Method and system for improving performance of metallurgical slag dry-process pelletizing device
A dry granulation and slag granulation technology, which is applied in the field of metallurgical energy saving, can solve the problems of agglomeration of plates and slag particles adhering to the wall, and achieve the effect of avoiding adhesion or agglomeration of plates.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
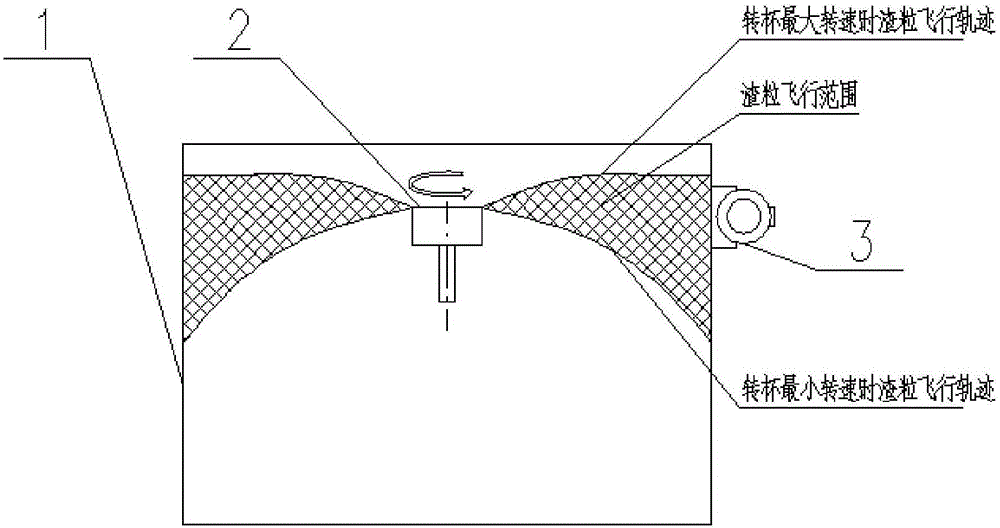
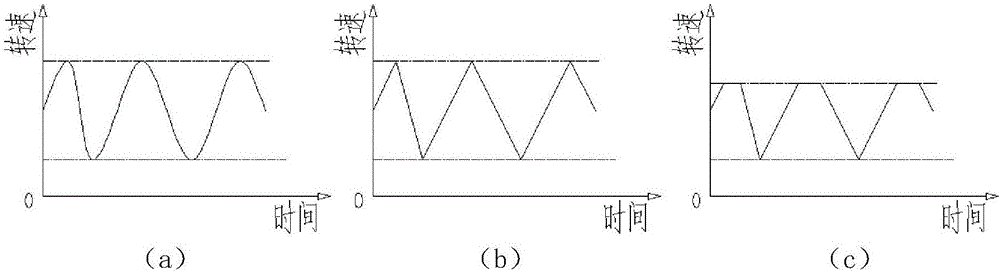
[0038] Such as Figure 1-2 , 5, because the flying speed of the slag particles is related to the rotating speed of the rotor, the flying speed of the slag particles is lower when the rotating cup is slow, and the flying speed of the slag particles is higher when the rotating cup is fast, so if the slag particles only keep constant When the speed hits the wall surface of the slag particle impact area of the slag receiving chamber, because too many slag particles continue to hit the same position on the inner wall surface, it is easy to cause the slag particles to stick and harden into blocks on the inner wall surface. Therefore, in this embodiment The characteristic is that the rotational speed of the rotor is not constant. Concretely, this method utilizes the rotational speed of the rotor to change periodically with time to carry out the slag granulation, including the following sub-steps: first, collect the minimum rotational speed and the maximum rotational speed of the ro...
Embodiment 2
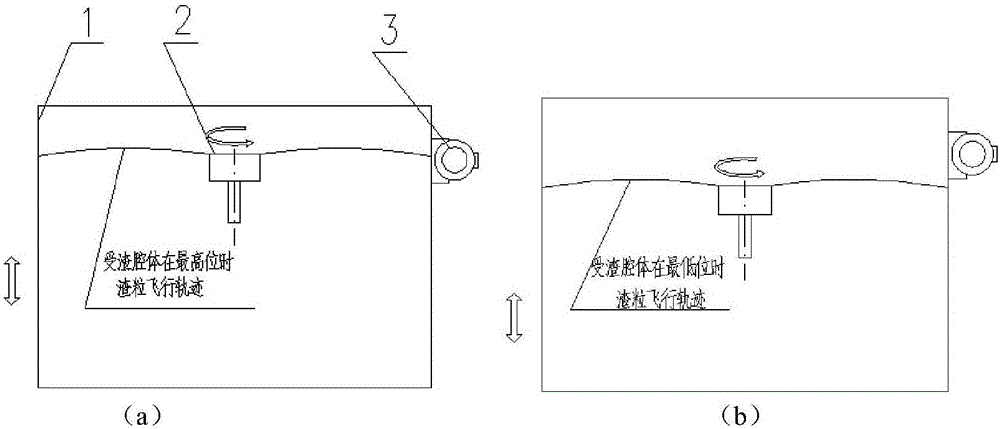
[0041] Such as Figure 3-5 As shown, since the slag particle bonding is related to the effective area of the wall surface of the slag particle impact area of the slag receiving cavity, that is, the half of the wall surface of the slag receiving cavity slag particle impact area usually adopts a water-cooled structure, and the slag particles hit the slag receiving cavity After the body slag particles hit the wall of the area, a certain cooling effect will be obtained. In this way, if the slag particles hit only one part of the inner wall surface, the temperature of the slag particles will drop slowly, which will easily cause the slag particles to stick and harden on the inner wall surface. Therefore, this embodiment is characterized in that the vertical height position of the slag receiving cavity is not constant. Specifically, this method uses the vertical height position of the slag receiving chamber to change periodically with time to carry out slag granulation, including...
Embodiment 3
[0044] This embodiment is to combine the two methods of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 at the same time, that is, to make the rotation speed of the rotor 2 and the vertical height position of the slag receiving chamber 1 not constant at the same time, and the specific details will not be repeated. In this way, the slag particles can also obtain different impact positions on the slag receiving chamber, so the contact point of the slag particles on the wall surface of the slag receiving chamber slag particle impact area will also change with the rotation speed of the rotor and the slag receiving chamber. Periodic changes occur due to changes in the vertical height position of the body, thus forming a relatively dispersed impact zone. In this way, since the impact points of the slag particles are scattered, the phenomenon of bonding and agglomeration is not easy to occur.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com