High-activity tumor inhibitor as well as preparation method and application thereof
A kind of function, amino acid technology, applied in the field of tumor treatment, can solve the problem of unsatisfactory curative effect and achieve the effect of tumor inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0220] Example 1 Screening of YAP inhibitory polypeptides
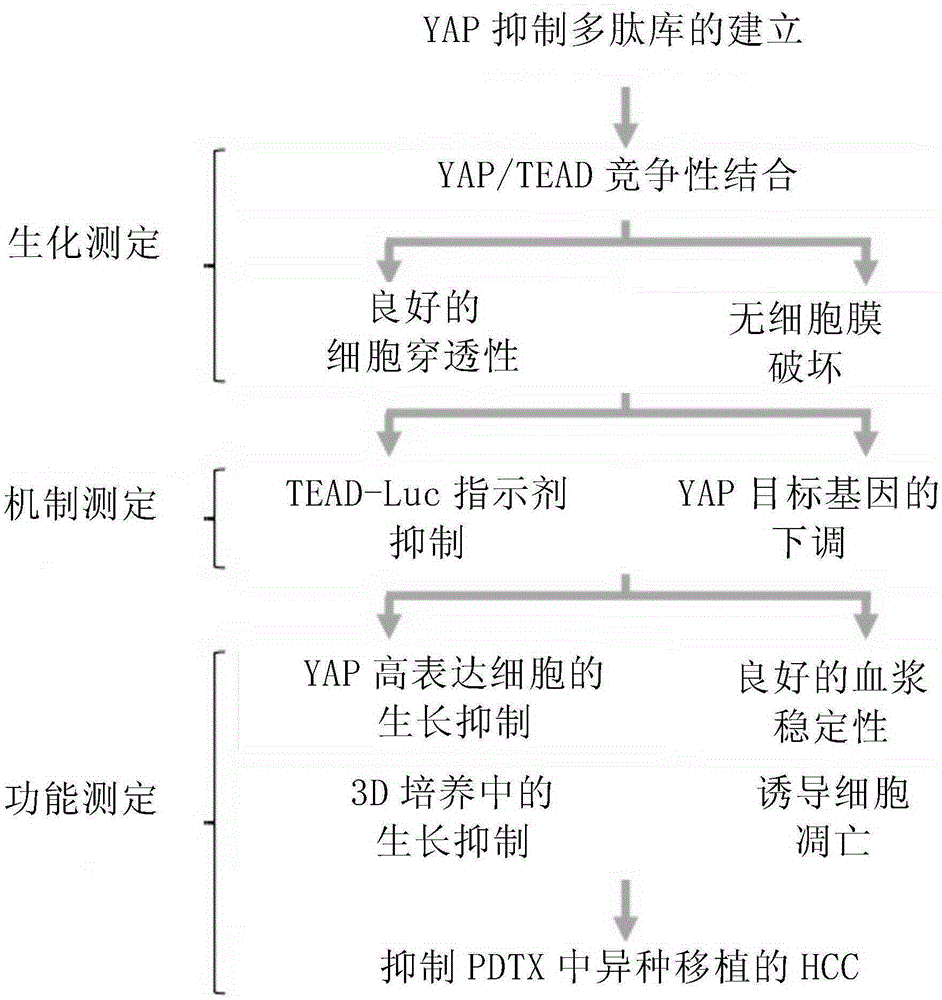
[0221] 1.1 The present inventors constructed different phage polypeptide libraries by using YAP protein arrays. Through multiple screening tests, candidate polypeptides capable of blocking YAP-TEAD binding are selected. Then screen out the inhibitory polypeptides that can effectively penetrate cells, reduce the activity of TEAD and down-regulate other YAP target genes from many candidate polypeptides. Test-tube test and PTDX animal experimental model were carried out on the YAP inhibitory polypeptide obtained through screening to confirm, and finally a successful YAP inhibitory polypeptide with curative effect was obtained.
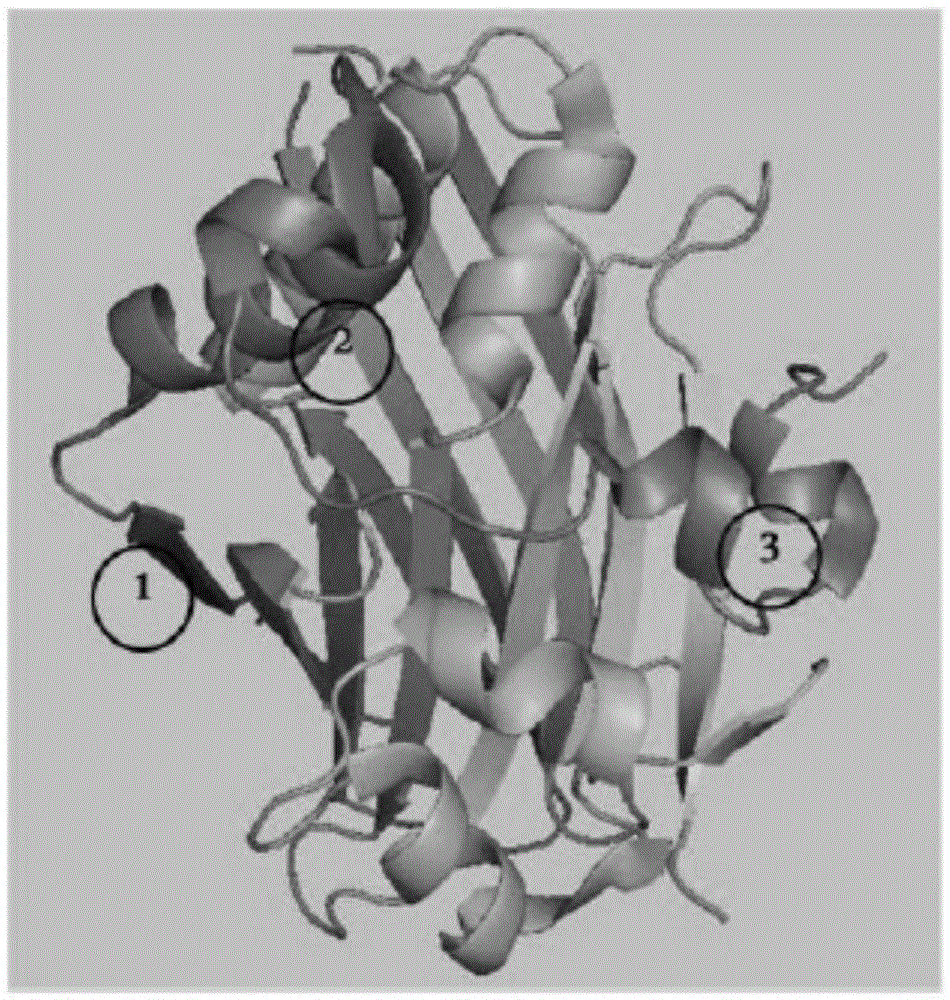
[0222] The findings reveal that YAP (AA50-171) interacts around the globular structure of TEAD1 (AA194-411) and forms extensive interactions through three highly conserved protein interfaces. Interface 1 is the antiparallel β-sheet structure of YAPβ1 (AA53-58) and TEADβ7. Interface 2 is the mu...
Embodiment 2
[0234] Example 2 Modification of YAP inhibitory polypeptide
[0235] Although the polypeptide shown in SEQ ID NO.:1 can bind to TEAD in vitro, further analysis found that it is difficult to be effectively taken up by cells and has low stability.
[0236] In this embodiment, the sequence is modified based on SEQ ID NO.:1. Some of the identified beneficial modifications include: increased intra-peptide disulfide bonds, increased cell penetrating elements.
[0237] The test results are shown in Table 2.
[0238] Table 2
[0239]
[0240] *Stability is the measured plasma stability, the percentage of peptide remaining at the time measured.
[0241] The results show that the plasma stability of the polypeptide shown in SEQ ID NO.:1 after adding a disulfide bond is significantly improved; 34), the proportion of polypeptides capable of penetrating cells increased from less than 10% to 100% (the penetration rate of polypeptides added with RRMKWKK was 100%) and 135%.
Embodiment 3
[0242] Example 3 Modification of YAP inhibitory polypeptide
[0243] Transformation based on the polypeptide of SEQ ID NO.:1:
[0244] a. A disulfide bond is added in the peptide of SEQ ID NO.:1, and the modified sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.:2;
[0245] b. Based on the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.:2, X 4 Respectively replaced by Orn or Dab, the transformed sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.:5 or 6.
[0246] IC for TEAD binding of engineered YAP inhibitory polypeptides in a and b 50 Value and the mensuration of blood plasma stability, test result is as shown in table 3:
[0247] table 3
[0248]
[0249]
[0250] The results showed that the plasma stability of the polypeptide added with disulfide bonds was significantly improved, and the stability was even better after further modification of the polypeptide. And the IC of all modified peptides 50 All values are in the nanomolar range.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com