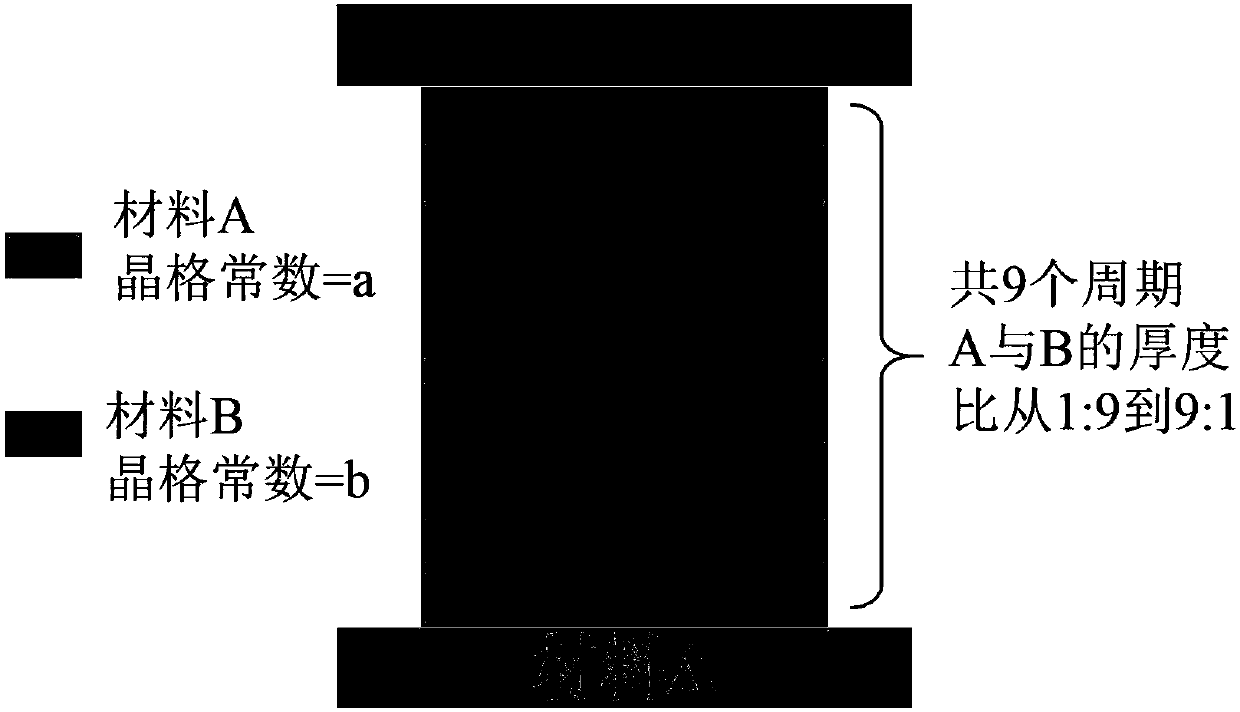
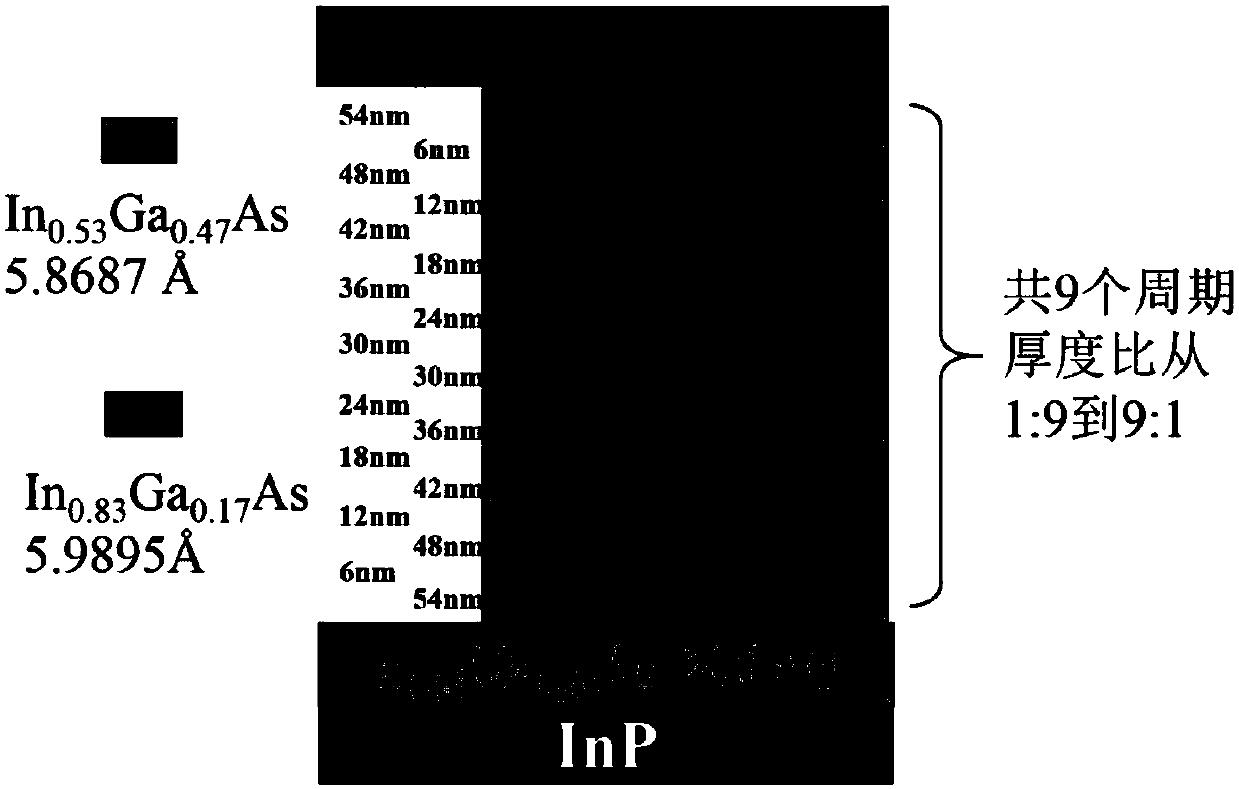
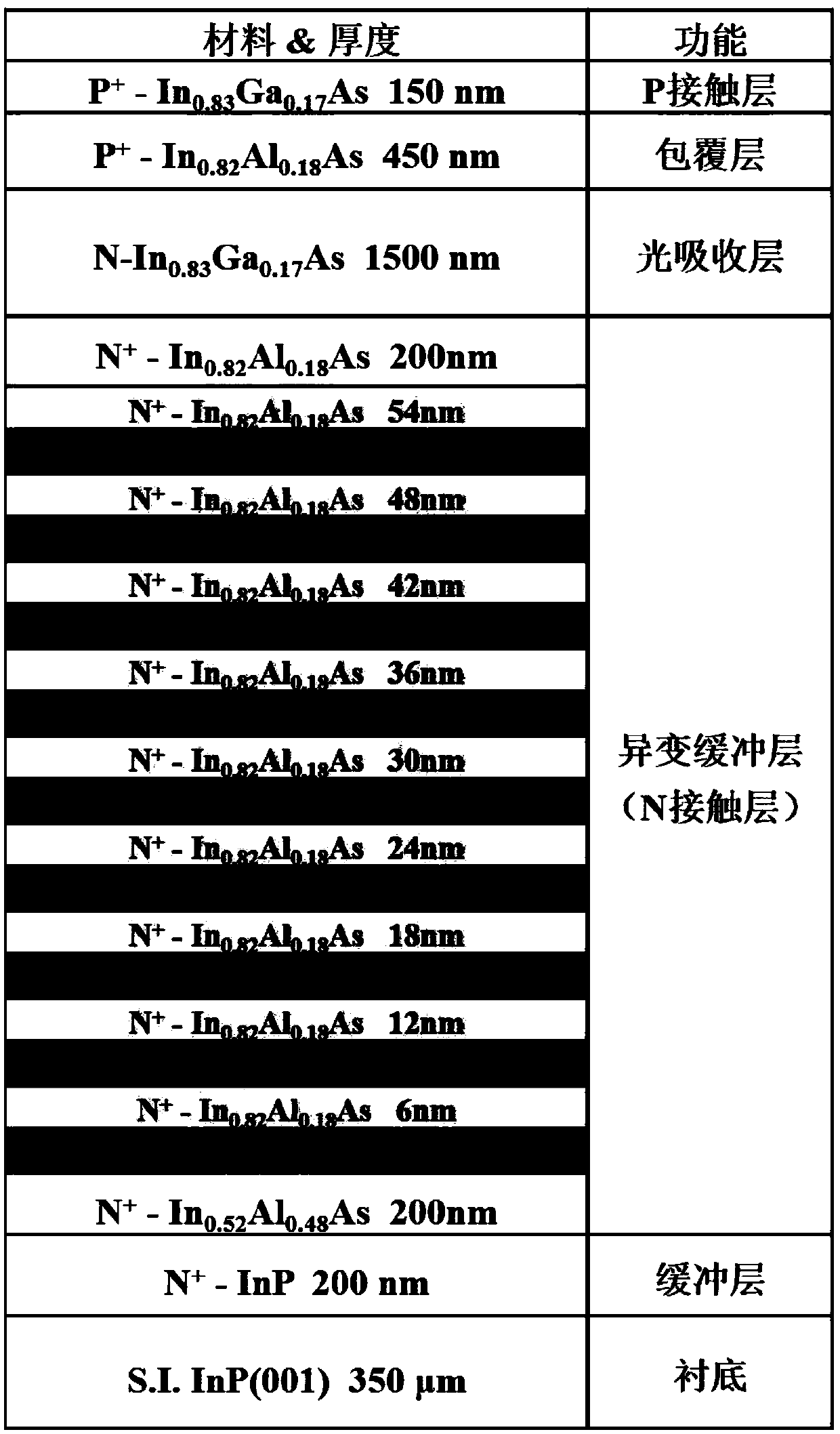
[0034] The purpose of this example is to epitaxially grow lattice-mismatched In on an InP substrate. 0.83 Ga 0.17 As the light-absorbing layer, the preparation of the detector material with the photoresponse cut-off wavelength at room temperature of 2.6 μm is realized. Since In 0.83 Ga 0.17 There is a lattice mismatch between As and the InP substrate, so the chirped digital gradient variation buffer layer growth technique was used to prepare In with an In composition of 0.82 0.82 Al 0.12 As virtual substrate, and on the basis of this virtual substrate, epitaxially grow PIN type photodiode device structure. The specific device structure is as image 3 shown. Its structure contains the following materials in order from bottom to top:
[0035] 1. Semi-insulating (S.I.) InP (001) substrate. Thickness 350μm, resistivity ρ≥1MΩ·cm.
[0036] 2. N-type heavy doping (N + ) InP buffer layer. Thickness 200nm, doping concentration 4×10 18 cm -3 .
[0037] 3. N-type heavy dopi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com