Method for extracting zinc from low-grade zinc-containing material leachate
A low-grade, leaching liquid technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of reducing economic benefits, increasing production costs, increasing concentration, etc., and achieves the effects of wide adaptability, high-efficiency extraction and enrichment, and high-efficiency extraction and recovery.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
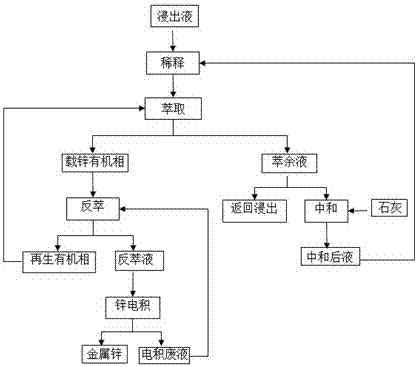
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, for the low-grade zinc calcined sand leach solution 1#, the zinc concentration is 45.50g / L, and the pH value is 4.5 after iron removal and purification. Mix 70% aviation kerosene with 30% (volume percentage) of P204 to extract the organic phase. Add 2.00L of zinc sulfate solution containing 0.50g / L of zinc per 1L of leaching solution to dilute to obtain 3.00L of extraction stock solution containing 15.50g / L of zinc; the stock solution and the organic phase are subjected to three-stage countercurrent extraction, and the O:A ratio is 2:1 , the extraction time is 5 minutes, the phase separation time is 3 minutes, the zinc concentration of the raffinate is 0.58g / L, and the zinc-loaded organic phase contains 8.01g / L of zinc; after extraction, 1L of the raffinate is returned to leaching, and the remaining 3.68L of the raffinate is added to the lime And to filter after pH value 4.5, filtrate stays to use for next dilution; Load zinc organic phase an...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, for low-grade zinc oxide ore acid leaching solution 2#, the zinc concentration is 26.38g / L, and the pH value is 4.5 after iron removal and purification. Mix 60% aviation kerosene with 40% (volume percentage) of P204 to extract the organic phase. Add 2.41L of zinc sulfate solution containing 3.21g / L of zinc to each 1L of leaching solution to dilute to obtain 3.41L of extracting solution containing 10.0g / L of zinc; the extracting solution and the organic phase are subjected to four-stage countercurrent extraction, and the ratio of O:A is 1:2 , the extraction time is 5 minutes, the phase separation time is 3 minutes, the zinc concentration of the raffinate is 3.21g / L, and the zinc-loaded organic phase contains 13.58g / L of zinc; after the extraction, 1L of the raffinate is returned to leaching, and the remaining 2.41L is added to lime to neutralize the pH value 4.5 Reserved for the next dilution; zinc-loaded organic phase and zinc electrowinning ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, for low-grade zinc sulfide ore oxygen pressure leaching solution 3#, the zinc concentration is 35.34g / L, and the pH value is 4.5 after iron removal and purification. Mix 60% aviation kerosene with 40% (volume percentage) of P204 to extract the organic phase. Add 1.57L of zinc sulfate solution containing 4.96g / L of zinc to each 1L of leaching solution to dilute to obtain 2.57L of extracting liquid containing 16.76g / L of zinc; the extracting liquid and the organic phase are subjected to four-stage countercurrent extraction, and the O:A ratio is 1.4:1 , the extraction time is 5 minutes, the phase separation time is 3 minutes, the zinc concentration of the raffinate is 4.96g / L, and the zinc-loaded organic phase contains 8.43g / L of zinc; after the extraction, 1L of the raffinate is returned to leaching, and the remaining 1.57L is added to lime to neutralize the pH value 4.5 Reserved for the next dilution; zinc-loaded organic phase and zinc electro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com