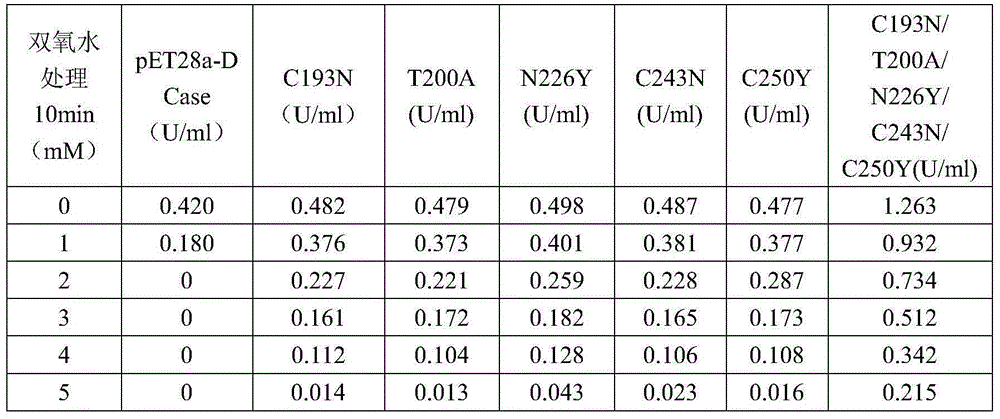
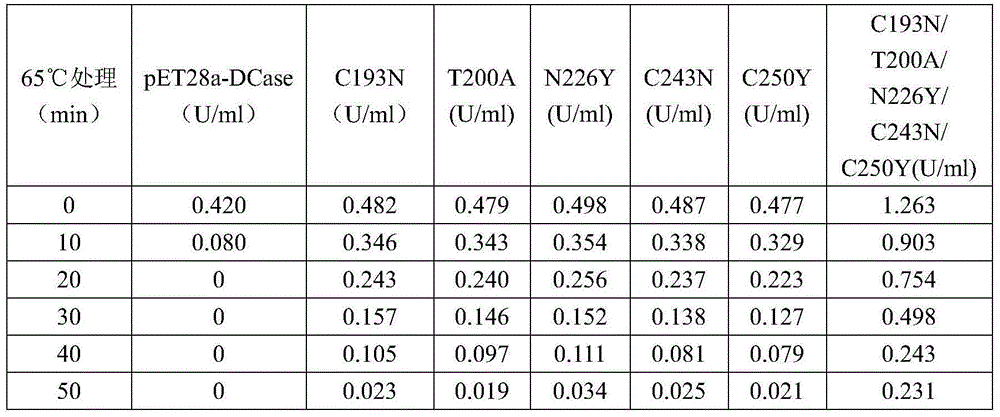
N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine hydrolase mutants and construction of engineering bacteria thereof
A technology of p-hydroxyphenylglycine and hydrolase, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of poor stability, increased enzyme activity stability, low enzyme activity of immobilized cells, etc., and achieve the effect of improving oxidation resistance and high temperature resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1, the cloning of N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine hydrolase gene
[0033] 1.1 PCR amplification
[0034] Primer design
[0035] DCase-F1: CGGGATCCGCTCGTCAGATGATATTCGCAG
[0036] DCase-R1: CTTACGATACTTGCCGACGATCTTG
[0037] DCase-F2: CAAGATCGTCGGCAAGTATCGTAAG
[0038] DCase-R2: GAGATGGTGGAAGGACGTCAGGTGG
[0039] DCase-F3: CCACCTGACGTCCTTTCCACCATCTC
[0040] DCase-R3: CCCAAGCTTGAGTTCCGCGATCAGACC
[0041] Using the pET28a-DCase plasmid as a template, PCR amplification was performed using primers DCase-F1 and DCase-R3. Amplification system: 2×PCR mix 10μl, dd H 2 O 8 μl, template DNA 1 μl (about 50ng-200ng), upstream and downstream primers 0.5 μl each (concentration 20 μM).
[0042] The PCR reaction conditions were: 96°C, 2min pre-denaturation; 96°C, 1min denaturation, 50°C, 30s annealing, 72°C extension 1min (30 cycles); finally 72°C extension 5min, 4°C storage.
[0043] 1.2 Construction of a plasmid containing N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine hy...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2, Directed mutation of N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine hydrolase expression gene
[0049] 2.1 Primer design
[0050] DCase-F1: CGGGATCCGCTCGTCAGATGATATTCGCAG
[0051] DCase-R1: CTTACGATACTTGCCGACGATCTTG
[0052] DCase-F2: CAAGATCGTCGGCAAGTATCGTAAG
[0053] DCase-R2: GAGATGGTGGAAGGACGTCAGGTGG
[0054] DCase-F3: CCACCTGACGTCCTTTCCACCATCTC
[0055] DCase-R3: CCCAAGCTTGAGTTCCGCGATCAGACC
[0056] Using the pET28a-DCase recombinant as a template, use primers DCase-F2 and DCase-R2 for error-prone PCR amplification, error-prone PCR reaction system (50ul): template gene 20ng, upper and lower primers 300pmol each, dATP0.2mm, dGTP0.2mm , dCTP1mm, dTTP1mm, MgCl 2 7mm, MnCl 2 0.1mm, Taq enzyme 2.5U (Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.).
[0057] The PCR conditions were: 96°C, 5min pre-denaturation; 96°C, 30s denaturation, 50°C, 30s annealing, 72°C extension 30s (30 cycles); finally 72°C extension 5min, 4°C storage.
[0058] 2.2 Construction of plasmid c...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3, Screening of N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine hydrolase mutation library
[0069] 3.1 Construction of engineering bacteria containing N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine hydrolase mutation library
[0070] Use a plasmid extraction kit (Beijing Kangwei Century Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) to extract recombinant plasmids, and then transform them into E.coli BL21 (Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) according to conventional methods. The transformed cells are coated on LB containing ampicillin antibiotics. Plates (tryptone 1%, yeast extract 0.5%, sodium chloride 1%, agar 1.5%) were cultured at 37°C.
[0071] 3.2 Screening and identification of N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine hydrolase mutants
[0072] Pick a single colony and culture it on a 96-well plate containing 200 ul of kana antibiotics (50 ug / ml). When the OD600 reaches 0.6, add 1 MIPTG to make the final concentration 0.2 mM, and culture overnight at 18 ° C.
[0073] Take out 150ul bacteri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com