Aluminum hydride surface coating modification method
A technology of aluminum trihydride and surface coating, applied in gaseous chemical plating, metal material coating process, coating and other directions, can solve the problems of decreased hydrogen content, explosion, easy decomposition, etc., and achieve the effect of improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
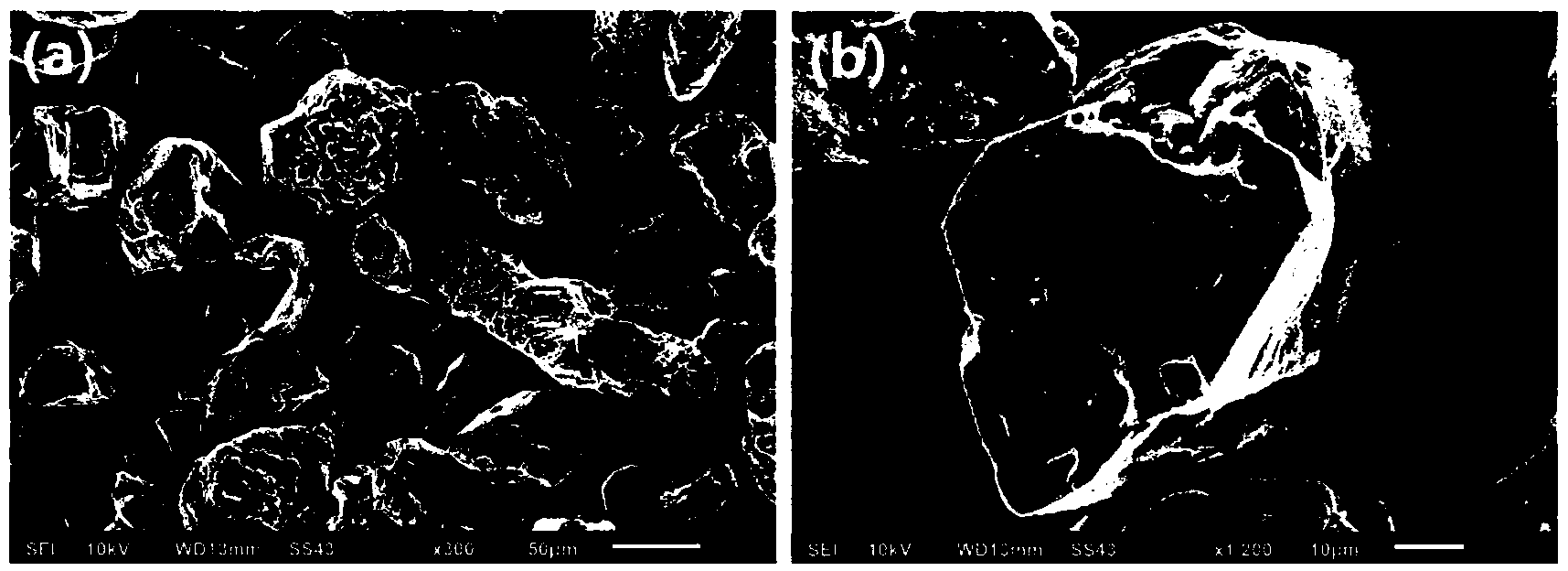
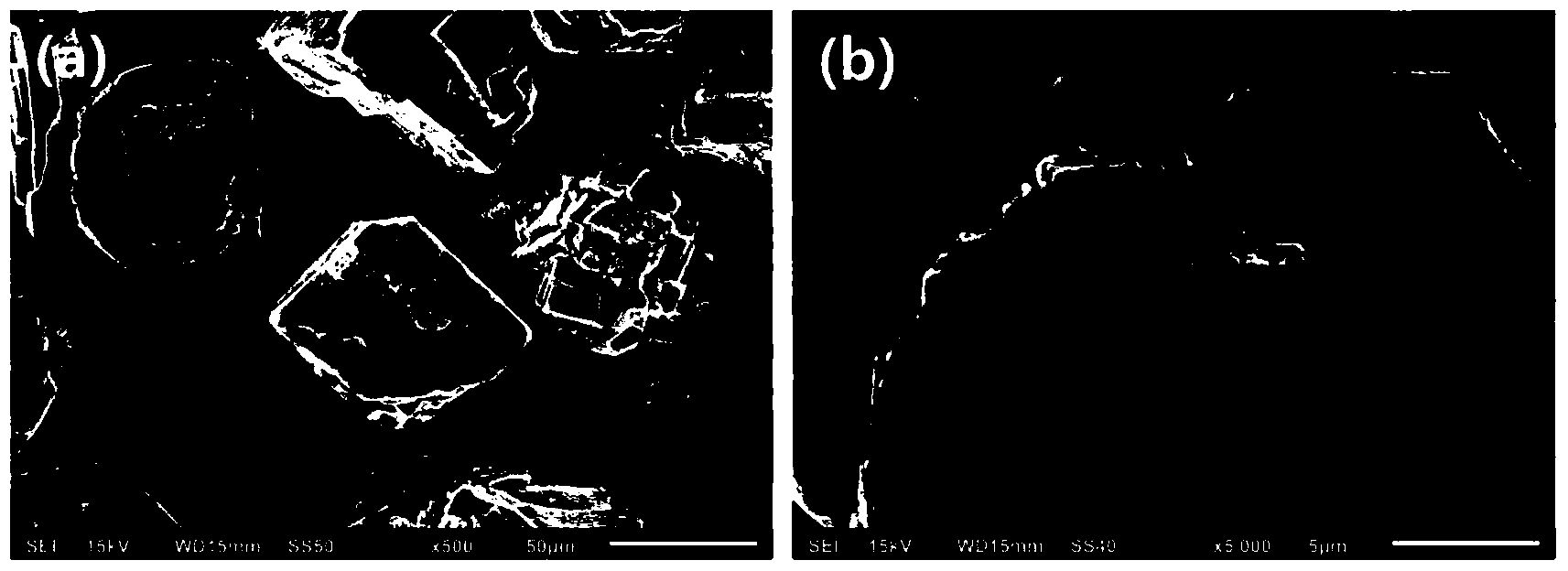
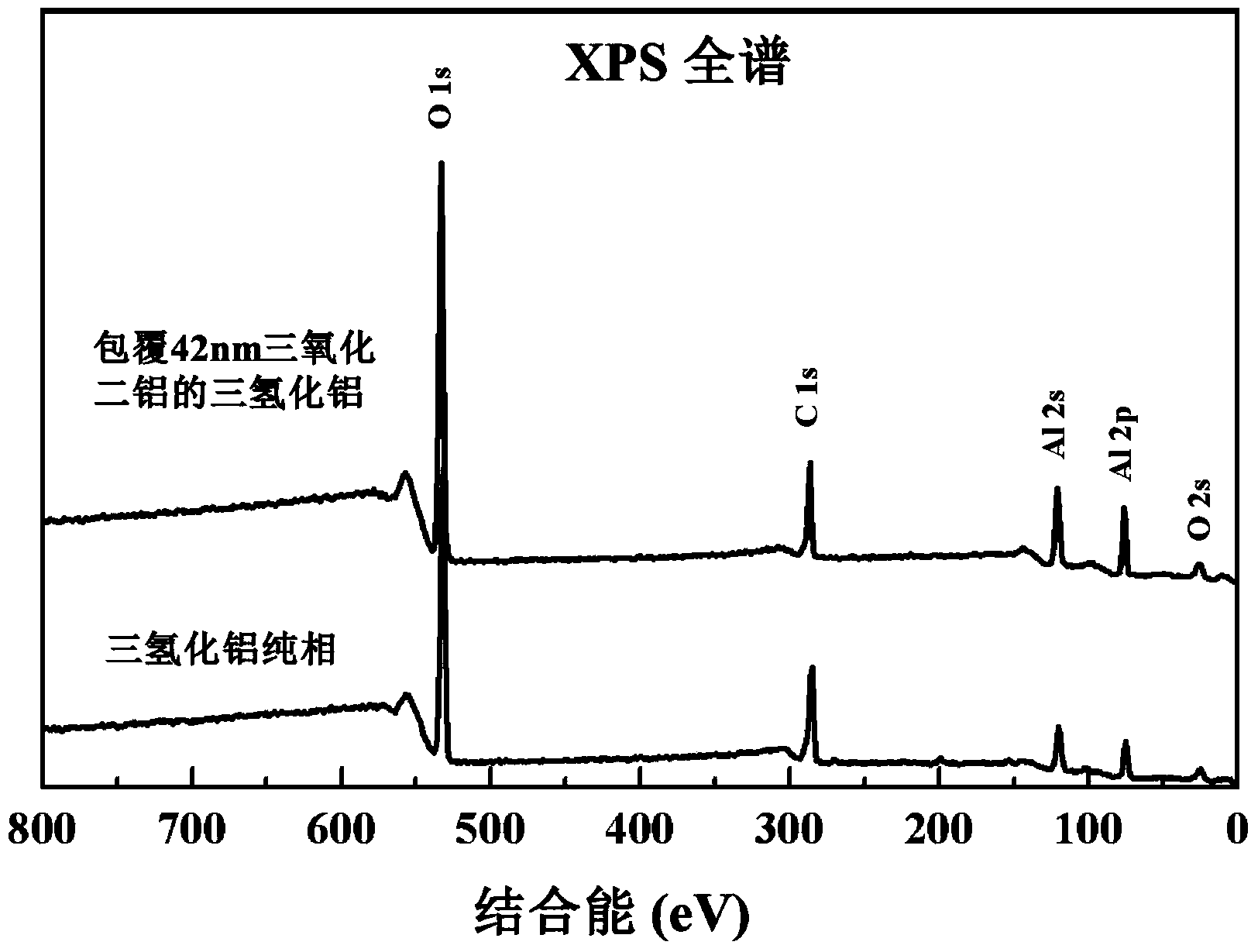
[0037]In this embodiment, the atomic deposition technology is used to coat the surface of the aluminum hydride powder with aluminum oxide having a thickness of 300 cycles (about 42nm), and the surface is coated and modified. The method includes the following steps:
[0038] S1: Weigh 0.05 grams of aluminum trihydride, spread it on the stainless steel filter of the powder holder, then put the powder holder into the atomic layer deposition reaction chamber, close the lid, start vacuuming, and the outlet of the chamber The pressure is 1Pa.
[0039] S2: Heating the cavity, the temperature inside the cavity is set at 50°C, during the heating process, nitrogen fluidizing gas is injected at 50 standard milliliters per minute to fully fluidize the powder, and the cavity outlet pressure is about 40Pa.
[0040] S3: After waiting for the temperature in the chamber to stabilize at 50°C, start the atomic layer deposition reaction. During the entire atomic layer deposition reaction process,...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The process of this embodiment is similar to that of Example 1, except that the quality of aluminum hydride, the temperature in the cavity, the flow rate of fluidization gas, the flow rate of carrier gas, the reaction time of aluminum hydride with the first precursor and the second precursor, etc. The key reaction parameters are different, and the cleaning time of the carrier gas is different. The specific differences are:
[0051] S1: different from step S1 in Example 1, the quality of aluminum trihydride is 2.50 grams;
[0052] S2: The difference from step S2 in Example 1 is that the temperature in the chamber is set to 90°C, and nitrogen gas is introduced at 300 standard milliliters per minute to fully fluidize the powder, and the outlet pressure of the chamber is about 300Pa;
[0053] S3: Different from step S3 in Example 1, the flow rate of the carrier gas is 75 standard milliliters per minute, the flow rate of the fluidizing gas is 100 standard milliliters per min...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The process of this embodiment is similar to that of Example 1, except that the quality of aluminum hydride, the temperature in the cavity, the flow rate of fluidization gas, the flow rate of carrier gas, the reaction time of aluminum hydride with the first precursor and the second precursor, etc. The key reaction parameters are different, and the cleaning time of the carrier gas is different. The specific differences are:
[0064] S1: different from step S1 in Example 1, the quality of aluminum trihydride is 5.00 grams;
[0065] S2: The difference from step S2 in Example 1 is that the temperature in the cavity is set to 130°C, and nitrogen gas is injected at 500 standard milliliters per minute to fully fluidize the powder, and the cavity outlet pressure is about 500Pa;
[0066] S3: Different from step S3 in Example 1, the flow rate of the carrier gas is 100 standard milliliters per minute, the flow rate of the fluidizing gas is 400 standard milliliters per minute, the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com