Composite nanofiber film of structure bionic skin extracellular matrix and producing method and application thereof
A technology for compounding nanofibers and skin cells, applied in the field of biomedical composite materials, can solve problems such as scars on wound surfaces, and achieve the effects of simple and easy preparation method, good biocompatibility and biomechanical strength, and abundant raw material resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
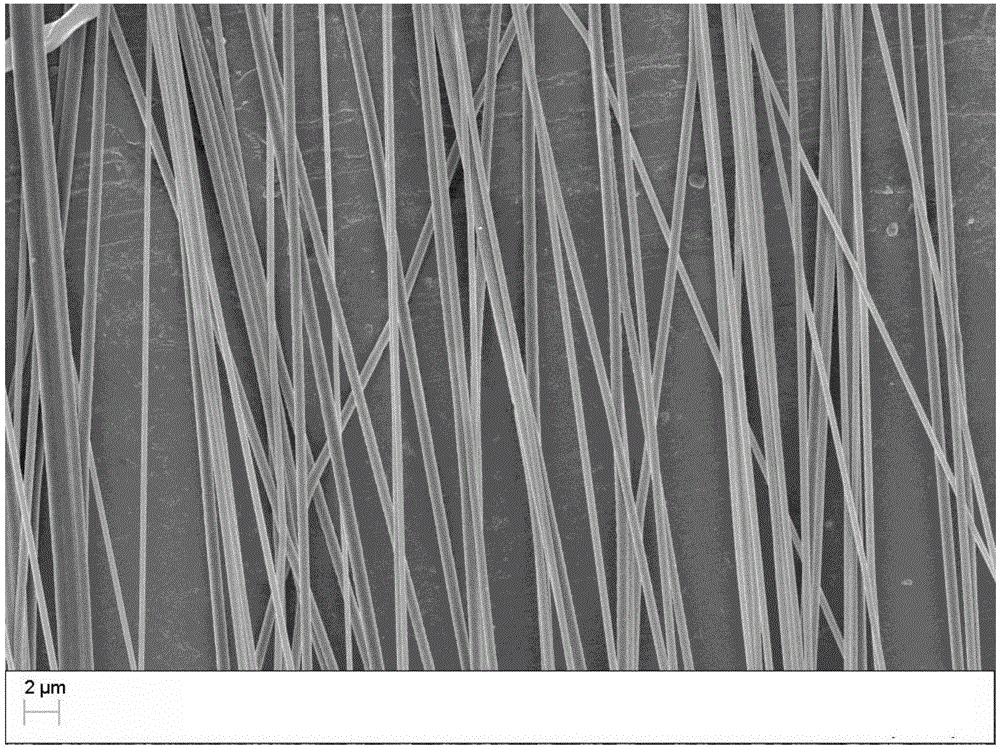
[0031] Weigh 0.35g PLA and 0.35g type I collagen (the mass ratio of PLA and collagen is 1:1) with an electronic balance, and dissolve them in 5ml hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain a solution with a mass-volume concentration of 14% (m / v). The solution was magnetically stirred at room temperature for 12 hours to dissolve completely, and after standing for 5 minutes, electrospinning was started; the parameters of electrospinning were: electrostatic voltage 24kV, receiving distance 15cm, spinning rate 1.5ml / h, relative humidity 50%. A high-speed rotating drum (2000 rpm) was used as a receiver to obtain a composite nanofiber membrane. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen from the scanning electron microscope image that the fiber orientation of the composite nanofibrous membrane prepared in this embodiment is consistent.
Embodiment 2
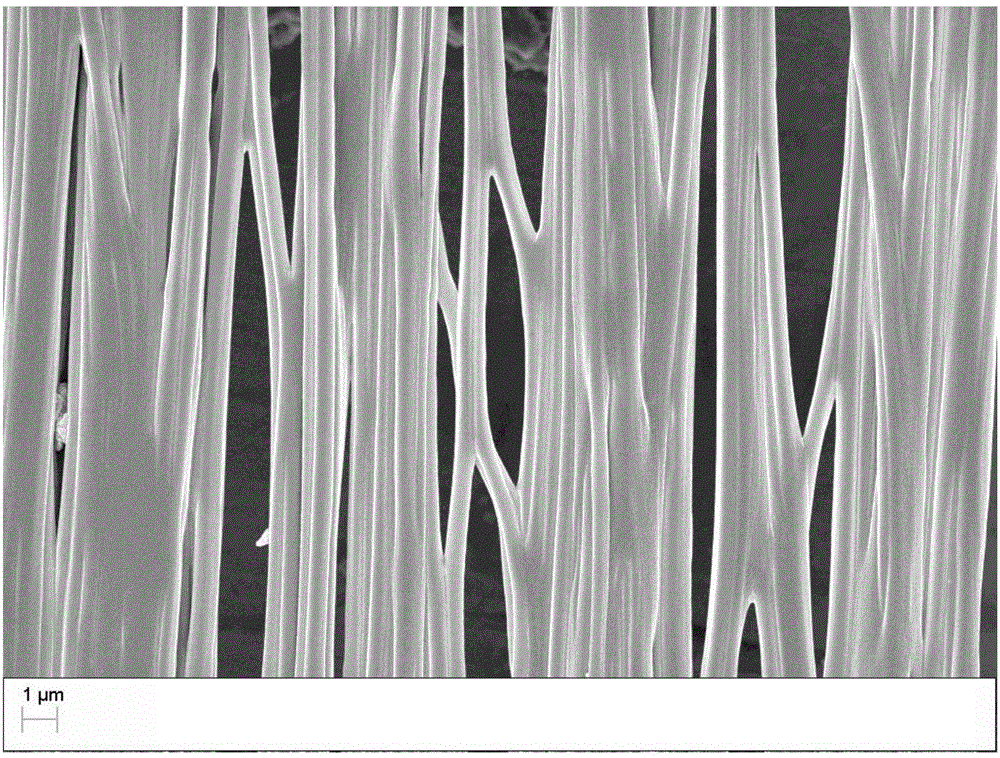
[0033] Weigh 0.75g PLGA with an electronic balance and dissolve it in 5ml of dichloromethane to obtain a solution with a mass-to-volume concentration of 15% (m / v). The solution is magnetically stirred at room temperature for 8 hours to dissolve completely, and after standing for 5 minutes, start electrospinning. silk; the parameters of electrospinning are: electrostatic voltage 14kV, receiving distance 6cm, spinning rate 3ml / h, relative humidity 80%. A glass slide sandwiched between two parallel copper strips is used as a receiver, and through the action of an additional electric field, the fibers fall on the glass slide in a parallel orientation to obtain a composite nanofiber film. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen from the scanning electron microscope images that the fiber orientations of the composite nanofiber membranes prepared in this embodiment are parallel to each other.
Embodiment 3
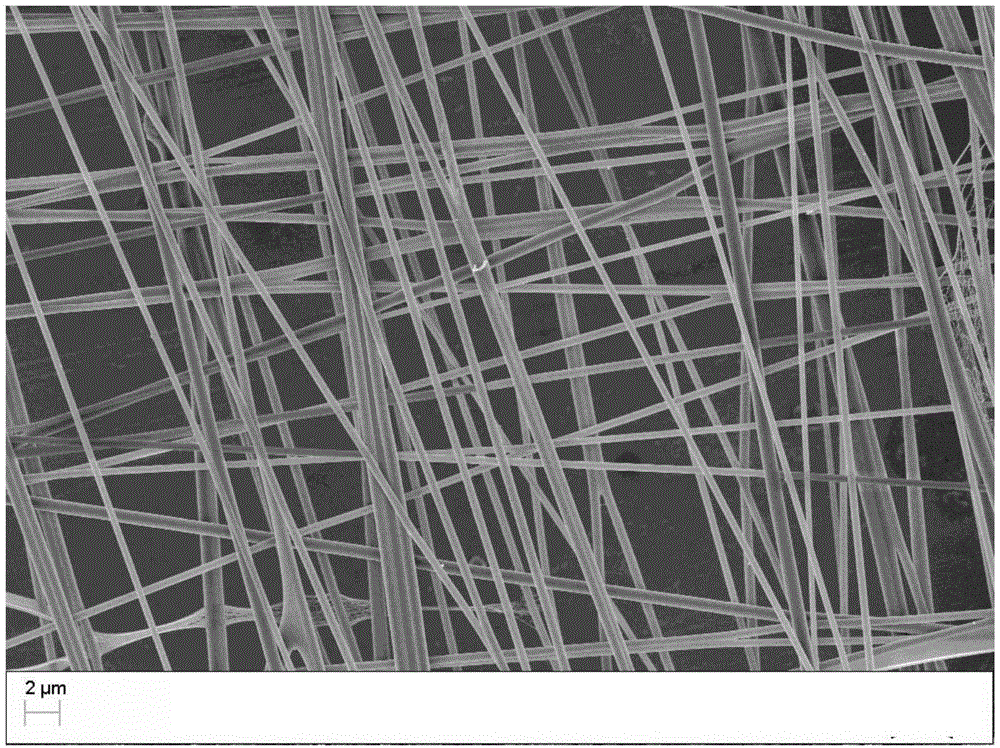
[0035] Weigh 0.525g of PCL and 0.175g of type I collagen (the mass ratio of PCL and collagen is 1:3) with an electronic balance, dissolve them in 5ml of hexafluoroisopropanol, and obtain a solution with a mass-volume concentration of 8% (m / v), The solution was magnetically stirred at room temperature for 12 hours to dissolve completely, and after standing for 5 minutes, electrospinning was started; the parameters of electrospinning were: electrostatic voltage 18kV, receiving distance 25cm, spinning rate 0.5ml / h, relative humidity 20%. A glass slide sandwiched between two parallel copper strips is used as a receiver, and through the action of an additional electric field, the fibers fall on the glass slide in a parallel orientation, and the glass slide is rotated 90 degrees at regular intervals to finally obtain a composite nanofiber film. Depend on image 3 It can be seen from the scanning electron microscope image that the fiber orientation of the composite nanofibrous membra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com