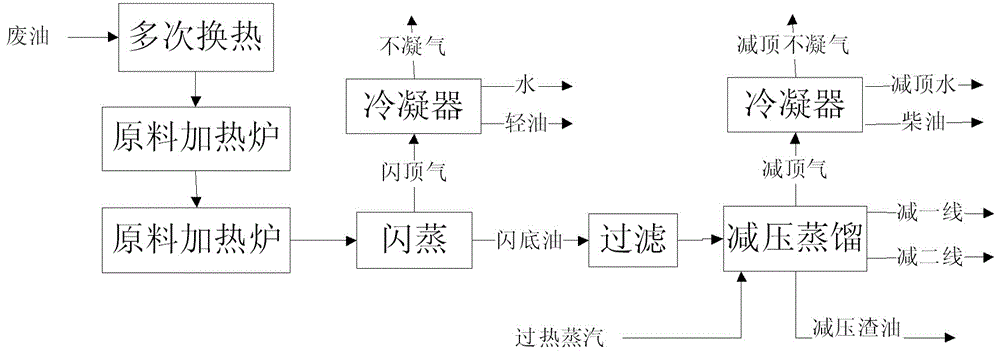
A continuous distillation process for regeneration of waste lubricating oil
A technology of waste lubricating oil and process, applied in the direction of lubricating composition, etc., can solve the problems of mixing, complicated process, etc., and achieve good technical and economic effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
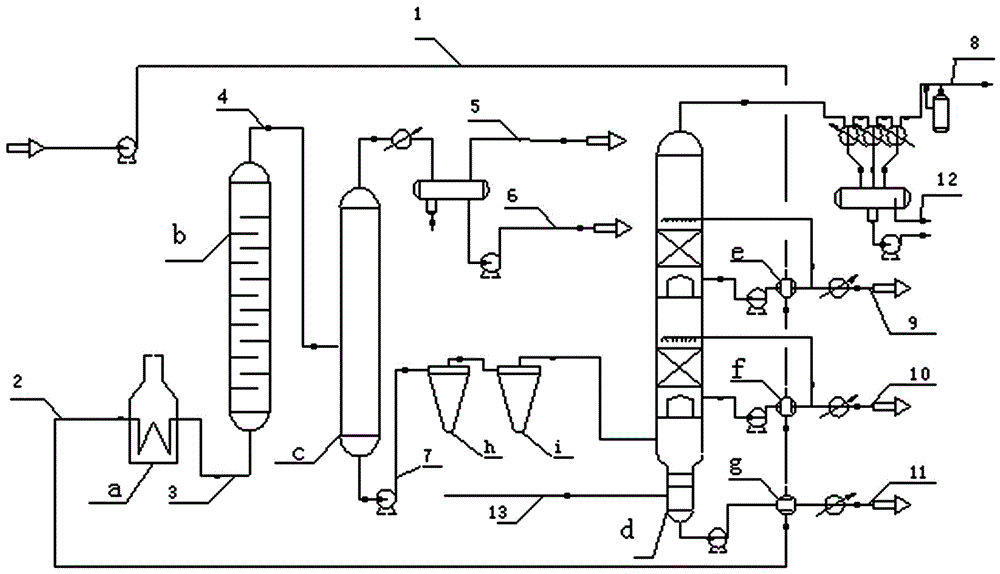
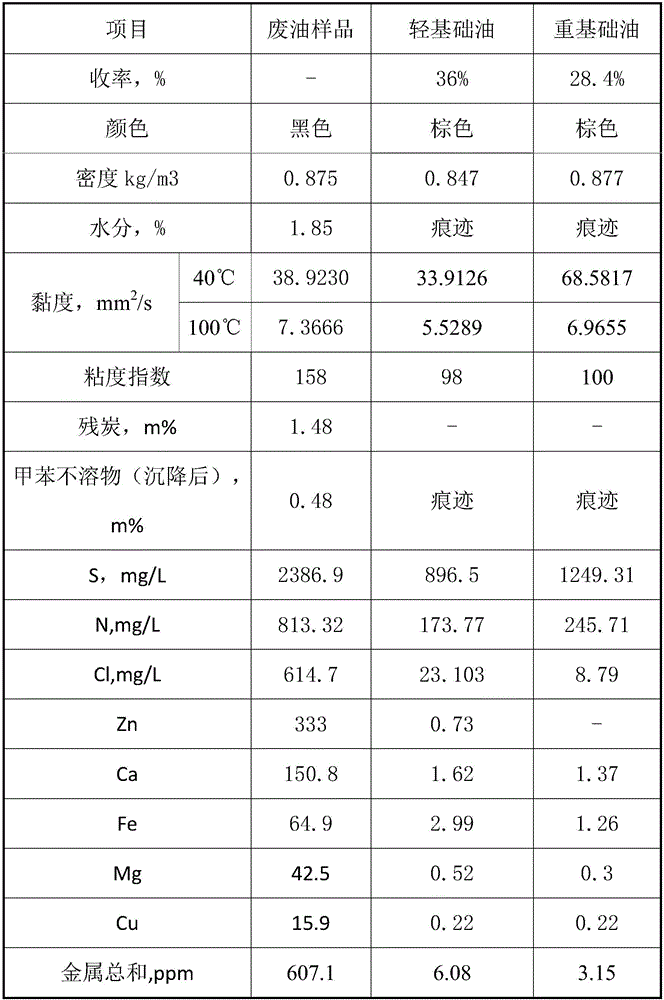
[0034] Embodiment 1: as figure 2 As shown, lubricating oil 1 coming from the tank area with a normal temperature of about 40°C and a flow rate of 12875kg / h conducts heat exchange with the fraction extracted from the side line of the minus line first in the raw oil-light base oil heat exchanger e, and then exchanges heat with the side line of the minus line The raw material oil-heavy base oil heat exchanger f performs heat exchange, and finally performs heat exchange with the raw material oil-vacuum residue heat exchanger g at the bottom of the vacuum tower to obtain stream 2, whose temperature is 240°C.
[0035] Stream 2 enters the feed heating furnace a and is heated to obtain stream 3 at 380°C. Stream 3 enters vis-reducing reaction tower b. The operating conditions are: temperature 380°C, residence time 1h.
[0036] The waste oil 4 after visbreaking heat treatment has a temperature of 377° C., and it directly enters the flash tower c for flash evaporation at an operating pr...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: The waste lubricating oil 1 from the tank farm at a normal temperature of about 40°C is first exchanged with the fraction extracted from the side line of the first line in the raw material oil-light base oil heat exchanger e, and then exchanged with the raw material oil of the side line of the second line reduction- The heavy base oil heat exchanger f performs heat exchange, and finally conducts heat exchange with the raw material oil at the bottom of the vacuum tower—vacuum residue heat exchanger g to obtain stream 2, whose temperature is 280°C.
[0039] Stream 2 enters the feed heating furnace a and is heated to obtain stream 3 at 320°C. Stream 3 enters vis-reducing reaction tower b. The operating conditions are: temperature 320°C, residence time 1.5h.
[0040] The waste oil 4 after visbreaking heat treatment has a temperature of 318° C., and it directly enters the flash tower c for flash evaporation at an operating pressure of 1 MPa. The top of the tower i...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: The normal temperature waste lubricating oil 1 from the tank area is first exchanged with the fraction extracted from the side line of the first line reduction in the raw material oil-light base oil heat exchanger e, and then exchanged with the raw material oil of the second line side line reduction-heavy base oil The heat exchanger f performs heat exchange, and finally exchanges heat with the raw material oil at the bottom of the vacuum tower—the vacuum residue heat exchanger g to obtain stream 2, whose temperature is 260°C.
[0043] Stream 2 enters the feed heating furnace a to be heated to obtain stream 3 at 350°C, and stream 3 enters vis-reducing reaction tower b. The operating conditions are: temperature 350°C, residence time 1h.
[0044] The waste oil 4 after visbreaking heat treatment has a temperature of 346°C, and it directly enters the flash tower c, where it is flashed at an operating pressure of 1 MPa. The top of the tower is condensed and separat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com