CRAS-PCR detection method of single base mutation of gene
A single base variation and detection method technology, applied in the fields of life sciences and biology, can solve the problems of lack of reliability in genotype detection, inability to completely suppress non-specific amplification, and false positive detection results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
[0050] Implementation case one: TPMT *2 Genotype detection
[0051] 1. Design and synthesis of allele-specific scorpion primers
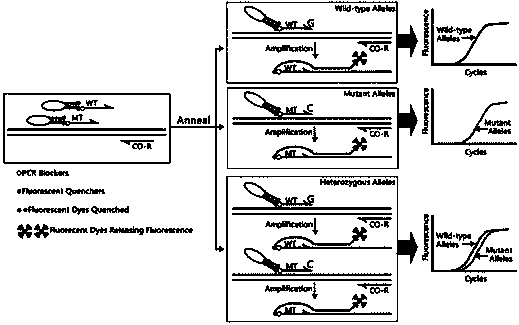
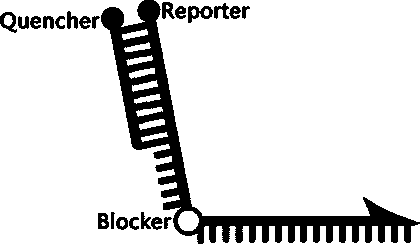
[0052] according to TPMT *2 (dbSNP ID: rs1800462; G238C) genotype nucleic acid sequence characteristics, respectively designed allele-specific scorpion primers matching its wild-type and mutant sequences, wherein, SEQ No. 1 and SEQ No. 2 and TPMT*2 (G238C) The reverse sequence is complementary, both are PCR amplification upstream primers, respectively used for specific amplification TPMT *2 (G238C) wild-type and mutant nucleic acid sequences. The 5'-end and 3'-end oligonucleotide sequences of the PCR blocker HEG in SEQ No.1 and SEQ No.2 are probe sequence region and primer sequence region respectively, and the effect of this PCR blocker is A common downstream primer (ie: SEQ No. 3) that prevents wild-type and mutant allele-specific scorpion primers from extending along the probe sequence. Among the above allele-specific scorpion primer sequen...
Embodiment example 2
[0068] Implementation case two: TPMT *3B and TPMT *Detection of 3C genotype
[0069] 1. Design and synthesis of single-stranded allele-specific scorpion primers and their common primers
[0070] according to TPMT *3B(dbSNP ID: rs1800460; G460A) and TPMT *3C (dbSNP ID: 1142345; A719G) genotype nucleic acid sequence characteristics, designed wild-type and mutant-matched allele-specific scorpion primers and their common primers. TPMT *3B The allele-specific scorpion primers matched by the wild type and the mutant type are Seq No. 4 and Seq No. 5, both of which are upstream primers, respectively labeled with HEX and FAM fluorescent reporter groups; the common primer is the downstream primer Seq No. 6. TPMT *The allele-specific scorpion primers matching the wild type and mutant type of 3C are Seq No. 8 and Seq No. 9, both of which are downstream primers, respectively labeled with HEX and FAM fluorescent reporter groups; the common primer is the upstream primer Seq No. 7. ...
Embodiment example 3
[0090] Implementation case three: BRAF Gene mutation detection at the 600th codon
[0091] 1. Design and synthesis of double-stranded allele-specific scorpion primers and their common primers
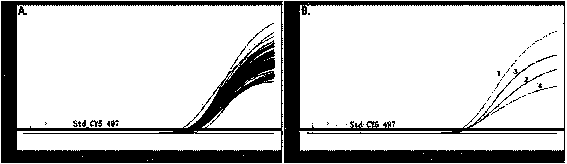
[0092] according to BRAF All mutations in the second base of the 600th codon (V600; GTG) were designed to target the wild type (V600; GTG) and V600E (GTG>GAG), V600A (GTG>GCG), V600G (GTG> GGG) and other three mutant double-stranded allele-specific scorpion primer probe-primer monomers. The probe-primer monomer targeting wild type (V600; GTG) is SEQ No. 11, the probe-primer monomer targeting mutant V600E (GTG>GAG) is SEQ No. 12, targeting mutant V600A The probe-primer monomer for (GTG>GCG) is SEQ No. 13, and the probe-primer monomer for targeting mutant V600G (GTG>GGG) is SEQ No. 14. The 5'-ends of SEQ No. 11~14 are respectively labeled with CY5, FAM, HEX and Texas Red fluorescent reporter groups, and between the probe sequence region and the primer sequence region is the PCR bl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com