A method for recycling valuable metals in waste circuit boards
A technology for waste circuit boards and valuable metals, which is used in the field of recycling valuable metals in waste circuit boards, can solve the problems of high equipment performance requirements, high exhaust gas treatment costs, and high environmental treatment costs, and achieves low recycling costs and reduced equipment. Requirements and the difficulty of exhaust gas treatment, the effect of low equipment performance requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
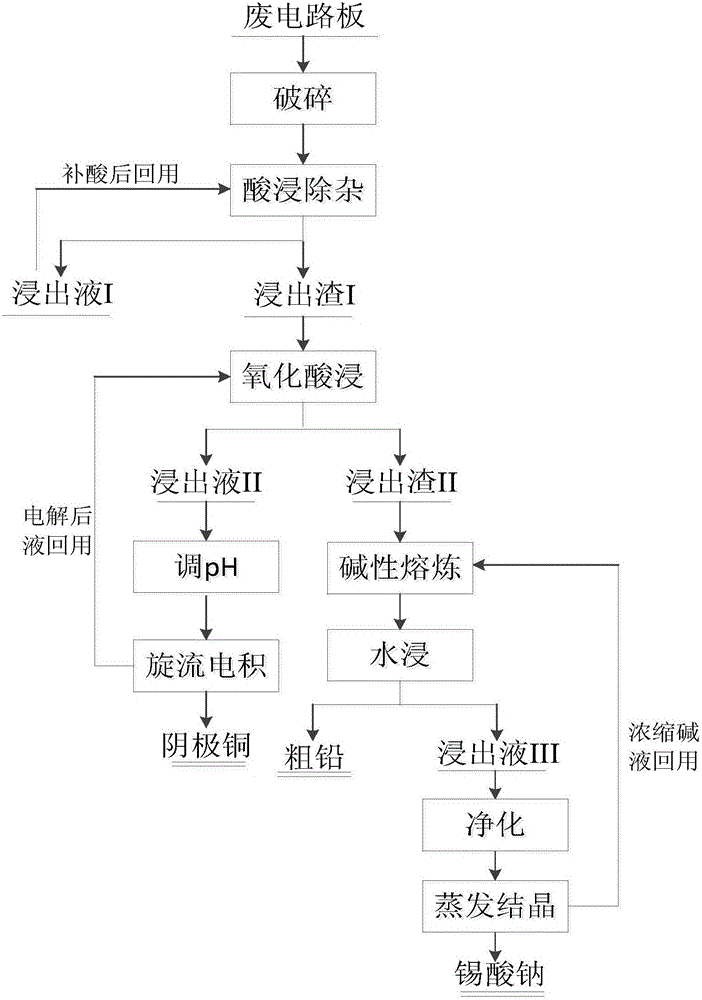
[0039] A method for recovering valuable metals in waste circuit boards of the present invention, its technological process is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0040] The waste circuit boards were crushed and re-selected to produce polymetallic powder. The chemical composition of the obtained polymetallic powder is shown in Table 1.
[0041] The chemical composition of table 1 multimetal powder
[0042]
[0043] Take 500g of polymetallic powder, press H 2 SO 4 The liquid-solid mass ratio of the solution to the polymetallic powder is 20:1, and the concentration of 0.5mol / L H is added. 2 SO 4 Solution, leaching, the leaching temperature is 30°C, the stirring power is 300r / min, and the leaching time is 120min. After leaching is completed, filter to obtain leaching residue I and leaching solution I. The more active aluminum, zinc, and iron in the multi-metal powder enter the leach solution I, and the leaching rates are 95.42%, 91.33%, and 90.06%,...
Embodiment 2
[0048] A method for recovering valuable metals in waste circuit boards of the present invention, its technological process is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0049] The waste circuit boards were crushed and re-selected to produce polymetallic powder. The chemical composition of the obtained polymetallic powder is shown in Table 1. Take 500g of polymetallic powder, press H 2 SO 4 The liquid-solid mass ratio of the solution to the polymetallic powder is 10:1, and the concentration of 2mol / L H is added. 2 SO 4 Solution, leaching, the leaching temperature is 40°C, the stirring power is 300r / min, and the leaching time is 80min. After leaching is completed, filter to obtain leaching residue I and leaching solution I. The more active aluminum, zinc, and iron in the multi-metal powder enter the leach solution I, and the leaching rates are 94.12%, 92.46%, and 91.34%, respectively. Copper, lead, tin and precious metal do not participate in reaction basi...
Embodiment 3
[0054] A method for recovering valuable metals in waste circuit boards of the present invention, its technological process is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0055] The waste circuit boards were crushed and re-selected to produce polymetallic powder. The chemical composition of the obtained polymetallic powder is shown in Table 1. Take 500g of polymetallic powder, press H 2 SO 4 The liquid-solid mass ratio of the solution to the polymetallic powder is 5:1, adding H at a concentration of 4mol / L 2 SO 4 Solution, leaching, the leaching temperature is 60°C, the stirring power is 300r / min, and the leaching time is 40min. After leaching is completed, filter to obtain leaching residue I and leaching solution I. The more active aluminum, zinc, and iron in the multi-metal powder enter the leach solution I, and the leaching rates are 91.42%, 90.39%, and 93.21%, respectively. Copper, lead, tin and precious metal do not participate in reaction substantial...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com