Lactobacillus fermentum strain suo for adjusting intestinal tract motion and preventing constipation and use thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus fermentum and intestinal motility, applied in the field of microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1: Isolation, purification and preliminary determination of Lactobacillus fermentum strain suo.
[0055] This embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0056] (1) Separation and purification of Lactobacillus fermentum strain suo.
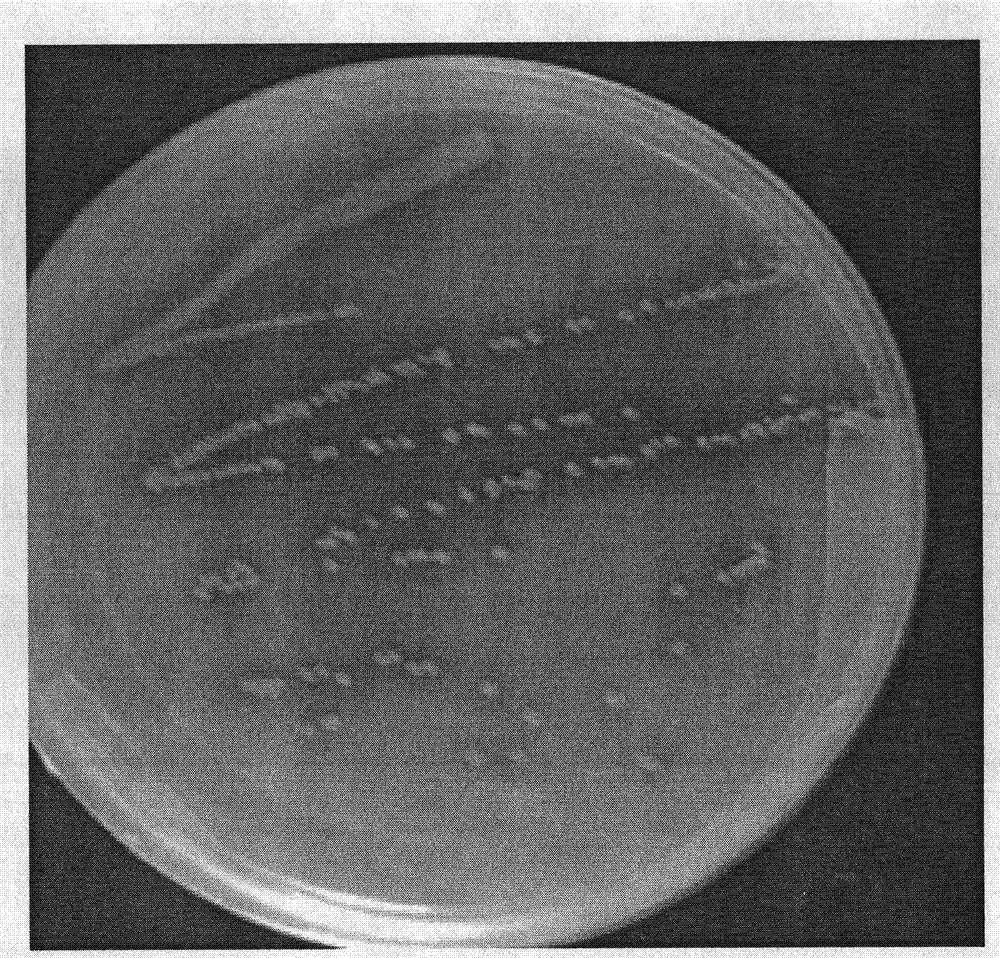
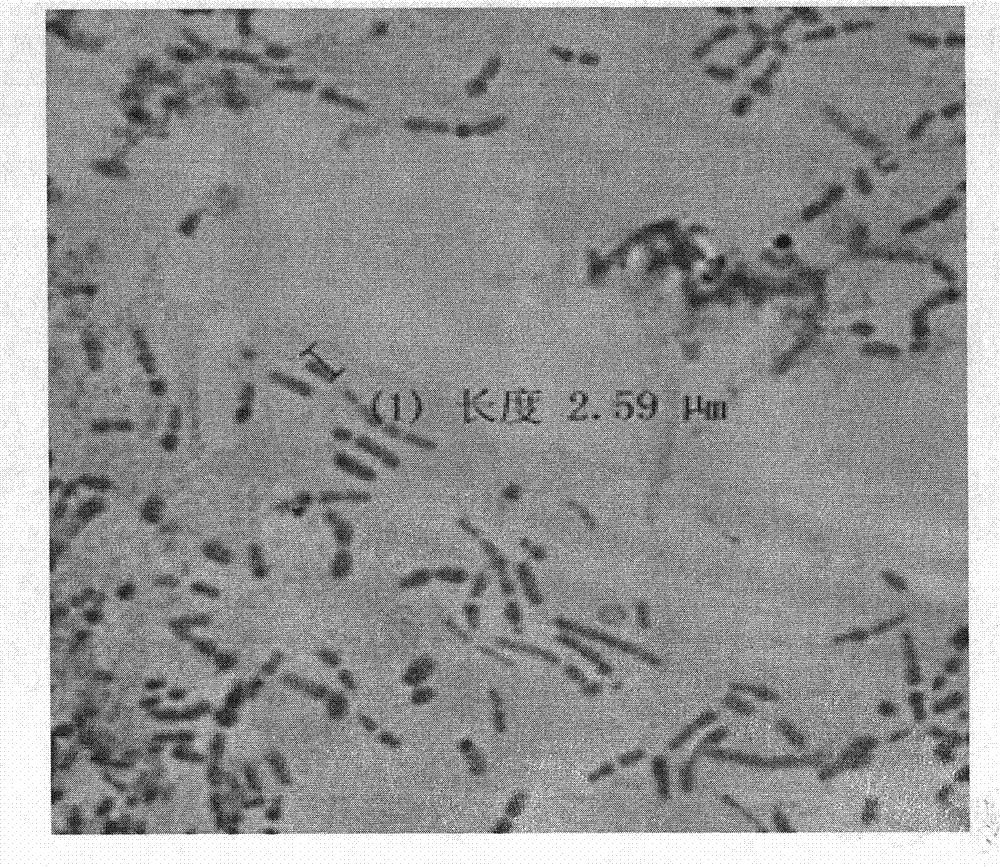
[0057] Draw 500 μL of traditional fermented yak yogurt sample by aseptic operation and add it to 5 mL sterilized saline to make a uniform dilution of 1:10, and continue to make a certain proportion of dilution. Select the appropriate gradient diluent, draw 100 μL each into the MRS solid plate medium with a sterile pipette tip, and incubate at 30°C for 48-72 hours, observe and record the colony morphology as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0058] Use an inoculation loop (or a sterilized toothpick) to pick different colonies from the surface and interior of the plate and inoculate them in the MRS liquid medium, and culture them on a shaker at 30°C and 300r / min for 24-48h; repeat the above steps for continuous activation...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2: In vitro screening of Lactobacillus fermentum strain suo.
[0065] (1) Screening of probiotics resistant to pH 3.0 artificial gastric juice.
[0066] Preparation of artificial gastric juice: 0.2% NaCl, 0.35% pepsin, adjust the pH value to 3.0 with 1M HCl, filter and sterilize with a vacuum pump in an aseptic operating table for later use.
[0067] Determination of the tolerance of probiotics to artificial gastric juice: take 5mL of the activated strain culture solution, pour it into a sterilized 10mL centrifuge tube in a sterile operating table, collect the bacteria by centrifugation at 3000r / min for 10min, add 5mL of sterilized Mix physiological saline to make bacterial suspension, take 1mL bacterial suspension and 9mL artificial gastric juice with pH3. Samples were taken, poured into MRS agar medium and cultured at 37°C for 48h. The number of viable bacteria was determined by plate counting method, and the survival rate (%) was calculated: survival rate (...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3: Activated carbon induced constipation experiment.
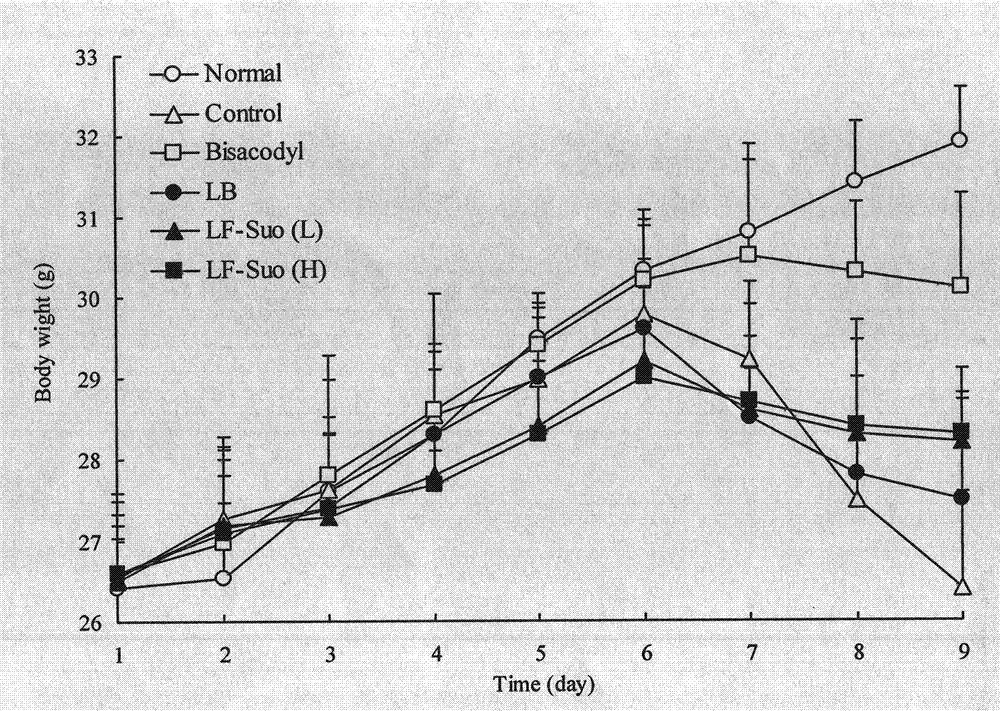
[0082] Feed healthy Kunming mice, 6 weeks old, weighing 23±2g, 50 females. After feeding the basal diet for 5 days, the mice were randomly divided into 5 groups according to body weight, namely: normal group, constipation control group, bisacodyl group, Lactobacillus bulgaricus group, and high and low intragastric dosage Lactobacillus fermentum strain suo group, 10 in each group. Raise them in stainless steel cages, keep room temperature at 24±2°C, relative humidity at 50±10%, and light-dark rotation for 12 hours (lighting at 8:00-20:00). During the whole experimental period, the normal group and the constipation control group were fed with the basal diet, and the mice in the experimental group were fed with 1.0×10 9 CFU / kg gavage probiotics. Two weeks later, at 9:00 every morning except the normal group, mice in the other five groups were given 10% activated carbon ice water at 2°C, 0.2 mL / mouse, once a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hydrophobicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com