Three-dimensional imaging optical thin film
A technology of imaging optics and thin films, applied in optics, optical elements, lenses, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenience, unrestricted position and coordinate relationship of microlens arrays, etc., achieve optimal light collection ability, large process tolerance, and reduce film thickness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
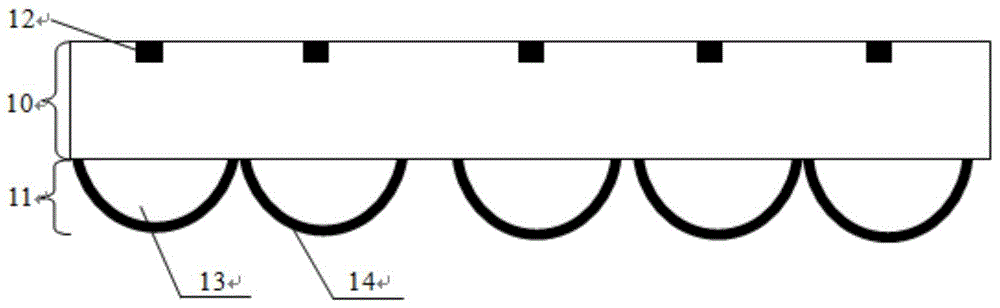
[0068] see Figure 1a , Schematic diagram of the structure of a 3D imaging optical film. The film has a three-layer structure: a transparent spacer layer 10 , a two-dimensional micro-reflective focusing unit array layer (or micro-reflective focusing unit array) 11 and a micro-text unit layer (micro-text unit) 12 . The two-dimensional micro-reflective focusing unit array layer 11 has a micro-focusing unit 13 and a micro-reflecting unit (or reflective layer) 14 .
[0069] The thickness of the transparent spacer layer 10 ranges from 10 microns to 5000 microns, preferably, the thickness of the transparent spacer layer is less than 1000 microns. The material of the transparent spacer layer can be PC, PVC, PET, PMMA, UV-sensitive curable glue, glass or BOPP, etc. Preferably, PET and UV-sensitive curable glue are selected.
[0070] The micro-focusing unit 13 and the micro-reflecting unit 14 focus the incident light from the second surface side of the transparent spacer layer on the ...
Embodiment 2
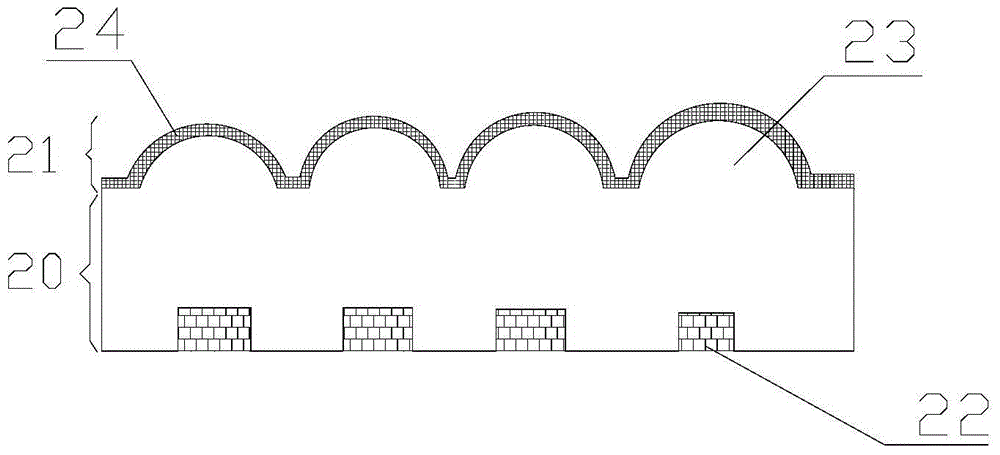
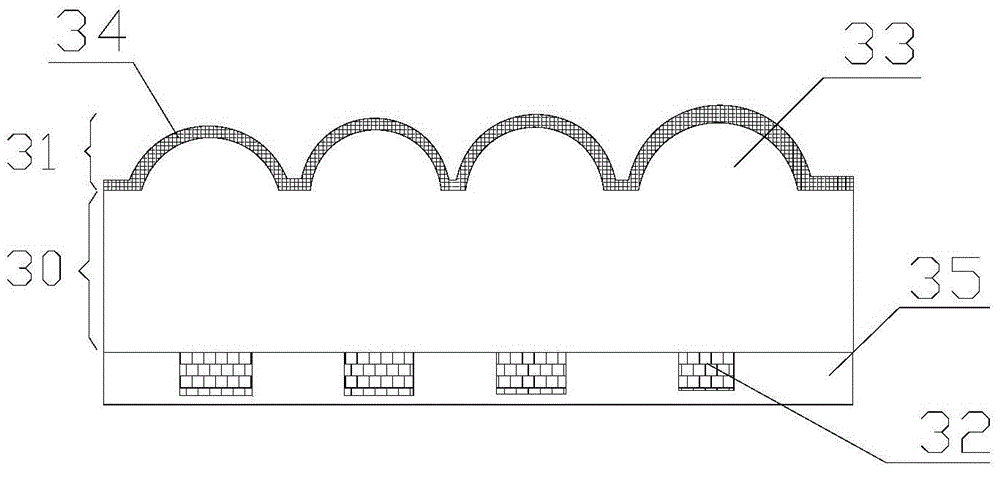
[0074] see Figure 4 , a schematic diagram of the visual effect of a 3D stereoscopic imaging film in the present invention. As described in the first embodiment of the present invention, the optical film can enlarge the micro-text 44 originally hidden in the micro-pattern layer so that the naked eye can directly distinguish it. The observer observes from the side of the second surface of the transparent spacer layer, and will see the only enlarged micro-text 45 suspended between the observer and the second surface of the transparent spacer layer. No matter when the imaging film is rotated along the horizontal axis 41 or the vertical axis 42, no other image of the second magnified microtext unit enters the viewing area. In addition, since the functioning micro-reflection focusing unit 43 is located on the second surface of the transparent spacer layer, it can be sealed with a protective material. When the first surface of the transparent spacer layer is covered by transparent...
Embodiment 3
[0076] The structure proposed by the present invention realizes the principle of floating 3D enlarged images as follows: Figure 5 shown. Set the radius of curvature R of the micro-reflection focusing unit, the focal length f, and the height di of the suspended image of the micro-graphic unit. then according to the attached Figure 5 Geometric relations in :
[0077] where x MLA Indicates the coordinate value of the micro-reflection focusing unit, x MPA Indicates the coordinate value of the microtext unit;
[0078] Get the height of the floating image:
[0079] d i = f - R 1 - x M P A x M L A + R . ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Focal length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com