A kind of preparation method of substituted acetylene helical polymer microsphere
An acetylene helix and polymer technology, applied in the field of preparation of substituted acetylene helix polymer microspheres, can solve problems such as no precedent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0046] Example 1: Dissolve 1g of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) in 49g of deionized water to prepare an aqueous solution of PVA with a mass concentration of 2%, and dissolve 0.1g of monomer M1a containing chiral propargyl amide groups in 1mL of chloroform to form Solution, stirred under nitrogen atmosphere for 10 minutes, added 0.0022g rhodium metal catalyst in the above solution, the mol ratio of catalyst and monomer was 1:100, stirred under nitrogen atmosphere for 10 minutes, under nitrogen protection, the above solution was added dropwise to In the PVA aqueous solution, carry out mechanical stirring at a speed of 350rpm, keep the temperature at 0°C for 4 hours, then rise to 30°C for 12 hours, filter after the reaction, wash with deionized water and ethanol in sequence, and vacuum dry for 24 hours, that is Yellow polymer microspheres were obtained.
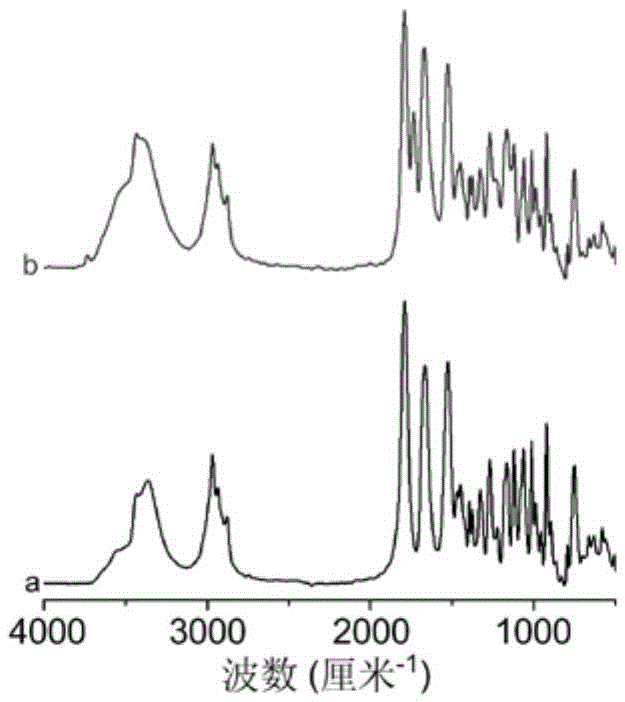
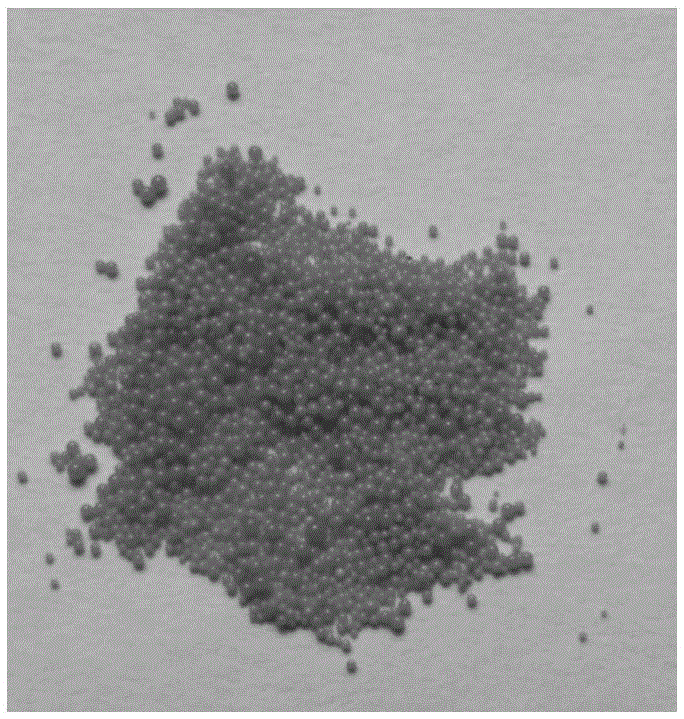
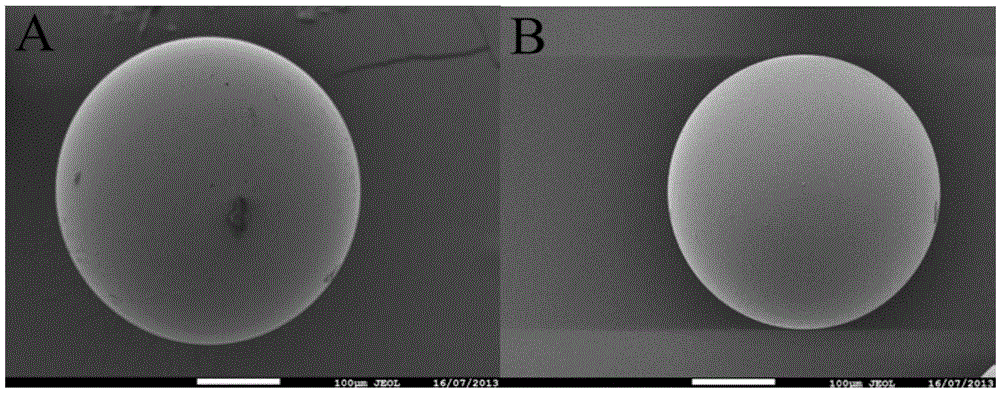
[0047] Result: the infrared spectrogram of example 1 is provided in the accompanying drawing figure 1 Curve a, photo of microspheres...
example 2
[0048] Example 2: The first step is to prepare the bis-alkynyl crosslinking agent M2, specifically as follows: adipic acid and propargyl alcohol are weighed according to the molar ratio of 1:3.5, and benzene is used as a solvent, and p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate is added as dehydration Refluxing reaction at 85°C for 3 hours, followed by extraction with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and saturated sodium chloride solution, drying over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and rotary evaporation to obtain a white solid, which is the diacetylenic crosslinking agent M2.
[0049] The second step is to prepare substituted acetylene helical polymer microspheres. Dissolve 1g of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) in 49g of deionized water to prepare an aqueous solution of PVA with a mass concentration of 2%. Dissolve 0.1g of monomer M1a containing chiral propargyl amide groups in 1mL of chloroform to form a solution. Stir under atmosphere for 10 minutes, add 0.0047g diacetylenic crosslinking ...
example 3
[0051] Example 3: The first step is to prepare the bis-alkyne-based crosslinking agent M2, and the specific steps are the same as in Example 2.
[0052] The second step is to prepare substituted acetylene helical polymer microspheres. Dissolve 1g of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) in 49g of deionized water to prepare an aqueous solution of PVA with a mass concentration of 2%. Dissolve 0.1g of monomer M1a containing chiral propargyl amide groups in 1mL of chloroform to form a solution. Stir under the atmosphere for 10 minutes, add 0.0094g diacetylenyl crosslinking agent to the above solution, stir under nitrogen atmosphere for 10 minutes, add 0.0026g rhodium metal catalyst to the above solution, the molar ratio of the catalyst to the total amount of the monomer crosslinking agent 1:100, stirred under nitrogen atmosphere for 10 minutes, under the protection of nitrogen, the above solution was added dropwise to the PVA aqueous solution, mechanically stirred at 350rpm, kept at 0°C for 4 h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com