A method for genotyping Mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotides encoded by melting point
A technology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and typing methods, applied in the field of Mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotide typing, can solve the problems of multiple manual operations, long detection time, PCR product contamination, etc., to improve detection throughput, Meet clinical needs, high detection throughput effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: System Design of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotide typing method coded by melting point
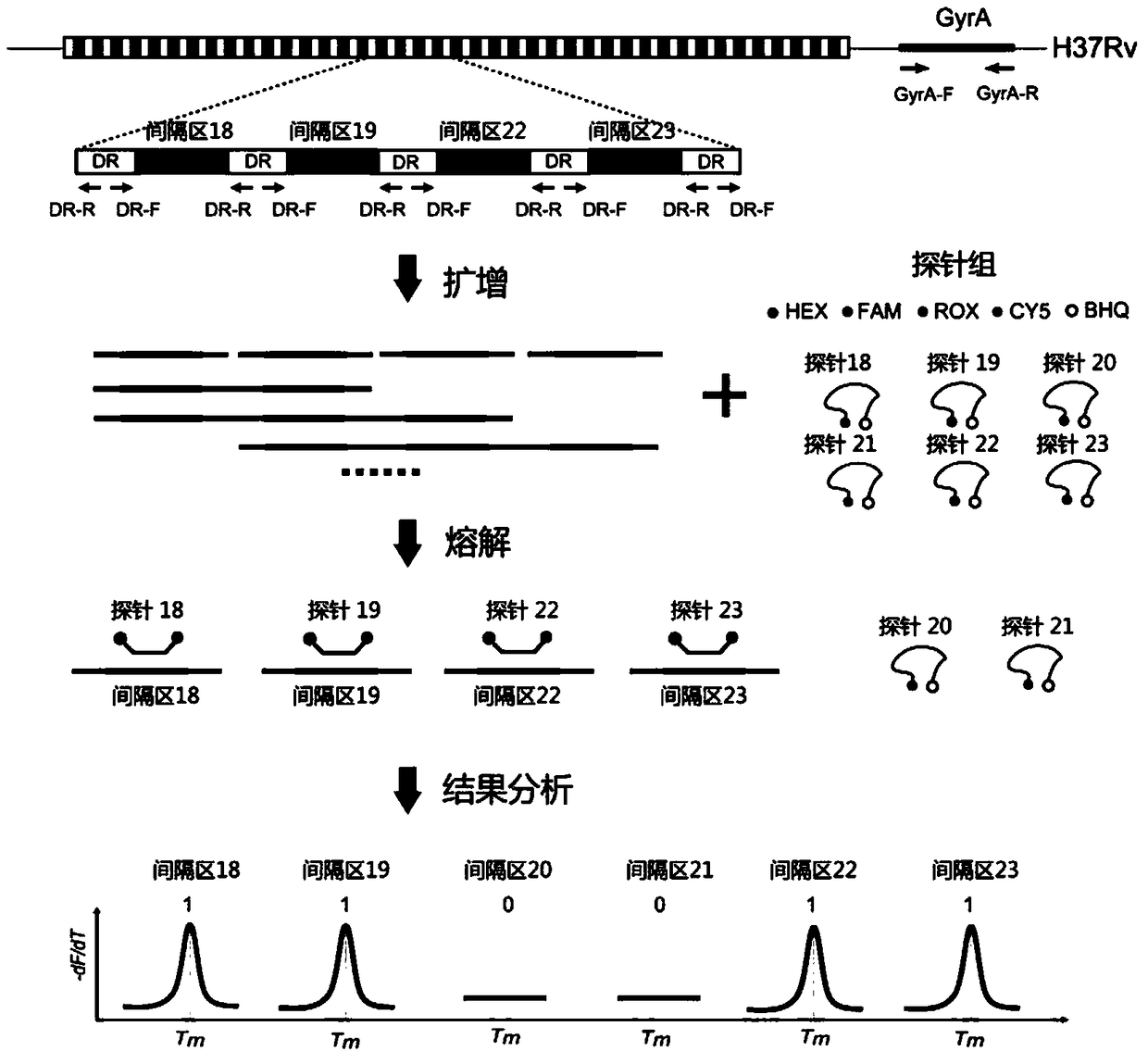
[0048] The technical principle of a melting point coded Mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotide typing method is as follows figure 1 Shown: There is a 36bp DNA fragment in the genome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which repeats in the genome, called direct repeat sequence, denoted as DR, these fragments are separated by 35-41bp spacers, these The sequence of the spacer is almost the same in all strains, but the insertion or deletion of a certain spacer may occur in different strains. Therefore, Mycobacterium tuberculosis can be typed and identified by detecting the presence or absence of the spacer. First, design a pair of universal primers on the direct repeat sequence in the genome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, denoted as DR-F and DR-R, use this pair of universal primers to amplify the PCR product of the spacer contained; A pair of amplifi...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: A method for genotyping H37Rv and BCG standard strains by a melting point coded Mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotide typing method
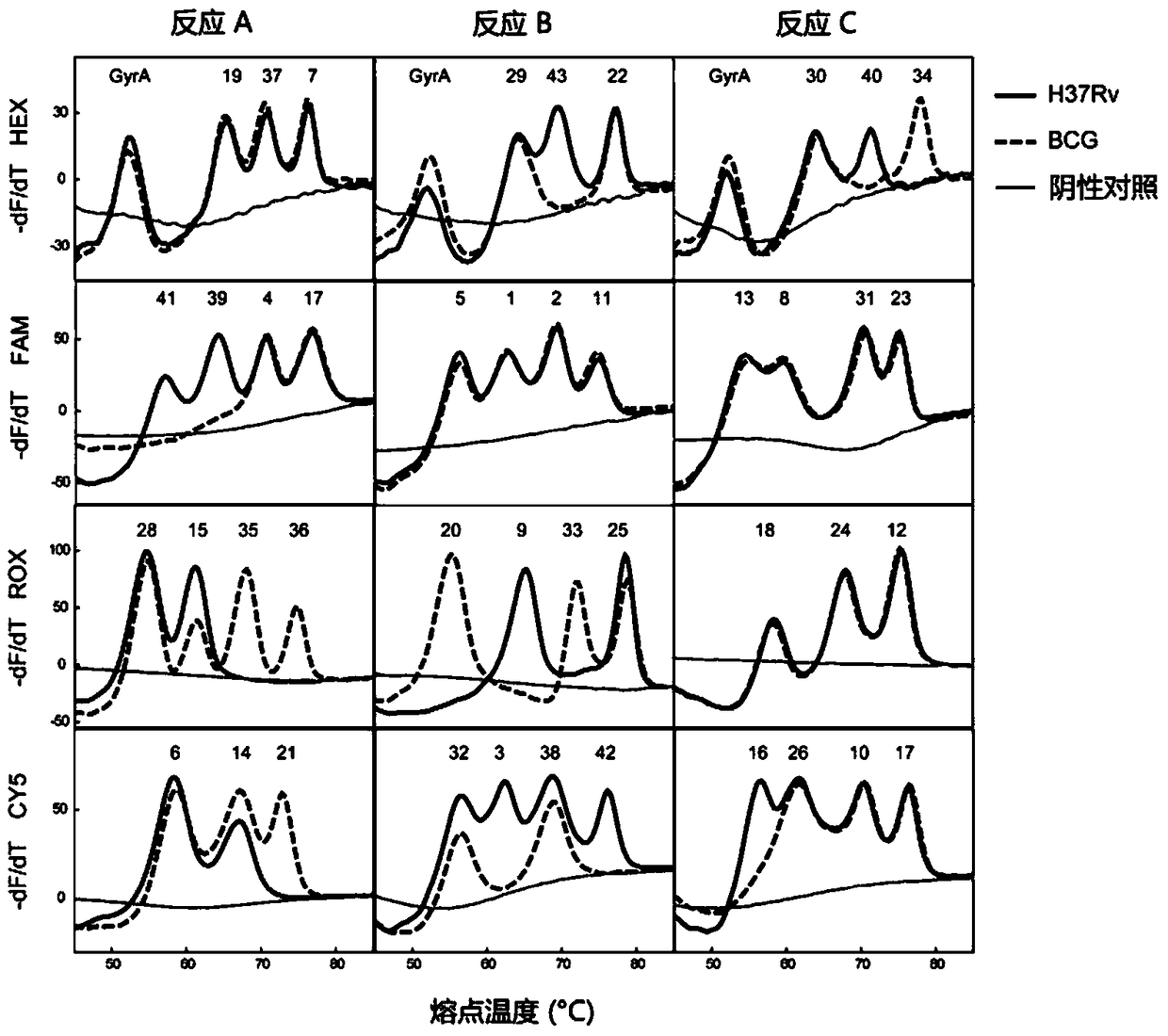
[0052] The present invention is used to carry out six repeated experiments on the DNA samples of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv standard strain and the BCG standard strain respectively, so as to investigate the repeatability of the Tm value detected by the system. Among them, the DNA samples of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv standard strain and BCG standard strain were provided by China National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products.
[0053] In this example, SLAN96 real-time fluorescent PCR instrument was used to complete the amplification curve and melting curve analysis.
[0054] reaction system:
[0055]Reaction A: The total reaction volume is 25 μL, including 1×PCR buffer (750mM Tris-HCl, 200mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 0.1% (v / v) Tween 20), 4mmol / L MgCl 2 , each dNTP 0.5mmol / L...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3: Sensitivity analysis of a melting point-coded Mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotide typing method
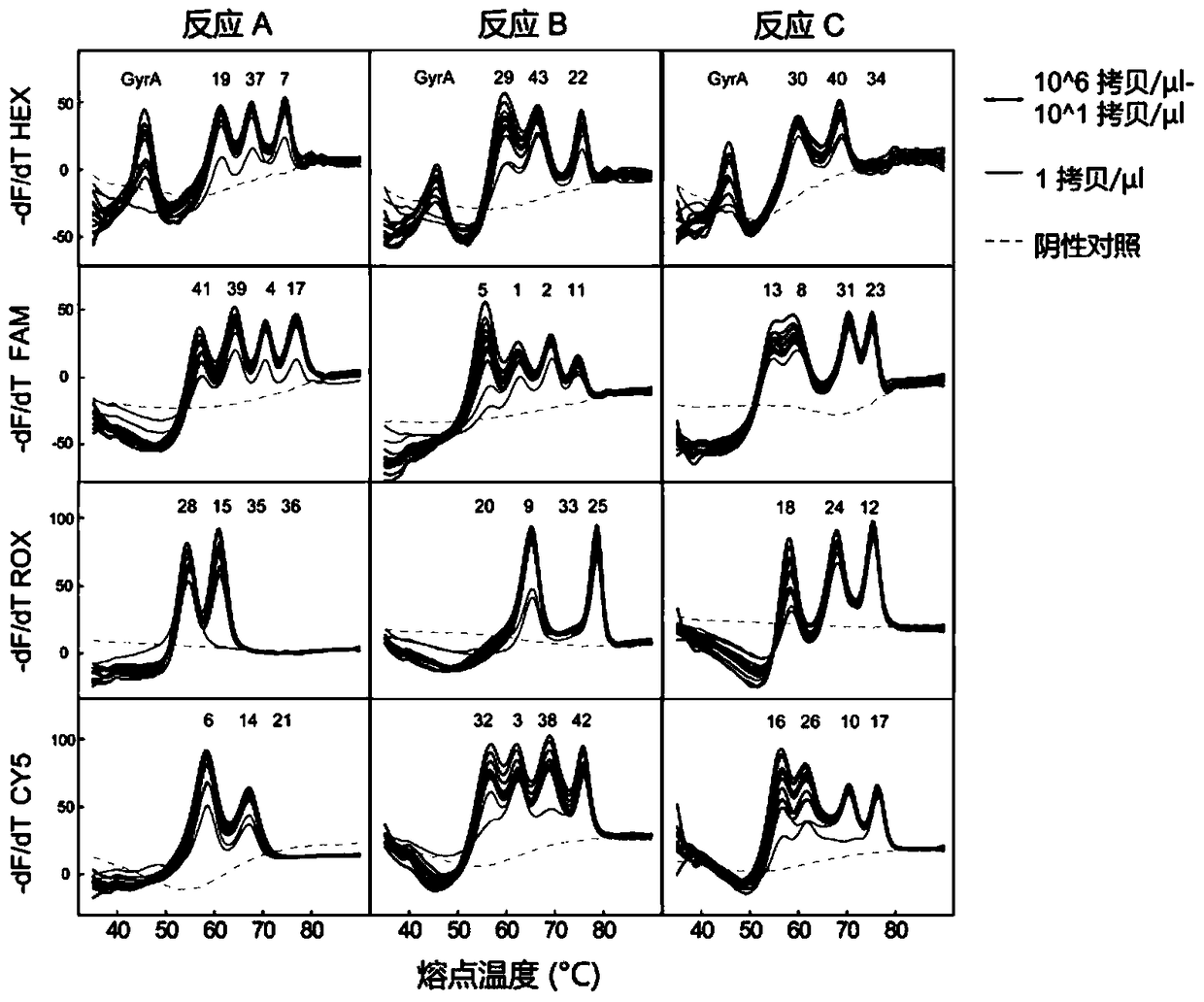
[0067] The invention is used to carry out experiments on the DNA sample of the tuberculosis mycobacterium H37Rv standard strain to investigate the effective template concentration range of the system for genotyping tuberculosis specimens. Among them, the DNA sample of the standard strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv was provided by the National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products.
[0068] In this example, SLAN96 real-time fluorescent PCR instrument was used to complete the amplification curve and melting curve analysis.
[0069] The experimental procedure is as follows:
[0070] (1) Gradient dilution of the H37Rv standard strain: the genomic DNA template of the H37Rv standard strain was diluted 10 times, so that the concentration of genomic DNA added to each gradient was 1×10 6 copies / μl, 1×10 5 copies / μl, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com