Method for detecting glycoprotein by molecularly imprinted microspheres based on boric acid fluorescence probe
A technology of molecularly imprinted microspheres and fluorescent probes, which is applied in the field of glycoprotein detection, can solve the time-consuming problems of biomolecules such as fragile proteins, and achieve the effects of avoiding sample processing, mild reaction conditions, and simplified operation processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] 1. Amino groups bonded to the surface of monodisperse porous cross-linked glycidyl methacrylate microspheres
[0030] Add 2.0 g of monodisperse porous cross-linked glycidyl methacrylate microspheres into 50 mL of 1 mol / mL sulfuric acid aqueous solution, stir in a water bath at 60 ° C for 24 hours, centrifuge, remove the supernatant, and wash the product with deionized water to medium properties, vacuum drying at 60°C to obtain monodisperse cross-linked glycidyl methacrylate microspheres with hydroxyl groups on the surface; disperse 0.5g of the microspheres in 100mL of absolute ethanol, add 1mL of ammonia water and 20mL of 3-aminopropyl Triethoxysilane, ultrasonically dispersed for 0.5 hours, stirred at room temperature for 12 hours, centrifuged to remove the supernatant, the precipitate was washed with absolute ethanol, and dried in vacuum at 60°C to obtain a monodisperse cross-linked methacrylic epoxy with amino groups on the surface Propyl ester microspheres.
[0031...
Embodiment 2
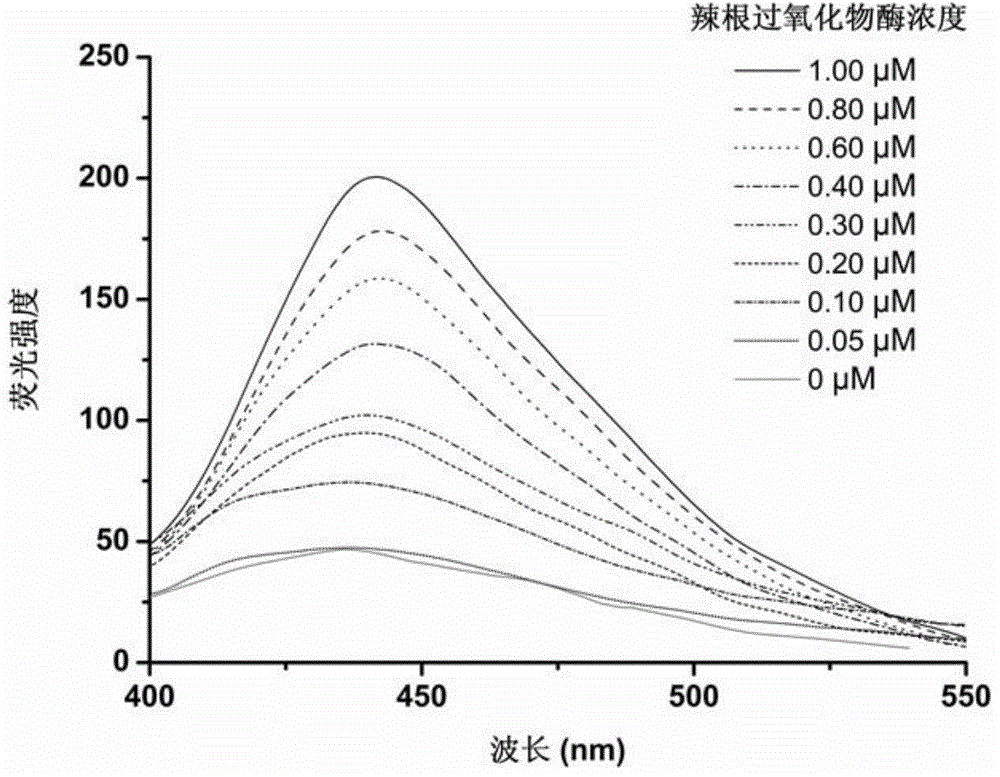
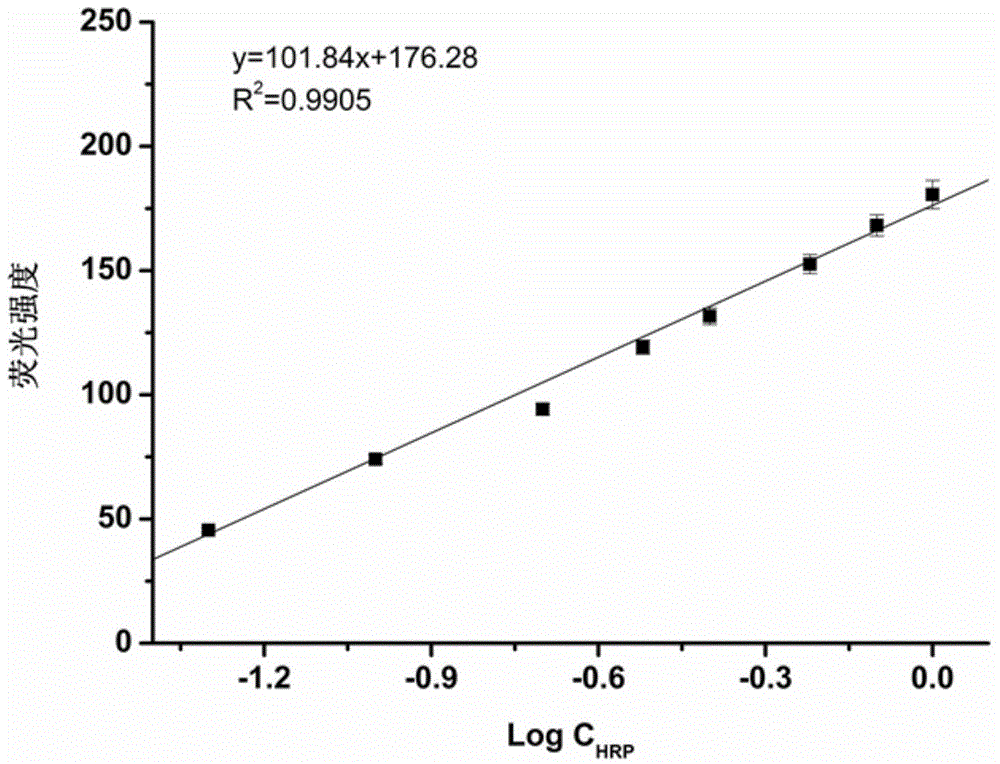
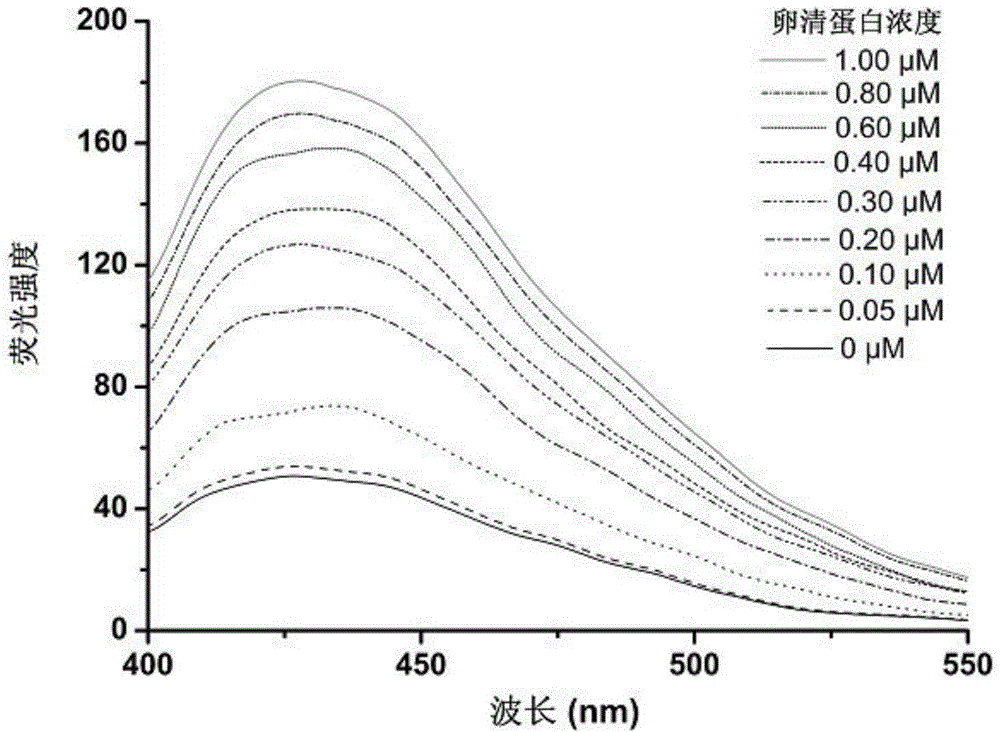
[0043] Monodisperse crosslinked glycidyl methacrylate microspheres with boric acid fluorescent probes bonded to the surface were prepared according to steps 1-2 of Example 1. In step 3 of Example 1, the horseradish peroxidase used was replaced with an equal mass of ovalbumin to obtain ovalbumin molecularly imprinted microspheres with fluorescent properties. According to the method of embodiment 1 step 4, the fluorescence spectrogram of fluorescence intensity changing with ovalbumin concentration and the standard curve of fluorescence intensity changing with the logarithmic value of ovalbumin concentration at the maximum emission wavelength of 430nm are drawn, the results are shown in Figure 3-4 .
[0044] Depend on Figure 3-4 It can be seen that under the same detection conditions, the ovalbumin molecularly imprinted microspheres with fluorescent properties have obvious fluorescent responses to the template molecule ovalbumin. When the concentration of ovalbumin is 0.05-1.0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com