Global offset table protection method based on address randomness and segment isolation
An offset table and address technology, which is applied in computer security devices, platform integrity maintenance, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming function analysis and analysis waste, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment one, see figure 1 As shown, the global offset table protection method based on random address and segment isolation includes the following steps:
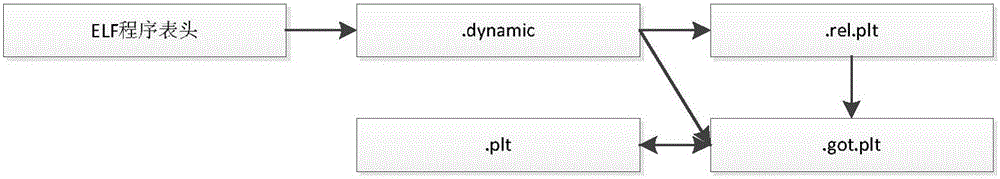
[0028] Step 1. After the ELF program is loaded, randomly apply for memory space, copy the content of the ELF segment to the memory space, assign a new segment name, and define the loading field PT_DYNAMIC in the ELF program header to describe .dynamic section information;
[0029] Step 2. Create a segment descriptor for the memory space randomly applied for in step 1, select a free segment register as a special segment register, and load the segment descriptor into the special segment register;
[0030] Step 3. Modify the program table header and the section content of the new section name in step 1 to make it meet the pointing relationship of the section in ELF, and modify the code in the .plt section to make it access GOT through a special section register surface;
[0031] Step 4. Initialize the dynamic link...
Embodiment 2
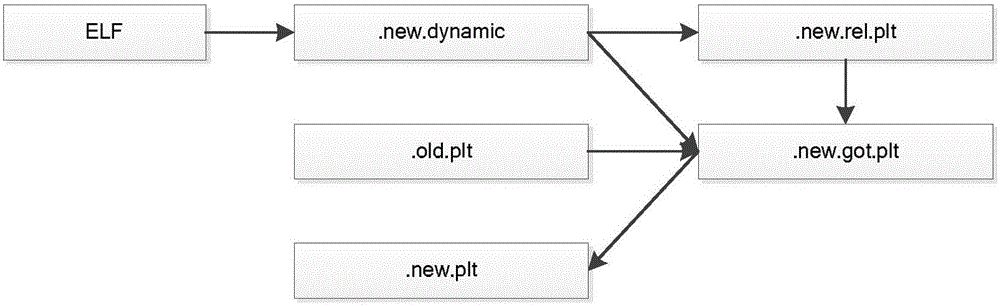
[0033] Embodiment two, see Figure 2~4 As shown, it is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that in the step 1, randomly applying for a memory space and copying the content of the ELF segment to the memory space specifically includes randomly applying for at least three pages of memory space on demand, including Readable and executable pages, readable-only pages, and readable and writable pages, among them, .plt is copied to the readable and executable pages, which is recorded as .new.plt; .rel.plt is copied to the read-only pages, recorded as .new.rel.plt; .dynamic and .got.plt are copied to readable and writable pages, and are recorded as .new.dynamic and .new.got.plt respectively. The three-page memory space can be any in the address space Three pages of unused memory.
[0034] Preferably, in step 1, the content of the ELF section is copied into the memory space, and the new section name given specifically includes: copying the contents of the .plt, .rel.p...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment three, in combination with specific embodiments, the technical solution of the present invention is further introduced, and the specific implementation process is as follows:
[0042] The ELF program header table contains a section of type PT_DYNAMIC, which contains the .dynamic section. By parsing the .dynamic section, the starting offset of the .plt.got, .rel.plt section, and .rel.plt section can be obtained size, the type of relocation items in .rel.plt; according to the obtained information about the .rel.plt section, you can know the number of library functions referenced by the program:
[0043] libfun_num=size(.rel.plt) / sizeof(Type_Rel)
[0044] Among them, Type_Rel is determined as Elf32_Rel or Elf32_Rela according to the type of the relocation table. The definitions of these two types are as follows Figure 8 shown.
[0045] According to the number of library functions, the size of .got.plt is calculated, size(.got.plt)=libfun_num*4+12, the library...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com