The method of re-hybridization of fish production
A technique of fluorescence in situ hybridization and coverslipping, which is applied in the field of molecular cytogenetics, can solve the problems of easily polluted environment, difficult to obtain, and difficult to wash off hybridization signals, and achieves the effect of reducing environmental pollution and saving experimental costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
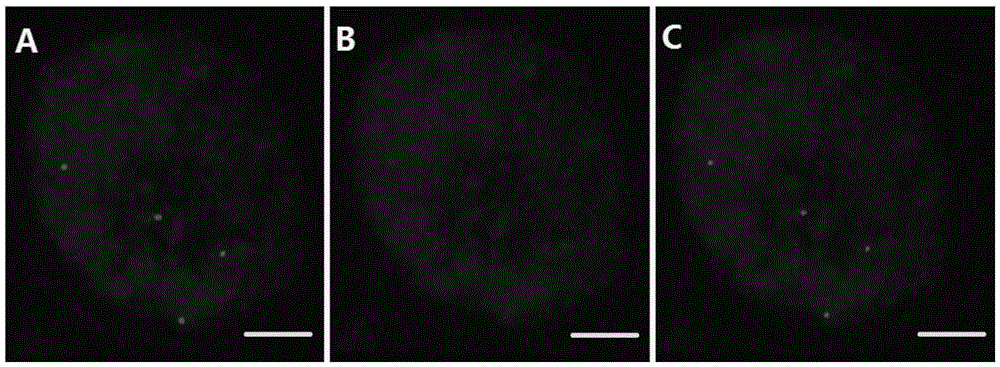
[0017] Embodiment 1 takes Raymond's cotton No. 1 chromosome-specific BAC clone as probe, Raymond's cotton (D 5 ) The mitotic metaphase chromosome was used as the target chromosome, and the FISH preparation was used for rehybridization experiments.
[0018] 1 Materials and methods
[0019] 1.1 Experimental materials
[0020] The experimental material is Raymond cotton, which comes from the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The BAC used was the specific BAC clone of chromosome 1 of Raymond cotton (WangK, 2007). Experimental reagents: cellulase OnazukaR-10 and pectinase PectolyaseY-23 were purchased from Solarbio Company, Digoxigenin Probe Labeling Kit was purchased from Roche Company, and other domestic reagents were of analytical grade.
[0021] 1.2 Experimental method
[0022] 1) Material collection and pretreatment: Soak the seeds of Raymond cotton in warm water for about 12 hours, and then cultivate them in a light incubator. When...
Embodiment 2
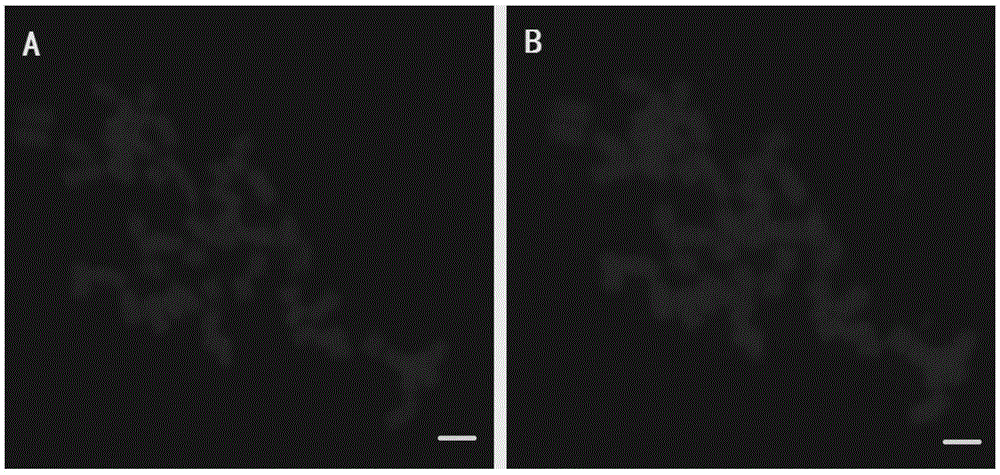
[0039] Example 2 Taking the mitotic metaphase chromosome 12 of Upland Cotton Cotton Center as the target chromosome, a rehybridization experiment of FISH preparation was carried out.
[0040] 1 Materials and methods
[0041] 1.1 Experimental materials
[0042] The experimental material is upland cotton Zhongmiansuo No. 12, which comes from the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Experimental reagents: cellulase OnazukaR-10 and pectinase PectolyaseY-23 were purchased from Solarbio Company, Digoxigenin Probe Labeling Kit was purchased from Roche Company, and other domestic reagents were of analytical grade.
[0043] 1.2 Experimental method
[0044] At step 9, extend the time in 70% deionized formamide at 78°C to 5 minutes. Other steps are the same as above.
[0045] 2 Experimental results
[0046] The experimental results found that when the processing time in step 9 was extended, the chromosome morphology was obviously expanded ( im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com