Acf detection method
A detection method and a technology for an area to be detected, applied in the field of detecting ACF
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
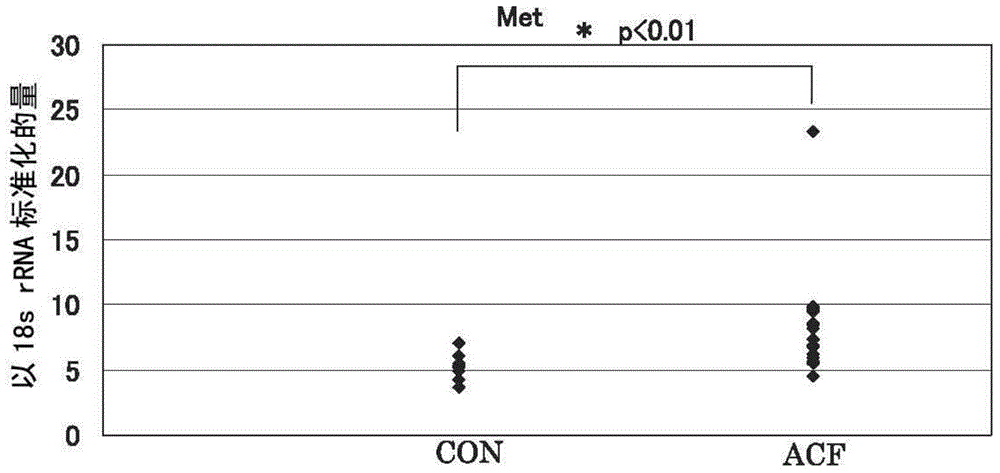
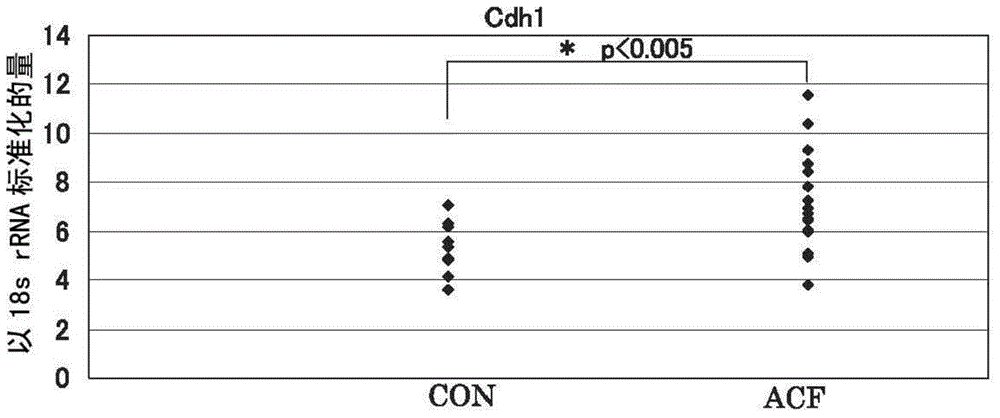
[0087] For all 11 candidate molecules, Met, Cdh1, Ctnnb1, GSTp1, EGFR, iNOS (NOS2), CD44, Fzd1, Ctsb (cathepsin B), PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen), and COX2, the peripheral normal Gene expression levels in tissues and regions suspected of ACF, identifying molecules among these candidate molecule panels whose gene expression levels are specifically upregulated in ACF.
[0088] Specifically, a sample of only an area confirmed as an ACF site under a microscope was collected from a large intestine biopsy sample collected from a patient undergoing lower endoscopy, and a normal tissue collected under a lower endoscope was prepared from the patient. samples, and measure and compare the expression levels of each molecule in each sample. It is shown in more detail below.
[0089] The collected large intestine mucosal tissue of the rectum was observed under a microscope, and only the site confirmed to be the ACF site was excised as an ACF sample. At this time, a commerciall...
Embodiment 2
[0100] According to the results of Example 1, high expression of GSTp1 was observed at both the mRNA level and the protein level in human large intestine ACF. Therefore, using the GSTp1 fluorescent probe, the probe response in surgical resection specimens of human large intestine was studied. The GSTp1 fluorescent probe used in this study is an enzyme activity detection fluorescent probe that has the substrate structure of GSTp1 and produces changes in fluorescence properties through the enzyme reaction with GSTp1, and has fluorescence properties of excitation wavelength 490nm / absorption wavelength 520nm ( Non-Patent Document 9).
[0101] Specifically, after spraying the GSTp1 fluorescent probe solution on the surgical resection specimen of human large intestine, the fluorescence of the ACF lesion was observed under a microscope and an endoscope. More specifically, first, for patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer or ulcerative colitis who underwent extirpation surgery, lo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com