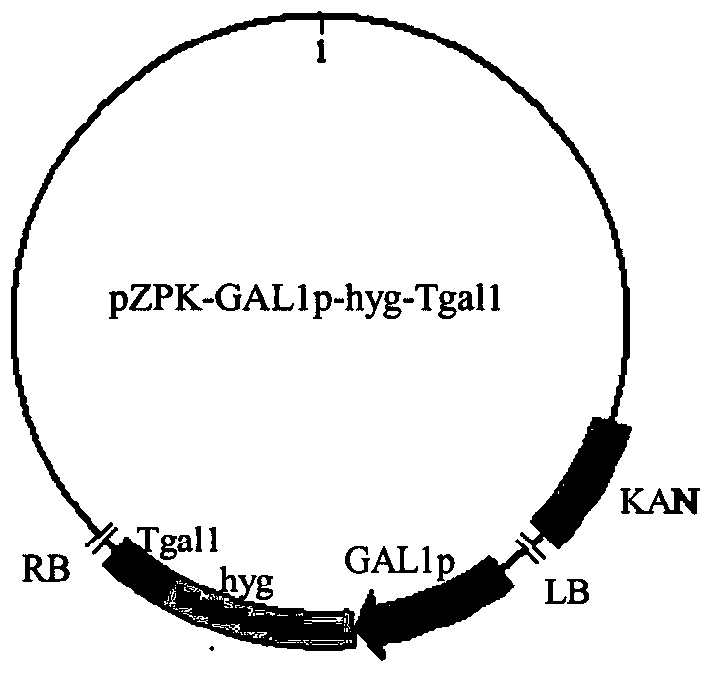
Galactokinase promoter and terminator and their application
A technology of galactokinase and promoter, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083]Embodiment 1: the extraction of Rhodosporidium toruloides (Rhodosporidium toruloides) CGMCC 2.1389 total RNA
[0084] Rhodosporidium toruloides (R. toruloides) CGMCC 2.1389 (purchased from China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC)) was inoculated into 10 mL YEPD liquid medium (glucose 20.0 g / L , yeast extract 10.0g / L, peptone 20.0g / L, pH 6.0), cultured on a shaker at 30°C for 24h, and then transferred the bacterial solution to 100mL YEPD liquid medium at a volume ratio of 1:50 , and cultured on a shaker at 30°C for 14h to reach the logarithmic growth phase. Centrifuge at 5000rpm for 4min at 4°C to collect the cells, quickly freeze the cells with liquid nitrogen, and grind to break the wall (Yang F, Tan HD, Zhou YJ, et al.Mol.Biotechnol.2010,47(2):144– 151.). Total RNA was extracted using the TakaRa RNAiso kit and following its standard procedures.
[0085] The RNA was subjected to 1.5% (mass / volume concentration) agarose gel electrophoresis, obse...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2: Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 cDNA first strand synthesis and GAL1 degenerate PCR
[0087] Using the total RNA of Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 as a template, the first strand of cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcription. First, mix 1.0 μL total RNA (about 2 μg), 1.0 μL primer SMART IV: 5′-AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGTGGCCATTACGGCCGGG-3′ and 1.0 μL oligo dT-linker primer CDSⅢ / 3′: 5′-ATTCTAGAGGCCGAGGCGGCCGACATG-d(T) 30N-1 N-3′, 2.0 μL of DEPC-treated water (diethyl pyrocarbonate-treated water, purchased from Dalian TakaRa Company), was added to the PCR tube and mixed evenly, kept at 72°C for 2 minutes, immediately placed on ice for 2 minutes, and 2.0 μL of 5×first-strand buffer (Clontech), 1.0 μL of DTT (20 mM), 1.0 μL of dNTP (10 mM), and 1.0 μL of powerscript reverse transcriptase (Clontech) were added to the system, and mixed. Extend the reaction at 42°C for 60 minutes, and end the reaction at 4°C, and store it at -20°C for later use.
...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3: Amplification of Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389RtGAL1 CDS
[0090] Genomic DNA of Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 was extracted by glass bead wall breaking method (Chapter 13 of the third edition of the Molecular Biology Experiment Guide, written by Osper et al., translated by Yan Ziying et al., published by Science Press). The prepared genomic DNA was measured by Nanodrop ND-1000, and the OD was measured 260 / OD 280 =1.85, indicating that the quality of genomic DNA is very good. The concentration was 280ng / μL, totaling 500μL, and the genomic DNA samples were frozen at -20°C for later use.
[0091] According to the galactokinase (RtGal1) cDNA sequence obtained in Example 2, a pair of gene-specific primers were designed, GAL1-p1: 5'-atgccctcgctcgagacgtcgccgctc-3' and GAL1-p2: 5'-tcaatccgagttctggaagaggagtgc-3', in circles Genomic DNA of Rhodosporidium CGMCC 2.1389 was used as a template, and PCR amplification was performed according to convent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com