Synthesis method and use of cholic acid-modified polyamino acid block copolymer
A technology of block copolymers and polyamino acids, which is applied in the direction of medical preparations of non-active ingredients, emulsion delivery, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of inability to deliver drugs to target sites, premature release of drugs, and insufficient micelles Stability and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving package efficiency, stability and efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
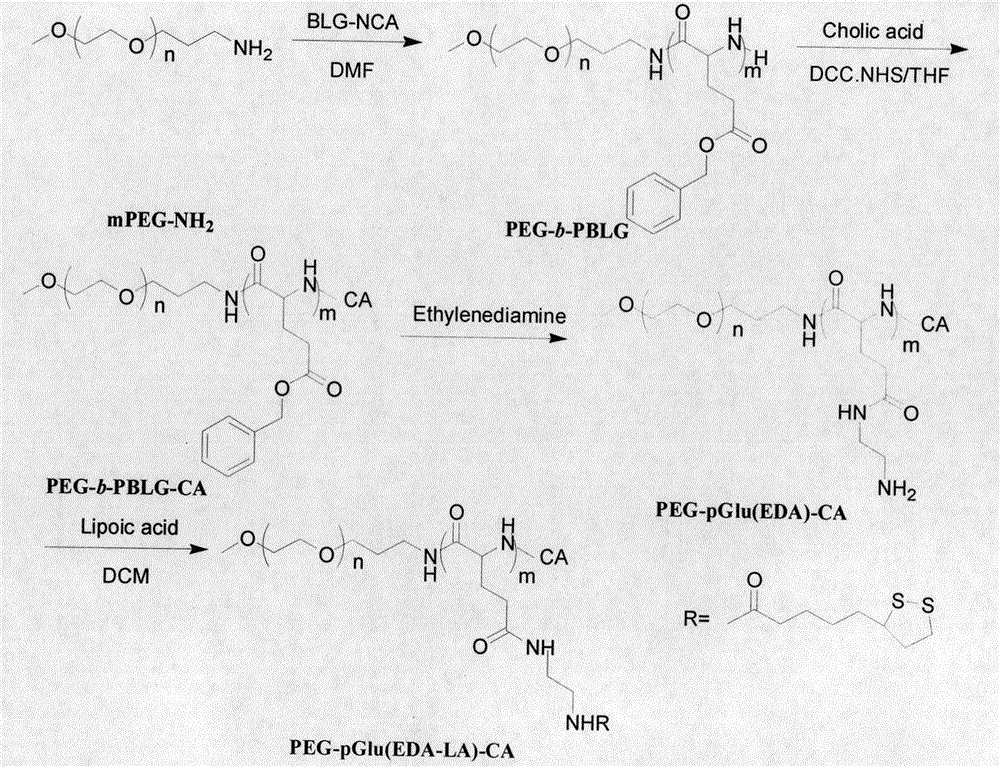
[0040] Embodiment one, synthetic polymer PEG-pGlu (EDA-LA) 15 -CA under nitrogen protection, the CH 3 O-PEG-NH 2 (1.00g, 0.20mmol) was dissolved in dry DMF (4mL), added to a 50mL airtight reaction bottle, and BLG-NCA (1.05g, 4mmol) was added thereto, and the bottle was placed in a 40°C oil bath, Stir the reaction for 48 hours, settle with anhydrous ether, filter with a sand core funnel, and finally vacuum-dry for 24 hours to obtain a white solid, namely PEG-b-PBLG amphiphilic polymer. Yield: 85%.
[0041] Under nitrogen protection, CA (0.33g, 0.04mmol) was dissolved in dry THF (4mL) and 1mL of anhydrous acetonitrile, and then NHS (0.03g, 0.23mmol) and DCC (0.04g, 0.19mmol) Dissolve in anhydrous THF and add to the above solution, stir and react at room temperature for 18h; filter with a 0.45μm filter membrane, dissolve PEG-b-PBLG polymer (0.50g, 0.06mmol) in anhydrous THF, add In the reactor, add the above-mentioned filtered solution, react at room temperature for 24 hours,...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment two, synthetic polymer PEG-pGlu (EDA-LA) 26 -CA
[0045] Under nitrogen protection, the CH 3 O-PEG-NH 2 (0.50g, 0.10mmol) was dissolved in dry DMF (5mL), added to a 50mL airtight reaction bottle, and then BLG-NCA (0.71g, 2.70mmol) was added to it, and the bottle was placed in a 40°C oil bath , stirred for 48 hours, settled with anhydrous ether, filtered through a sand core funnel, and finally dried in vacuum for 24 hours to obtain a white solid, namely PEG-PBLG amphiphilic polymer. Yield: 84%
[0046] Under nitrogen protection, CA (0.13g, 0.34mmol) was dissolved in dry THF (3mL) and 1mL of anhydrous acetonitrile, added to the closed reactor, and NHS (0.05g, 0.40mmol) and DCC ( 0.07g, 0.34mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous THF and added to the above solution, stirred and reacted at room temperature for 18h; filtered with a 0.45μm filter membrane, and PEG-b-PBLG polymer (0.40g, 0.04mmol) was dissolved in THF in water was added to a closed reactor, and then t...
Embodiment 3
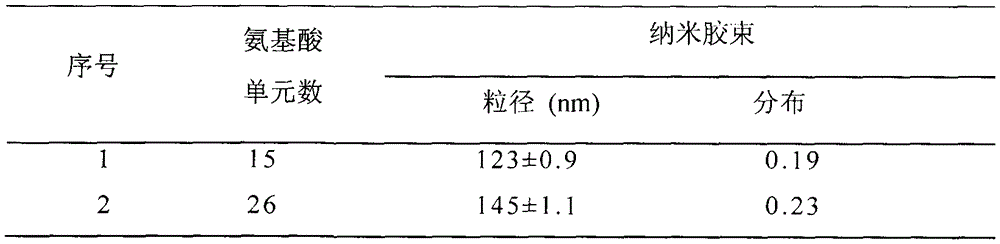
[0051] Example three, polymer PEG-pGlu (EDA-LA) 15 -CA nanomicelle preparation
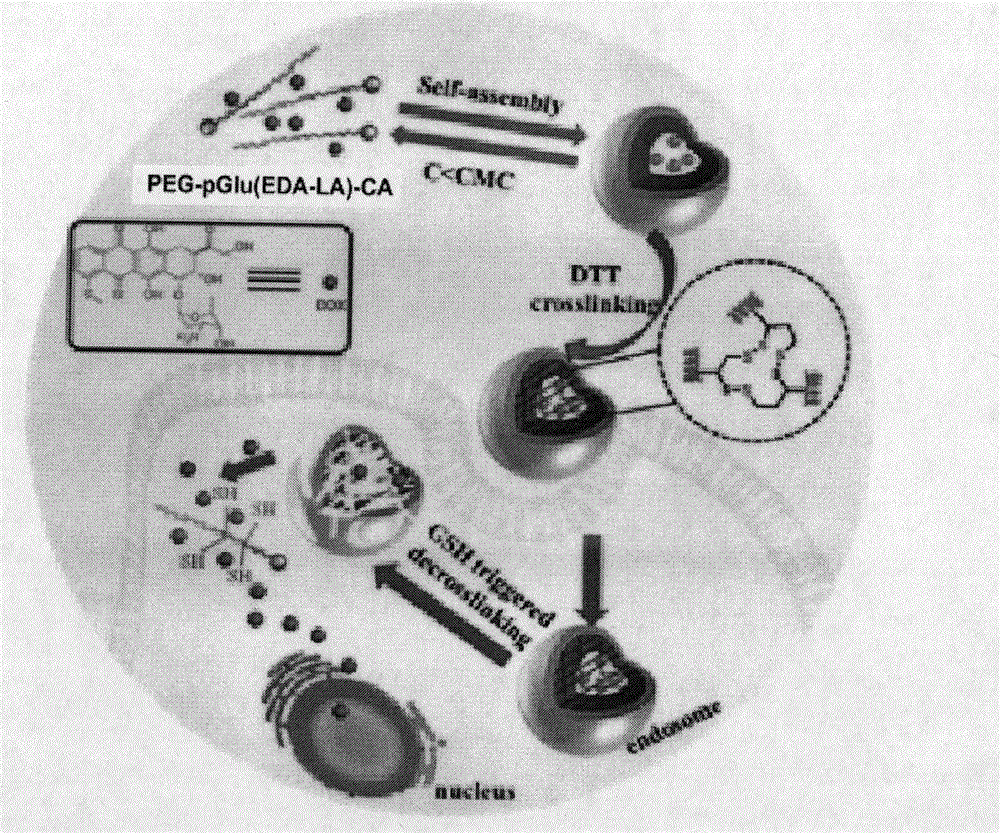
[0052] Polymer PEG-LA nanomicelles were prepared by dialysis method. The specific process is: 1 mg polymer PEG-pGlu (EDA-LA) 15 -CA was dissolved in 1 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, and 3 mL of secondary water was added dropwise thereto under stirring at 25°C. After the obtained solution was stirred for 05 h, it was loaded into a pre-prepared dialysis bag (MWCO3500), and dialyzed against deionized water for 24 h to obtain polymer nanomicelles.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com