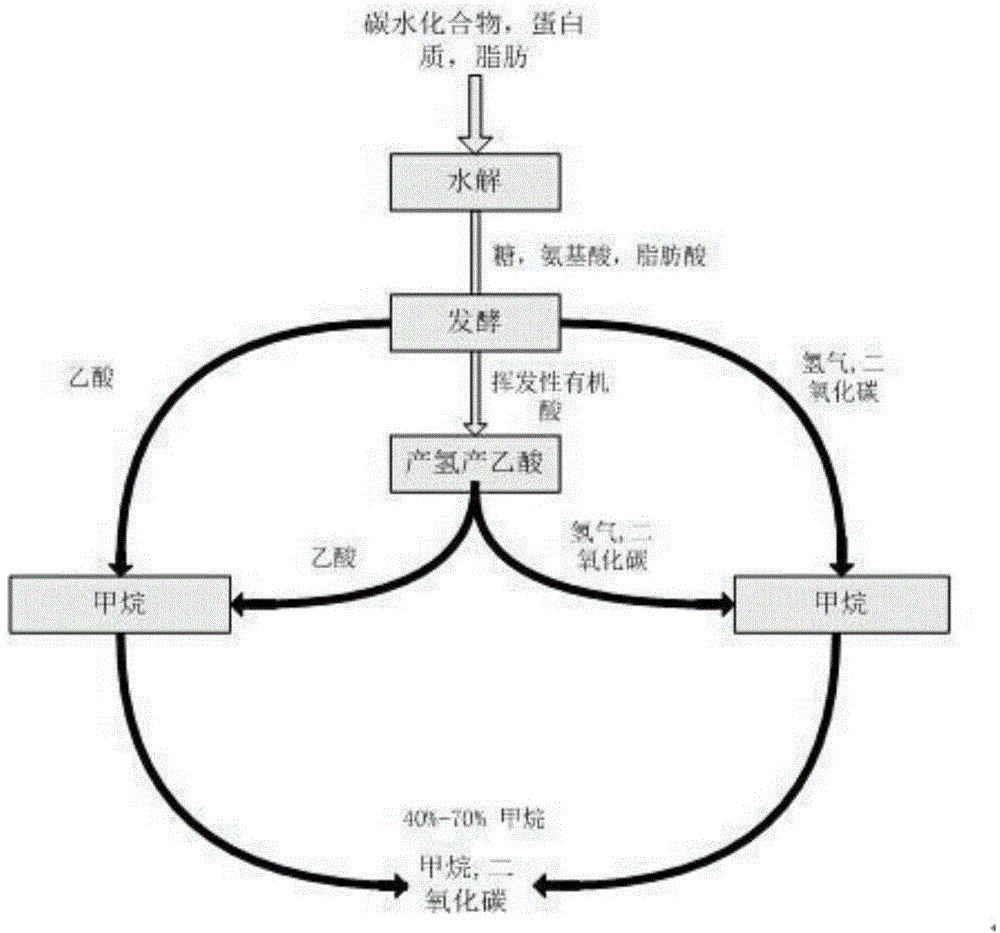
Method for producing methane through mixed slaking of straw stalks subjected to alkali treatment and surplus sludge
A technology for excess sludge and straw straws, which is applied in biological sludge treatment, biosynthesis, waste fuel and other directions, can solve the problems of not being properly treated and the low efficiency of separate digestion of straw straws, etc., and achieves improved anaerobic digestion performance. Synergistic effect, the effect of increasing economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
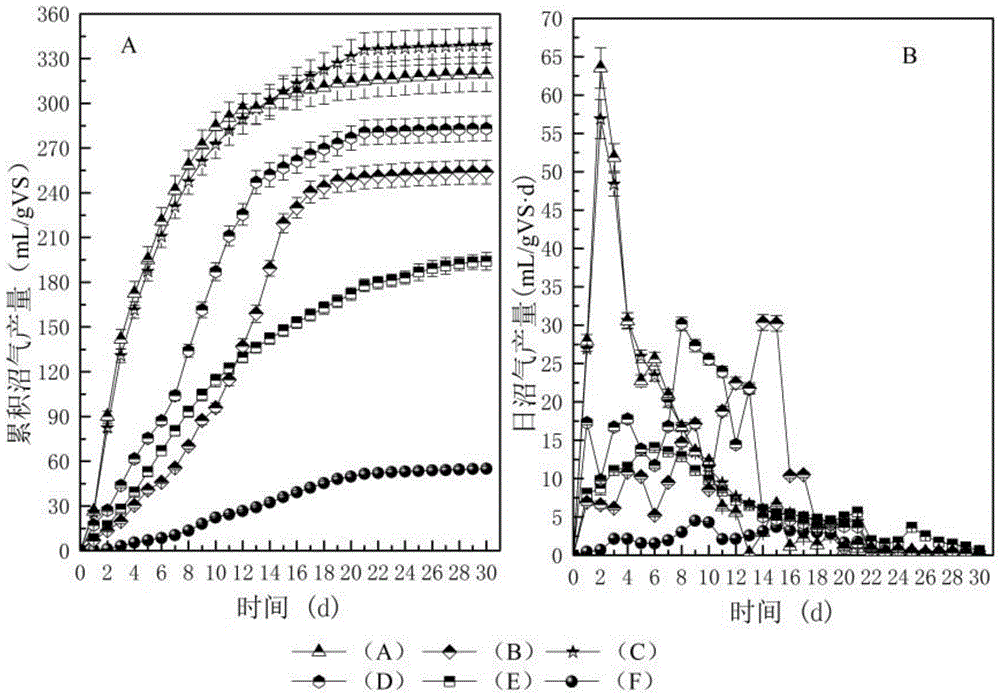
[0033] Example 1 Changes in cumulative biogas production during mixed digestion of rice straw and excess sludge
[0034] like figure 2 As shown in A, the gas production of group F without adding inoculated sludge was the lowest, and the cumulative gas production was only 54.9mL / gVS, which may be due to the inability of microorganisms in the remaining sludge to degrade rice straw and its own hydrolyzed products. The biogas production of group E was lower, finally 194.1mL / gVS. The biogas yields of group B and group D were 253.9mL / gVS and 283.1mL / gVS, respectively, while the biogas yields of group A and group C after alkali treatment were 319.6mL / gVS and 338.9mL / gVS, respectively, compared with the two groups without alkali treatment An increase of 25.88% and 19.71%, respectively.
[0035] figure 2 B is the change of daily biogas production during anaerobic digestion. It can be seen from the figure that the biogas production lasted until about 22 days, and the gas productio...
Embodiment 2
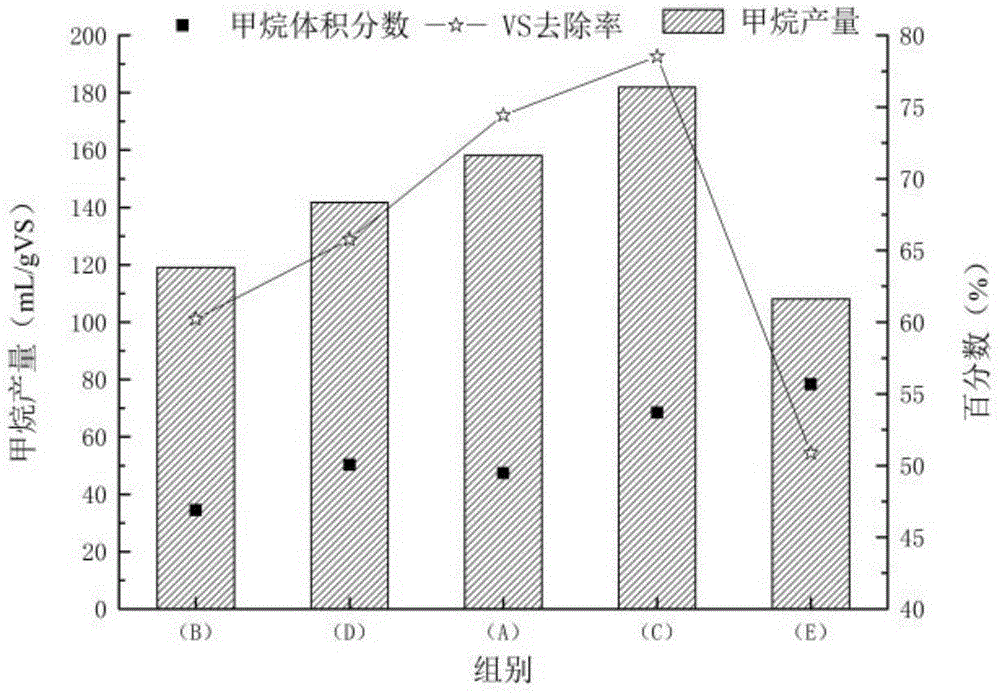
[0036] Example 2 Changes in cumulative biogas production during mixed digestion of rice straw and excess sludge
[0037] image 3is the average methane volume fraction, methane production and VS removal rate during the reaction. It can be seen from the figure that the average volume fraction of methane in biogas is about 50%, among which, the volume fraction of methane in group B is the lowest at 46.89%, and that in group A after alkali treatment slightly increases to 49.48%. The methane volume fractions of these two groups in alkali treatment group C were 50.06% and 53.69%, respectively, and the methane volume fraction in group E was the highest at 55.68%. This is because the main components of rice straw are carbohydrates such as cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, and the organic matter in the remaining sludge is mainly protein. The higher the protein content, the higher the methane content in the generated gas. According to the measured biogas production and methane vol...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3 Changes in pH and ammonia nitrogen in the digestion process
[0043] pH changes during digestion Figure 4 As shown in A, it can be seen that the overall pH showed a trend of first decreasing and then increasing. Due to the small amount of methanogenic bacteria in group F, the hydrolyzate could not be further utilized, and the pH dropped rapidly to 5.7. In the subsequent stage, although the hydrolysis of excess sludge produced substances with a buffering effect, the pH rose slightly and remained at about 6.3. Conducive to biogas generation. The pH of groups A and C treated with alkali reached the lowest value on the 2nd day, and then due to the hydrolysis of excess sludge and the subsequent reaction, the pH gradually increased and stabilized at about 7.5, maintaining the optimum value required by methanogens. pH range. In the two groups without alkali treatment, the pH decreased slowly and did not begin to rise until the 10th day. The results showed that al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com