Thermo-sensitive in-situ gel for articular cavity injection and preparation method thereof
A temperature-sensitive gel, joint cavity technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of difficulty in use, short residence time, and no encapsulation of therapeutic drugs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
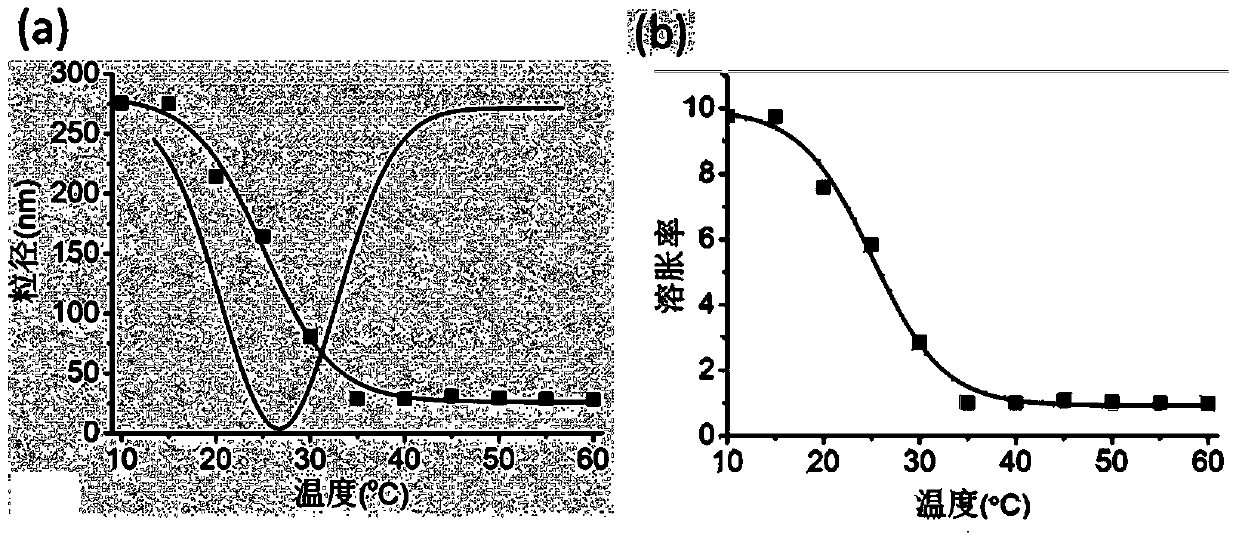
[0020] The activated proxamer F127 and hyaluronic acid were dissolved in deionized water at a molar ratio of 1:5, copper sulfate and sodium ascorbate were added, and the reaction was carried out at 40°C under nitrogen protection for 48 hours. After the reaction, dialyze in deionized water for 3 days with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 25 kDa, and freeze-dry to obtain the polymer. The polymer was suspended in PBS buffer (pH 7.4), and the probe was sonicated for 6 minutes (working power 90W, working pulse was working for 1s and pausing for 5s), and a blank nanogel suspension was obtained. Determination of the state of the nanogel suspension at different concentrations and temperatures ( figure 1 ). Dissolve rofecoxib in DMF solution, dissolve the copolymer in formamide solution, mix after stirring overnight, dialyze with PBS buffer (pH 7.4) for 12 hours, centrifuge to take supernatant, filter and lyophilize to obtain Drug-loaded thermosensitive nanogel suspe...
Embodiment 2
[0022] The activated proxamer F68 and hyaluronic acid were dissolved in deionized water at a molar ratio of 1:2, copper sulfate and sodium ascorbate were added, and the reaction was carried out at 40°C under nitrogen protection for 48 hours. After the reaction, dialyze in deionized water for 3 days with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 25 kDa, and freeze-dry to obtain the polymer. The polymer was suspended in PBS buffer (pH 7.4), and the probe was sonicated for 6 minutes (working power 90W, working pulse was working for 1s and pausing for 5s), and a blank nanogel suspension was obtained, and the morphology was observed under a transmission electron microscope ( figure 2 ). Dissolve indomethacin in DMF solution, copolymer in formamide solution, mix after stirring overnight, dialyze with PBS buffer (pH 7.4) for 12 hours, centrifuge to get supernatant, filter and lyophilize to obtain Drug-loaded thermosensitive nanogel suspension.
Embodiment 3
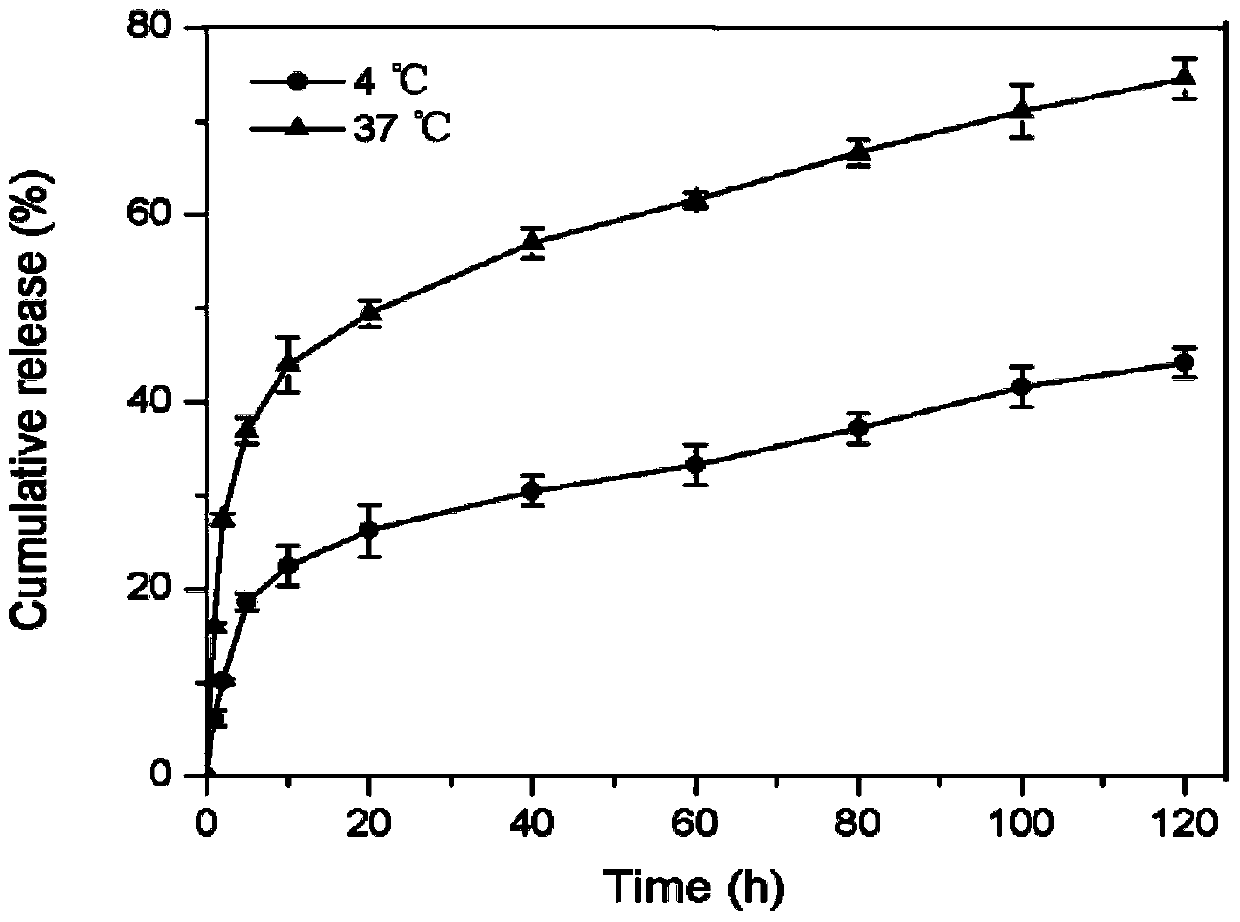
[0024] The activated proxamer F127 and hyaluronic acid were dissolved in deionized water at a molar ratio of 1:4, copper sulfate and sodium ascorbate were added, and the reaction was carried out at 40°C under nitrogen protection for 48 hours. After the reaction, dialyze in deionized water for 3 days with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 25 kDa, and freeze-dry to obtain the polymer. Dissolve celecoxib in DMF solution, dissolve the copolymer in formamide solution, stir overnight and mix, then dialyze with PBS buffer (pH 7.4) for 12h, centrifuge to get the supernatant, filter and lyophilize to obtain Drug-loaded thermosensitive nanogel suspension. Drug release behavior at different temperatures as image 3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com