A method for producing probiotic dendrobium enzyme using dendrobium leaves
A technology of probiotics and dendrobium leaves, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of low content of active ingredients prebiotics, long fermentation cycle, difficult enzyme product efficacy, etc., to enhance immunity, improve digestive function, and promote digestive tract microecology. balanced effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
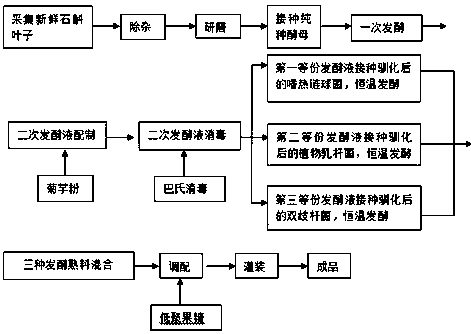
[0061] A kind of production technology of novel probiotic dendrobium ferment, comprises the steps:
[0062] Step (1), impurity removal, washing and shade-drying of dendrobium leaves:
[0063] The discarded dendrobium leaves are collected when the dendrobium is harvested, screened to remove moldy, moth-eaten, and rotten leaves, washed with clean water, and then placed in a cool place to dry.
[0064] Step (2), the grinding of dendrobium leaf:
[0065] Grinding the dendrobium leaf obtained in step (1) to a slurry state to obtain the protoplasm of the dendrobium leaf;
[0066] Step (3), primary fermentation:
[0067] Take the protoplasm of dendrobium leaves obtained in step (2) as the fermentation substrate, mix the pure yeast strain and the fermentation substrate evenly in a weight ratio of 5:100, place them at 28°C, and first feed sterile air to Oxygen fermentation for 23 hours, followed by anaerobic fermentation for 47 hours, and the fermentation was stopped to obtain a pri...
Embodiment 2
[0081] A kind of production technology of novel probiotic dendrobium ferment, comprises the steps:
[0082] Step (1), impurity removal, washing and shade-drying of dendrobium leaves:
[0083] The discarded dendrobium leaves are collected when the dendrobium is harvested, screened to remove moldy, moth-eaten, and rotten leaves, washed with clean water, and then placed in a cool place to dry.
[0084] Step (2), the grinding of dendrobium leaf:
[0085] Grinding the dendrobium leaf obtained in step (1) to a slurry state to obtain the protoplasm of the dendrobium leaf;
[0086] Step (3), primary fermentation: take the protoplasm of dendrobium leaves obtained in step (2) as the fermentation substrate, mix the pure yeast strain and the fermentation substrate evenly in a weight ratio of 7:100, and place at 36°C Next, feed in sterile air for 25 hours of aerobic fermentation, then anaerobic fermentation for 50 hours, stop the fermentation, and obtain a fermentation liquid;
[0087] ...
Embodiment 3
[0100] A kind of production technology of novel probiotic dendrobium ferment, comprises the steps:
[0101] Step (1), impurity removal, washing and shade-drying of dendrobium leaves:
[0102] The discarded dendrobium leaves are collected when the dendrobium is harvested, screened to remove moldy, moth-eaten, and rotten leaves, washed with clean water, and then placed in a cool place to dry.
[0103] Step (2), the grinding of dendrobium leaf:
[0104] Grinding the dendrobium leaf obtained in step (1) to a slurry state to obtain the protoplasm of the dendrobium leaf;
[0105] Step (3), primary fermentation:
[0106] Take the protoplasm of dendrobium leaves obtained in step (2) as the fermentation substrate, mix the pure yeast strain and the fermentation substrate evenly in a weight ratio of 6.5:100, place them at 33° C., and first feed sterile air to Oxygen fermentation 23.5h, after anaerobic fermentation 48h, stop fermentation, obtain primary fermented liquid;
[0107] Step...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com