Rabies Vaccine
A technology of rabies virus and attenuated rabies virus, applied in the field of rabies vaccine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1 Mutated rabies virus
[0066] Mutation of N at the phosphorylation site reduces RV transcription and replication rates, leading to further attenuation
[0067] RV N plays an important role in the regulation of viral transcription and regulation, and RV N is phosphorylated on serine at position 389. Our studies demonstrated that N mutations at phosphorylation sites suppress minigenome transcription and replication rates (Yang et al., 1999, J. Virol. 73: 1661-1664). In order to determine whether the same mutation can reduce the rate of viral replication in fully infectious virus, the S389A, S389D and S389E mutations of N on the fully infectious clone L16 (Wu et al., J. Virol. 2002, 76: 4153 -4161). Mutations from S to A and S to D were found to result in a decrease in viral transcription and replication. Northern blot hybridization with the RV probe revealed an almost 90% reduction in the rate of viral transcription (mRNA) and replication (genomic RNA), espec...
Embodiment II
[0081] In the CNS, attenuated rabies virus activates, while pathogenic rabies virus evades, host innate immune responses.
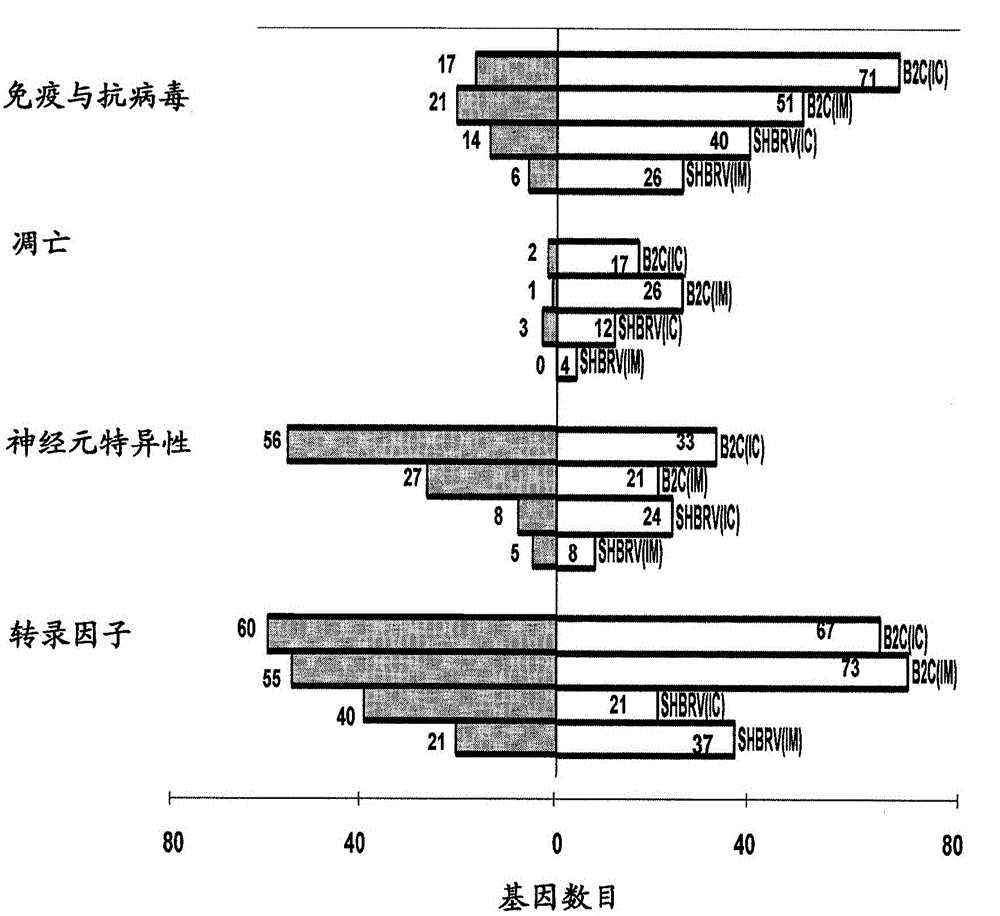
[0082] Rabies virus (RV) induces encephalomyelitis in humans and animals. However, the pathogenic mechanism of rabies is not fully understood. To investigate host responses to RV infection, we used mouse genome arrays to study and compare pathological changes, especially inflammatory responses and Gene expression profiles. Oligonucleotide microarrays (Affymetrix Mouse Expression Set MOE430A) and real-time PCR were used to identify candidate genes differentially expressed in the CNS of mice infected with pathogenic SHBRV or attenuated B2C.
[0083] Extensive inflammatory responses were observed in animals infected with attenuated RV, but little or no inflammatory response was seen in mice infected with wt RV. Moreover, attenuated RV induced the expression of genes involved in innate immunity and antiviral responses, especially those related to the IFN-α...
Embodiment III
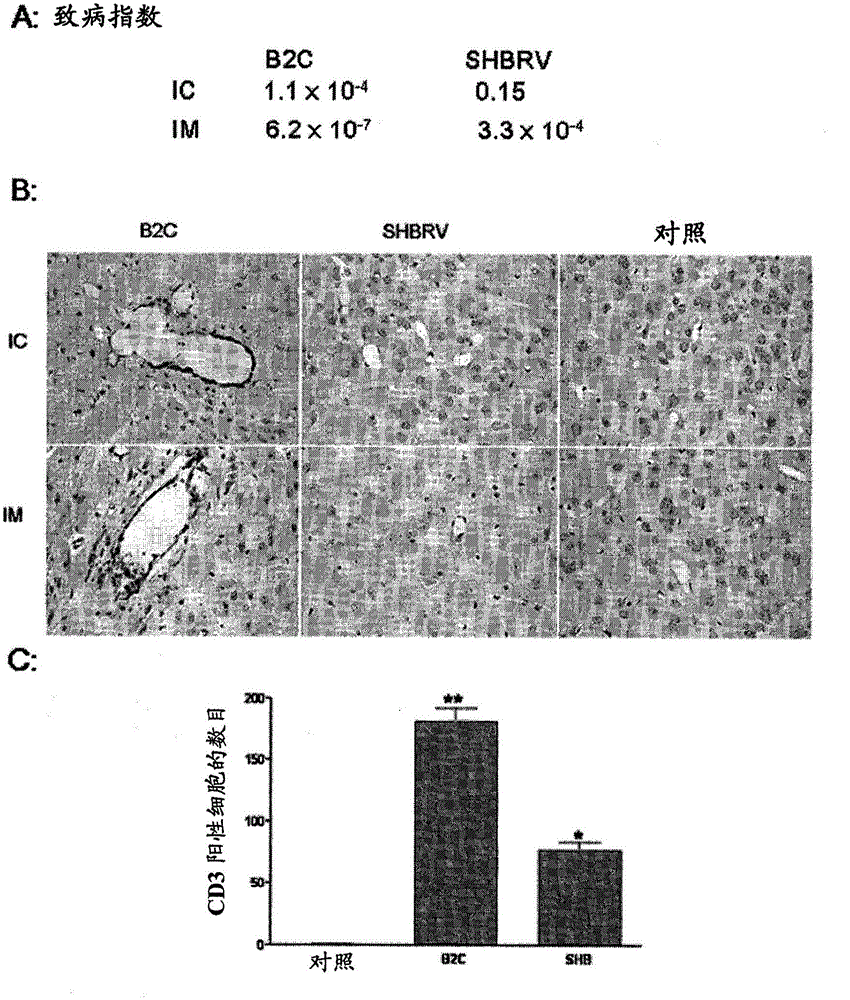
[0144] Example III. Comparison of SHBRV, B2C and L16 Rabies Viruses
[0145] Host gene expression profiling
[0146] In Example II we profiled host gene expression in a mouse model using two viruses, SHBRV and B2C. Here we describe another comparison with L16. L16 was cloned from vaccine strain SAD-B19 by reverse genetics technique (Schnell et al. Infectious RV from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1994;13:4195-4203; Wu et al. "Both viral transcription and replication are reduced when the rabies virus nucleoprotein is not phosphorylated (when the rabies virus nucleoprotein is not phosphorylated, viral transcription and replication are reduced)" J. Virol. 2002; 76: 4153-61). The virulence of these viruses was initially compared. Virus titers were determined in BHK cells and measured as focus forming units (ffu) and 50% intracerebral lethal dose (ICLD 50 ) and 50% of the intramuscular lethal dose (IMLD 50 ). from log ICLD 50 / ml or logIMLD 50 IC and IM pathogenicity indices were cal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com