Ethylenediamine waste water recovery technology
A wastewater recovery and ethylenediamine technology, which is applied in water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high treatment cost of amine-containing wastewater and low EDA recovery rate. Low cost, high oil-water separation efficiency, and small footprint
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
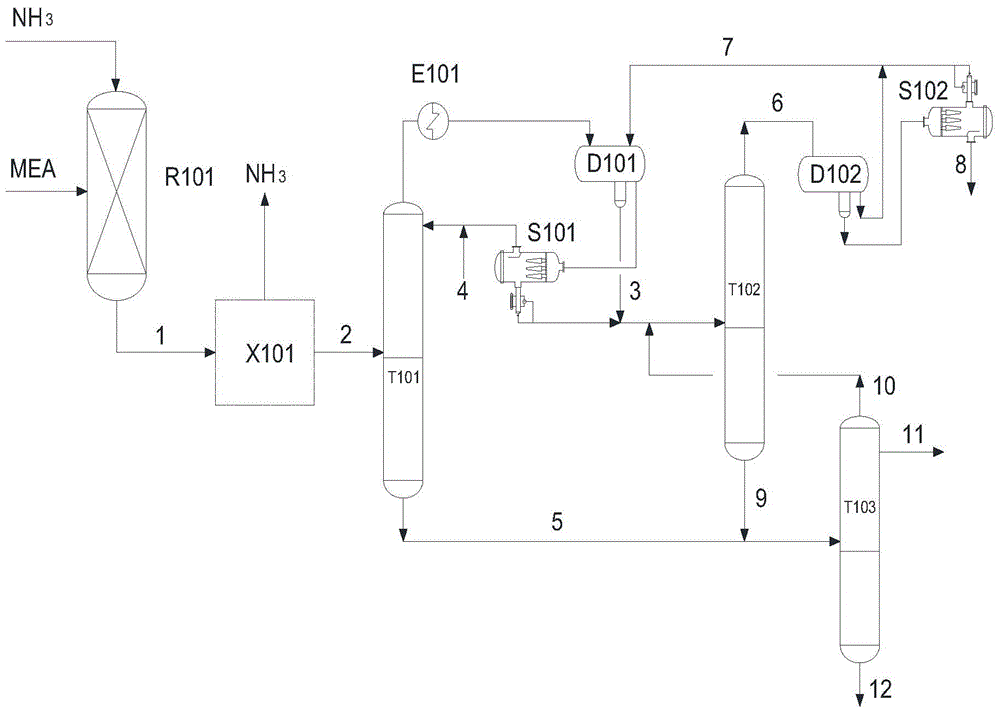
[0039] Liquid ammonia and MEA enter R101 after being heated and gasified, and the reaction product (stream 1) enters the ammonia recovery system X101 to recover ammonia. After the ammonia is recovered, the mixture containing MEA (stream 2) enters the dehydration tower T101 for azeotropic distillation and dehydration, and the top gas passes through Condenser E-101 enters the dehydration tower phase separation tank D101 to stand still (the standing time exceeds 60 minutes). The organic phase behind the water is refluxed as the dehydration tower T101, and waste water (stream 3) and residual water enter the EDA recovery tower T102 (supplementary entrainer (stream 4) joins the reflux line), pressurized rectification, and the tower top production liquid (stream 6) It mainly contains entraining agent and a small amount of water and EDA. It is sent to the EDA recovery tower T102 phase separation tank D102 to stand still (the standing time exceeds 60 minutes). After the phase separation...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment is identical with embodiment 1.
[0048] Wherein, entrainer is cyclohexane.
[0049] The theoretical plate number of the dehydration tower T101 is 40, the operating pressure is 0.05MPaA, the temperature at the top of the tower is 79.5°C, and the phase separation temperature of the phase separation tank at the top of the dehydration tower is 45°C.
[0050] The theoretical plate number of EDA recovery tower T102 is 65, the operating pressure is 0.50MPaA, and the temperature at the top of the tower is 152°C. Under this pressure, EDA and water azeotrope disappear, the light component rises to the top of the tower, and the heavy component EDA goes to the bottom of the tower. When the water rises to the top of the tower, it forms an azeotrope with the entrainer and entrains the entrainer.
[0051] The theoretical plate number of the EDA product column is 70, the operating pressure is 0.05MPaA, and the temperature at the top of the column is 82.3°C. The EDA produc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com