Method for screening DNA bar code universal sequences of seven major forage grass varieties of gramineous family
A universal sequence and screening method technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient variation, poor universality of primers, and only 22.2%
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
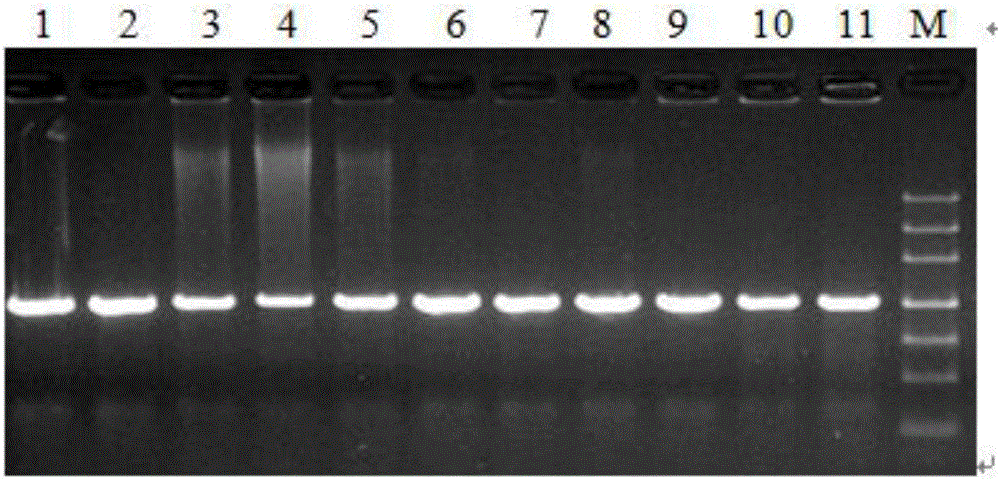
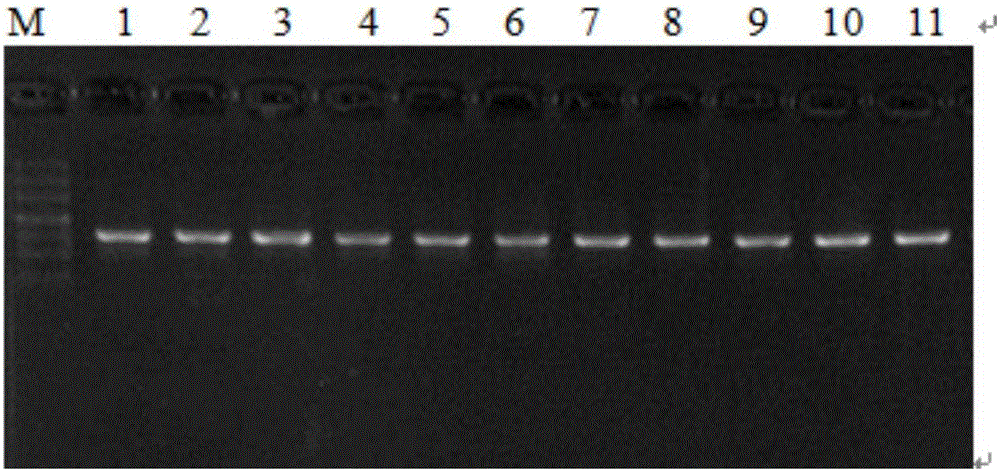
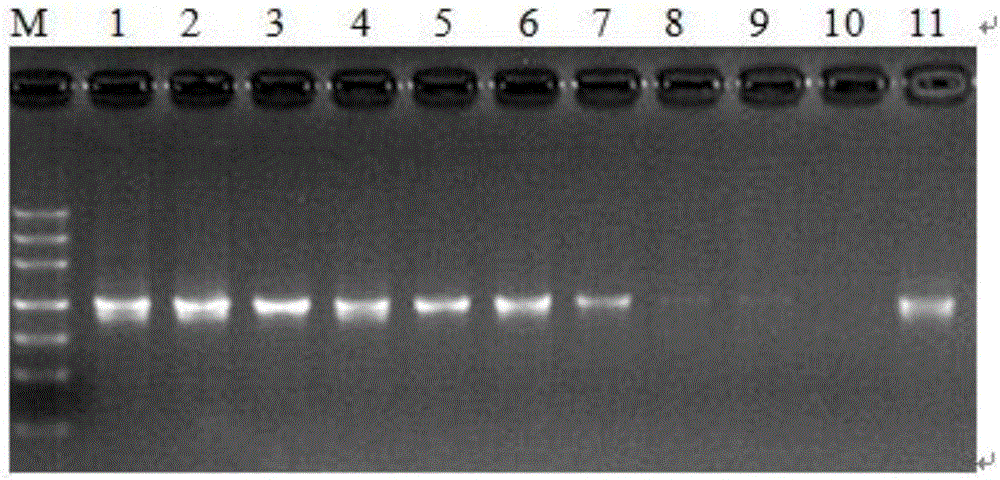
[0025] 1. Genomic DNA extraction, PCR amplification and sequencing
[0026] About 10 mg of plant leaves were weighed, ground to powder with liquid nitrogen, genomic DNA was extracted by CTAB method, and dissolved in TE. A 50ul system was used for PCR amplification: dNTP (2.5mmol / L) 2μL, 10×Buffer 5μL, Taq DNA polymerase (5U / μL) 0.4μL, DNA template 2μL, upstream and downstream primers 1μL (10μmol / L), add wxya 2 0 to 50 μL. PCR reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 2min; denaturation at 94°C for 40s, annealing for 30s, extension at 72°C for 30s (30 cycles); extension at 72°C for 10min; storage at 4°C. PCR amplification products were checked by agarose gel electrophoresis (30min, 150V). PCR amplification products were sent to Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd. for sequencing.
[0027] 2. Data processing
[0028] Chromas 2.33 was used to proofread and edit the sequencing results, MEGA 5.0 was used for sequence alignment, and Dnasp 5.10 was used to analyze ha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com