Active quenching circuit used for APD detector in Geiger mode
A technology of quenching circuit and Geiger mode, which is applied in the direction of protection equipment, etc., can solve the problems that continuous random detection cannot be realized, and achieve the effect of random continuous detection, simple and compact circuit structure, and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The technical solution of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, and the described specific embodiments are only for explaining and illustrating the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention.
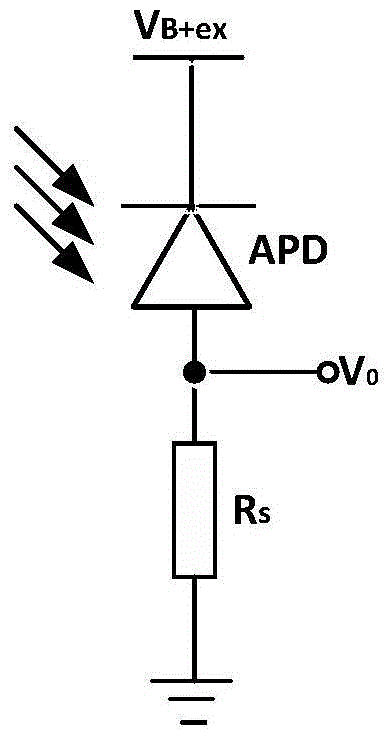
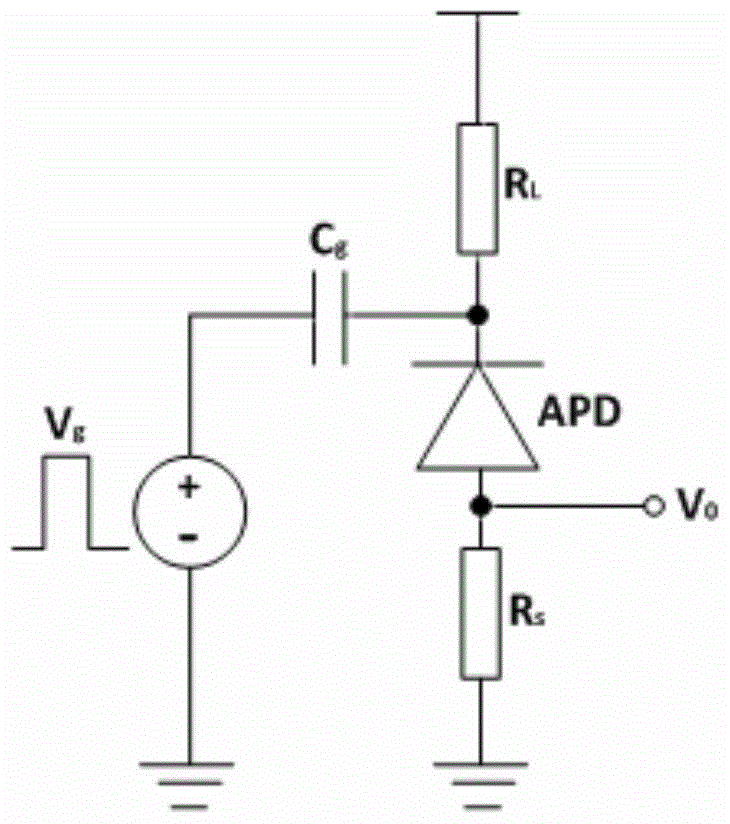
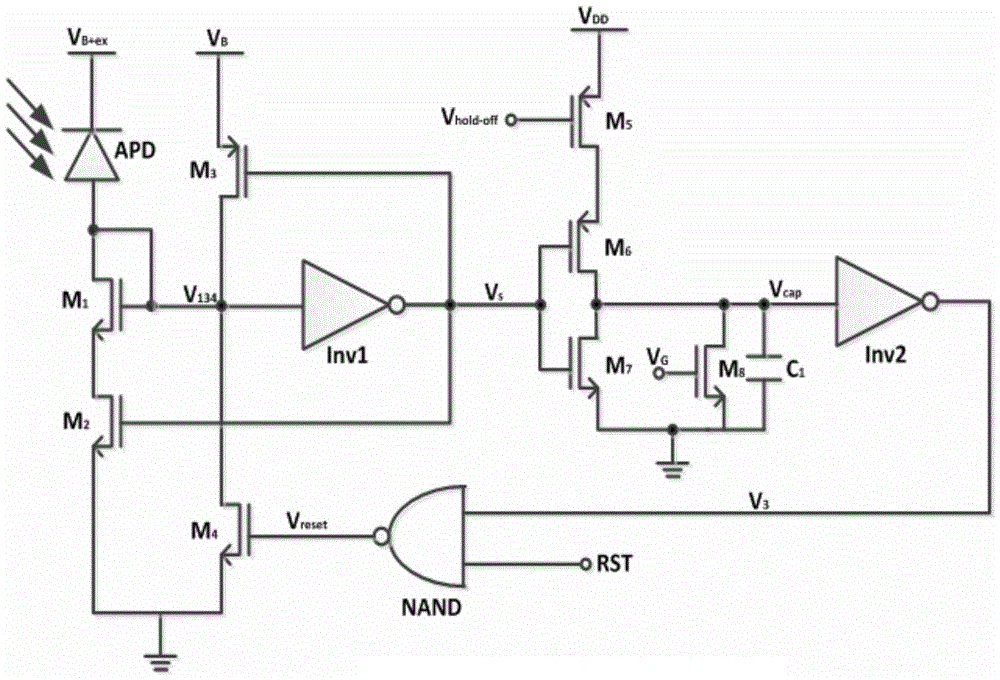
[0022] Compared with passive quenching circuits and gated mode circuits, active quenching circuits are more versatile. In general, the design idea is to convert the avalanche current into an avalanche voltage signal, and make the bias voltage between the two poles of the APD detector lower than the avalanche voltage V through the feedback structure. B , to achieve quenching of the APD detector. At the same time, the avalanche voltage signal will turn on the hold-off circuit behind to delay the APD detector to ensure that the photoelectrons captured by the trap can be released and annihilated by the trap within this delay, thereby reducing the after-pulse e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com