Rice black-streaked dwarf virus RNAi multivalent target gene sequence and application
A technology for dwarfing black stripes and targeting genes in rice, applied in DNA/RNA fragmentation, application, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of lack of resistance resources, long breeding cycle, and accelerated rice disease resistance breeding.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 3
[0017] Nucleotide sequence and cloning of embodiment 1 trivalent RNAi gene fragment
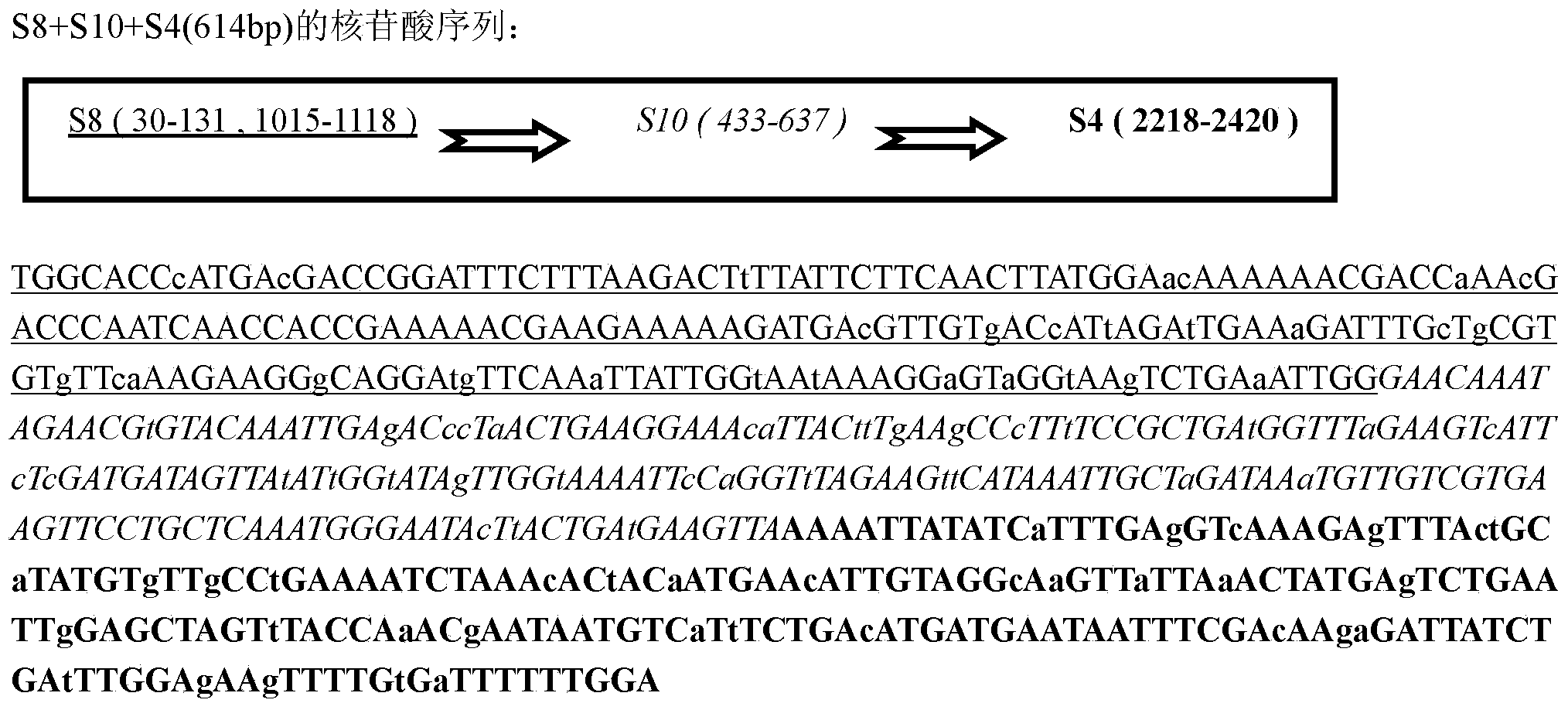
[0018] According to the RBSDV sequence submitted by NCBI, multiple sequence alignment and restriction enzyme analysis were performed on DNAMAN6.0.3.99, and the relatively conserved S8, S10, and S4 coding region genes that did not contain BamHI and XhoI restriction sites were selected For fragments, the online design software of Wuhan Jingsai Bioengineering Technology Co., Ltd. was used to predict the siRNA target site, and the off-target effect was predicted in the rice genome database (http: / / signal.salk.edu / cgi-bin / RiceGE). Optimized to obtain 614bp RNAi multivalent target gene sequence (such as figure 1 shown; as shown in SEQ ID NO.1), which in turn includes the 206bp fragment of the S8 coding region (corresponding to S8 gene 30~131bp, 1015~1118bp), the 205bp of the S10 coding region (corresponding to the S10 gene 433~637bp), S4 203bp of the coding region (corresponding to 2218~2420bp of ...
Embodiment 2 3
[0019] Example 2 Construction of Trivalent RNAi Plant Expression Vector
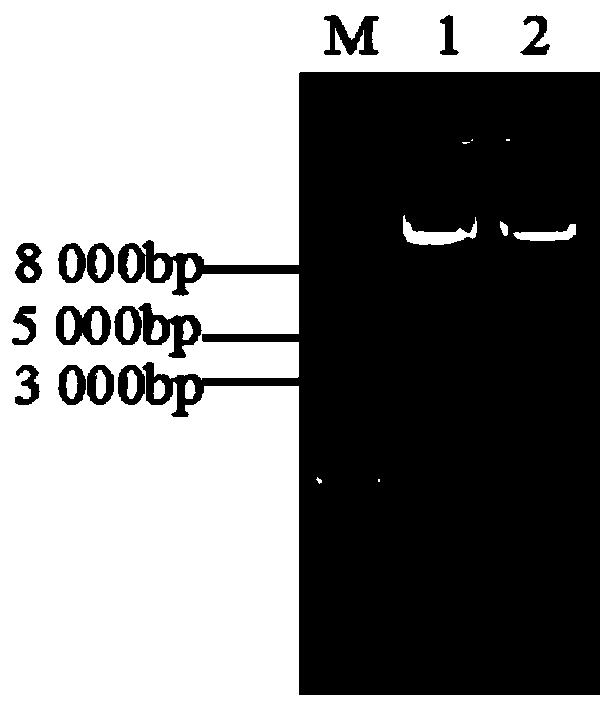
[0020] The concentration and purity of the entry vector tENTRA-S2+S6+S10 and the destination vector pBDL03 were detected by ultraviolet spectrophotometer and agarose gel electrophoresis, and then the entry vector and the destination vector were subjected to LR reaction at a ratio of 1:1. According to Gat LR Clonase TM II Enzyme Mix (Invitrogen) kit instructions Construct 10ul reaction system, overnight at 25°C, add 1ul Proteinase K solution, treat at 37°C for 10min to terminate the reaction. Take 1ul of the above reaction solution to transform trans5α competent cells, after centrifugation, spread it evenly on a solid LB plate containing 50mg / L kanamycin, pick a single clone for plasmid extraction and double enzyme digestion verification ( figure 2 ), and designed primers GUS3 (5'-CAGTCCATTAATGCGTGGTCGT-3') and GUS4 (5'-TGTATCACCGCGTCTTTGATCG-3') according to the Gus-linker sequence on the target vec...
Embodiment 3
[0021] Embodiment 3 Agrobacterium transformation and the acquisition of transgenic rice
[0022] The RNAi plant expression vector pBDL03-S8+S10+S4 was transformed into the rice variety Taijing 394 by the Agrobacterium-mediated method, and the specific experimental steps were as follows:
[0023] (1) Induction of callus
[0024] a: select fine rice mature seeds and shell them into brown rice. Transfer an appropriate amount of brown rice to a 50ml centrifuge tube (the following steps require aseptic operation), add 75% ethanol solution to infiltrate and wash the brown rice for 2 minutes, pour off the ethanol solution, and rinse the seeds twice with sterile water.
[0025] b: Wash the seeds once with 2% sodium hypochlorite with available chlorine, and shake the centrifuge tube intermittently for 30 minutes. Pour off the sodium hypochlorite solution, rinse the seeds with sterile water 4 times, five minutes each time for the first three times, soak for 30 minutes for the last tim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com