Method for extracting and recycling residual potassium chloride from salt-lake tail salt and waste carnallite
A carnallite and potassium chloride technology, applied in the direction of alkali metal halide purification, etc., can solve the problems of difficult application, long process time, waste of resources, etc., to solve the problem of solution loss, simple process flow, and prolong flow time. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
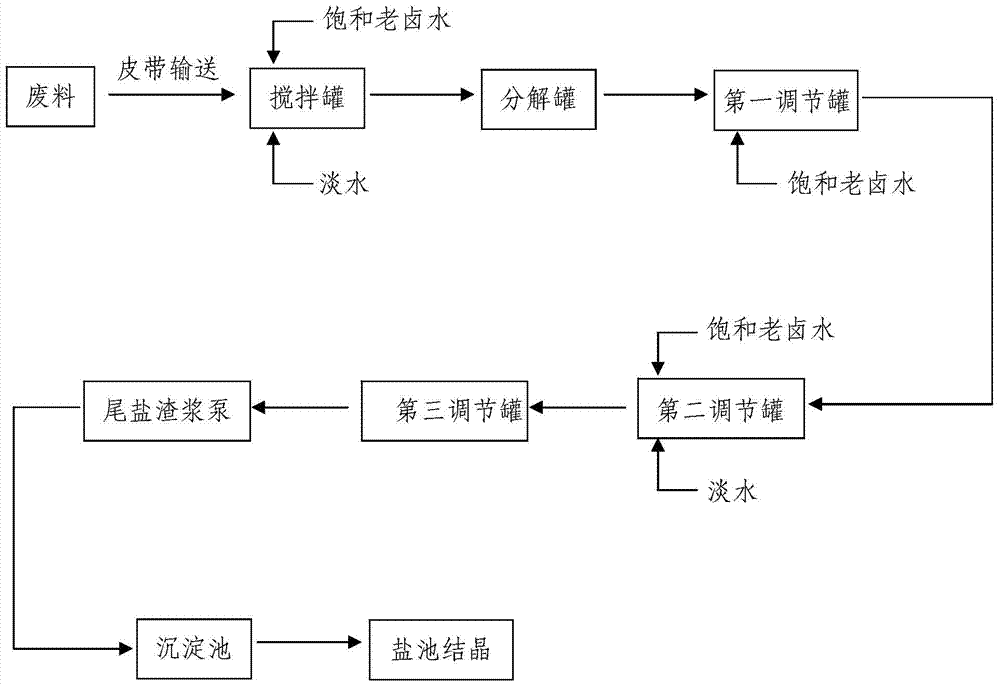
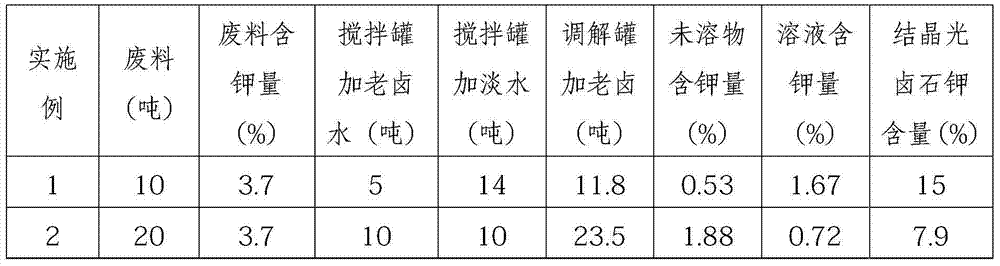
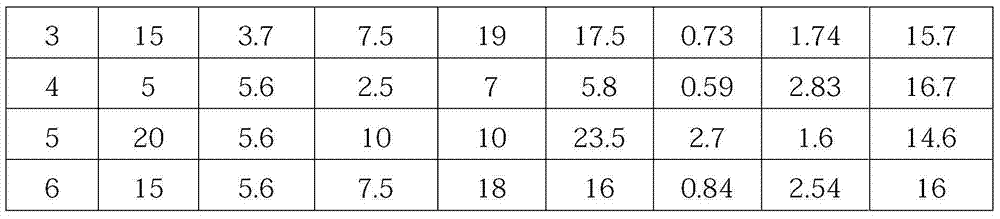
[0062] 10 tons of waste materials with a potassium content of 3.7% are conveyed to the mixing tank by a belt, and saturated old brine and fresh water are added to the mixing tank in the ratio of waste: saturated old brine: fresh water is 1: 0.5: 1.4, wherein the saturated old brine 5 tons of brine and 14 tons of fresh water. After being stirred by a stirrer, a solution of waste material is obtained. The waste solution flows into the decomposition tank through the connecting pipe, and then the potassium chloride in the waste solution is fully dissolved in water after being stirred by the agitator. Detect gained solution Baume degree in the decomposition tank, determine to add the total amount of saturated old brine in the first adjustment tank and the second adjustment tank to be 11.8 tons, after the first adjustment tank and the second adjustment tank are allocated, the solution Baume degree is 29°Be~31.5°Be. There is no specific limit to the addition amount of the saturated...
Embodiment 2
[0065] 20 tons of waste materials with a potassium content of 3.7% are transported to the mixing tank by a belt, and saturated old brine and fresh water are added to the mixing tank in a ratio of waste: saturated old brine: fresh water of 1: 0.5: 0.5, wherein the saturated old brine 10 tons of brine and 10 tons of fresh water. After being stirred by a stirrer, a solution of waste material is obtained. The waste solution flows into the decomposition tank through the connecting pipe, and then the potassium chloride in the waste solution is fully dissolved in water after being stirred by the agitator. Detect gained solution Baume degree in the decomposition tank, determine to add the total amount of saturated old brine in the first adjustment tank and the second adjustment tank to be 23.5 tons, after the first adjustment tank and the second adjustment tank are allocated, the solution Baume degree is 29°Be~31.5°Be. The solution obtained in the second adjustment tank flows into t...
Embodiment 3
[0068] 15 tons of waste materials with a potassium content of 3.7% are transported to the mixing tank by a belt, and saturated old brine and fresh water are added to the mixing tank in the ratio of waste: saturated old brine: fresh water is 1: 0.5: 1.3, wherein the saturated old brine 7.5 tons of brine and 19 tons of fresh water. After being stirred by a stirrer, a solution of waste material is obtained. The waste solution flows into the decomposition tank through the connecting pipe, and then the potassium chloride in the waste solution is fully dissolved in water after being stirred by the agitator. Detect gained solution Baume degree in the decomposition tank, determine to add the total amount of saturated old brine in the first adjustment tank and the second adjustment tank to be 17.5 tons, after the first adjustment tank and the second adjustment tank are allocated, the solution Baume degree is 29°Be~31.5°Be. The solution obtained in the second adjustment tank flows int...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com