A terahertz-driven subfemtosecond time-resolved streak camera
A time-resolved, streak camera technology, used in devices and instruments for measuring time intervals, can solve problems such as the need for a power-driven system and limit time resolution, and achieve the effects of good synchronization, improved order of magnitude, and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
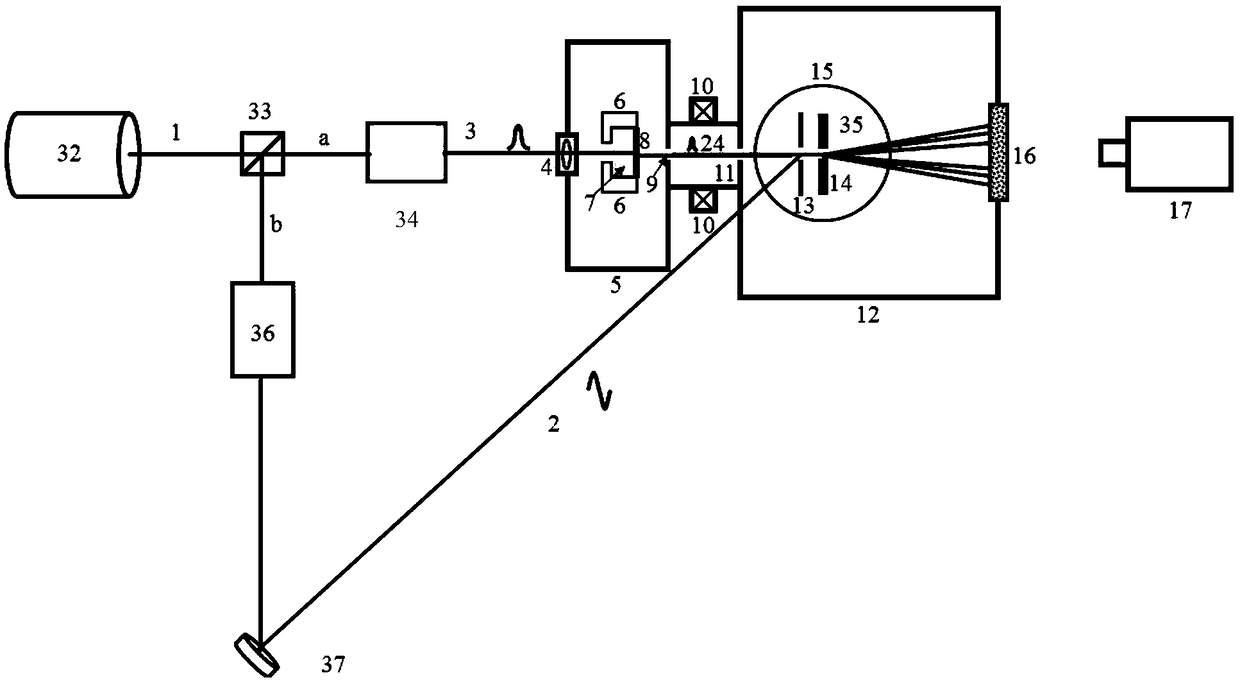
[0034] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the streak camera includes a femtosecond laser 32, a beam splitter 33, an ultraviolet pulse generator 34, a DC electron gun, a DC gun magnetic focusing device 10, a deflection yoke 35, a fluorescent screen 16, and an EBCCD camera 17;
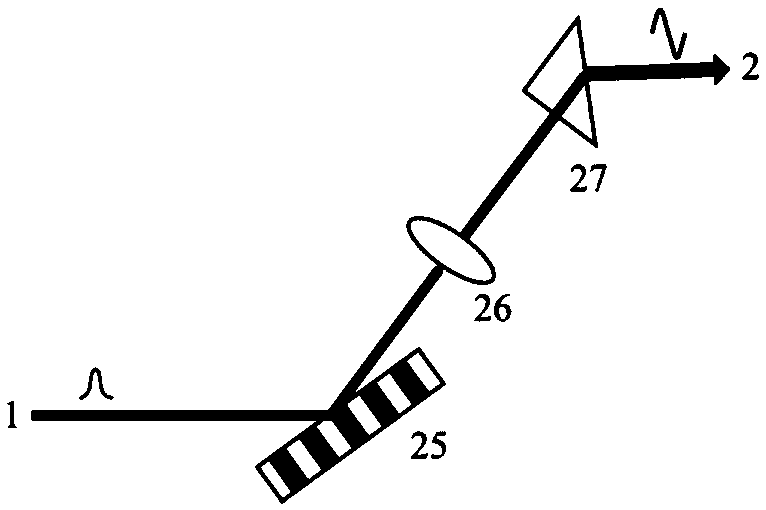
[0035] The femtosecond laser (a) emitted by the femtosecond laser 32 passes through the beam splitter 33 and then a beam of femtosecond laser enters the ultraviolet laser pulse generator 34, and another beam of femtosecond laser (b) enters the deflection yoke 35;
[0036] The DC electron gun comprises a DC electron gun chamber 5, a first lens 4, a cathode assembly and an anode 9; the front end of the DC electron gun chamber 5 is equipped with the first lens 4, and the rear end is provided with an anode 9; the cathode assembly is installed in the DC electron gun chamber 5; The assembly and anode 9 generate an accelerating electric field; the cathode assembly includes a cathode frame 6, a metal cath...
Embodiment 2
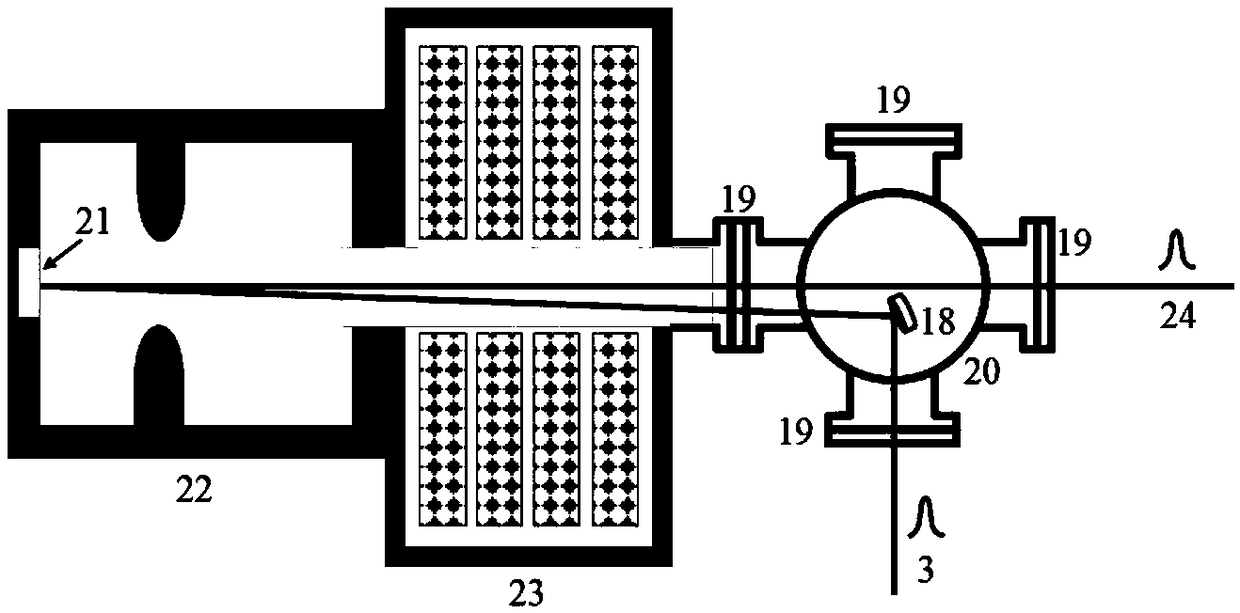
[0044] The invention can not only be used to characterize non-relativistic electrons accelerated by a DC gun, but also can characterize the time characteristics of relativistic ultrafast electron pulses. The specific embodiment is to use an RF accelerating gun to accelerate electron beams. image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram of the structure of the RF accelerator gun,
[0045] A bundle of femtosecond laser pulses (a) generates ultraviolet light pulses through the ultraviolet light pulse generator, and the ultraviolet light pulses pass the ultraviolet laser pulses through the second vacuum flange 19 (the second vacuum flanges are evenly distributed outside the laser chamber, a total of four 1) is introduced into the laser chamber; the ultraviolet light pulse 3 is reflected and irradiated on the photocathode 21 in the radio frequency chamber 22 through the reflection mirror 18 in the laser chamber 20, and the external photoelectric effect occurs, which is generated in the ultra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com