High-yield N-acetylneuraminic acid metabolic engineering bacterium and construction method and application
A technology of acetylneuraminic acid and metabolic engineering, which is applied in the field of high-yield N-acetylneuraminic acid metabolic engineering bacteria and construction, can solve the problems of restricting large-scale application, high cost, and low production of N-acetylneuraminic acid. Achieve the effect of improving synthesis efficiency and reducing the accumulation of by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
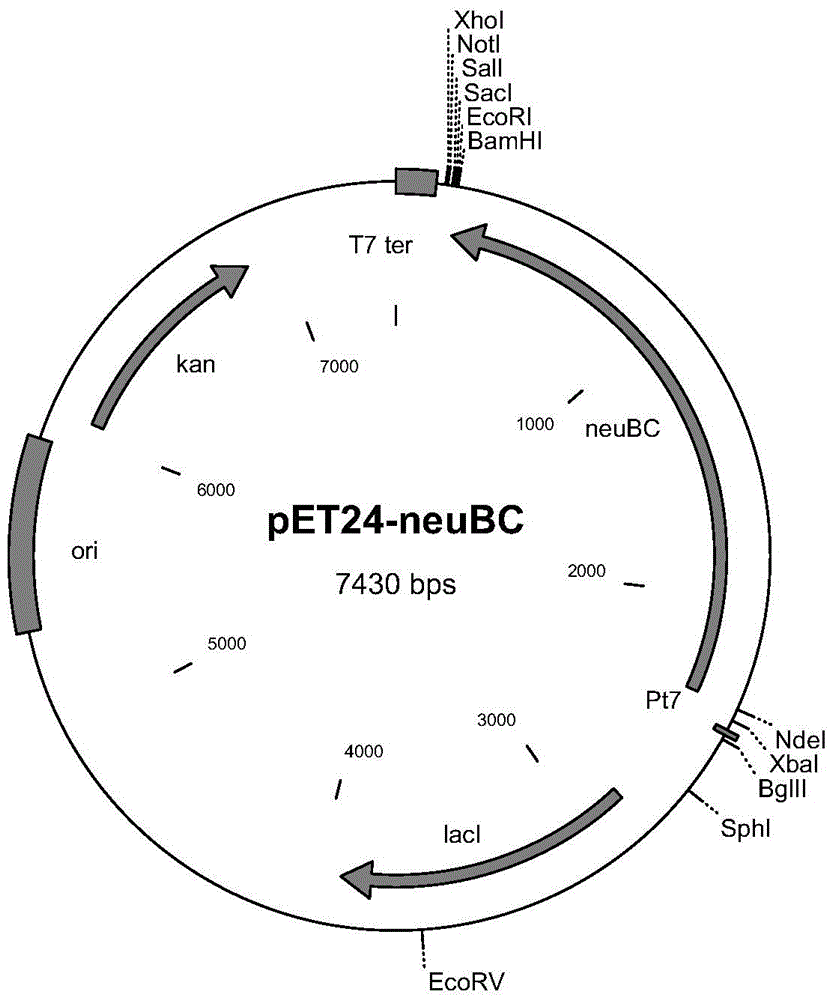
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: Construction of high-yield N-acetylneuraminic acid genetically engineered bacteria
[0027] 1. Using the Red recombination method to knock out the nanATEK gene cluster in the strain, the specific steps are as follows:
[0028] 1. Knockout of nanATEK gene cluster
[0029] 1) According to the sequence of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) genome (Genbank No.CP001509), design primers: upstream primer F-nanA:
[0030] GCAACGAATTTACGTGGCGTAATGGCTGCACTCCTGACTATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC (shown in SEQ ID NO.1) and downstream primer R-nanK:
[0031] TTTTTCTCCCCTGGGCCAACAGCGCAGCCCCAAGTAAACCTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC (shown in SEQ ID NO.2), using primers F-nanA and R-nanK, using plasmid pKD13 as a template, using commercial PCR reagents, a DNA fragment was obtained by PCR amplification, and purified for later use.
[0032] 2) Cultivate Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) in LB medium at 37 overnight, prepare competent cells by calcium chloride method, transform pKD46, coat ampicillin-resistant L...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Glucose is used as carbon source to ferment and produce N-acetylneuraminic acid
[0049] 1. Seed and fermentation medium (1L):
[0050] (NH4) 2 SO 4 4g / L; KH 2 PO 4 6g;K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 8g; Yeast extract (purchased from OXOID company) 5g; Peptone 10g / L; Glucose 5g.
[0051] Feed solution: 500g / L glucose.
[0052] 2. Fermentation process:
[0053] 1) Pick a single CASOV-2 colony and place it in a 4ml LB test tube, and culture it at 37°C for 8-12 hours.
[0054] 2) Inoculate 2ml of primary seeds into 200ml of seed culture medium and culture at 37°C for 8-10 hours.
[0055] 3) Secondary seeds are inoculated in a fermenter with a liquid volume of 3.5 L at 37° C., stirring speed is 300-800 rpm, dissolved oxygen is kept above 30%, and pH is controlled at 6.9 with ammonia water.
[0056] 4) After the glucose is exhausted, add glucose at a rate of 5g / L.h.
[0057] 5) OD of fermentation broth 600 =25~30 o'clock, add IPTG (IPTG final concentration is 0.2mM)...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3 Glycerol is used as carbon source to ferment and produce N-acetylneuraminic acid
[0060] Replace glucose with glycerol of 20g / L, other components of fermentation medium are the same as embodiment 2, and feeding medium is 600g / L glycerol;
[0061] The fermentation process is the same as in Example 2.
[0062] Finally, after about 80 hours of fermentation, the concentration of the product N-acetylneuraminic acid can reach more than 70 g / L.
[0063] The above culture results show that the genetically engineered bacteria constructed by the metabolic engineering technology have the ability of high-yield N-acetylglucosamine, and have the potential of industrialization.
[0064]
[0065]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com