Technology for identifying HBV (hepatitis B virus) gene integration sites and recurrently targeted genes in host genome
A technology of integration sites and genomes, which can be used in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve the problem that the sequencing throughput cannot identify integration sites.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0140] 1. Experimental samples
[0141] Tissue samples used in this application were agreed to by each patient and the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, which approved this study.
[0142] HBV-positive HCC tissue samples were obtained from clinical tissue sections of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine. Each case was divided into cancer tissue and paracancerous tissue, a total of 40 pairs of tissue sections. Tissue samples were stored in a -80°C freezer.
[0143] 2. Reagents and equipment
[0144] 1) Reagent
[0145] Kits: DNA extraction kit (DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit, QIAGEN), DNA general purification kit (QIAquick PCR Purification Kit, QIAGEN), DNA tapping gel purification kit (QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit, QIAGEN).
[0146]Enzymes: T4DNA Polymerase (T4DNA Polymerase, NEB), T4DNA Ligase (T4DNA Ligase, NEB), T4 Polynucleotide Kinase (T4Polynucleotide Kinase, NEB), Klenow DNA Polymerase (DNA Polymer...
Embodiment 2
[0222] In this example, the integration sites found in Example 1 were randomly selected for verification.
[0223] 1. PCR verification and Sanger sequencing verification
[0224] 1) Primer design
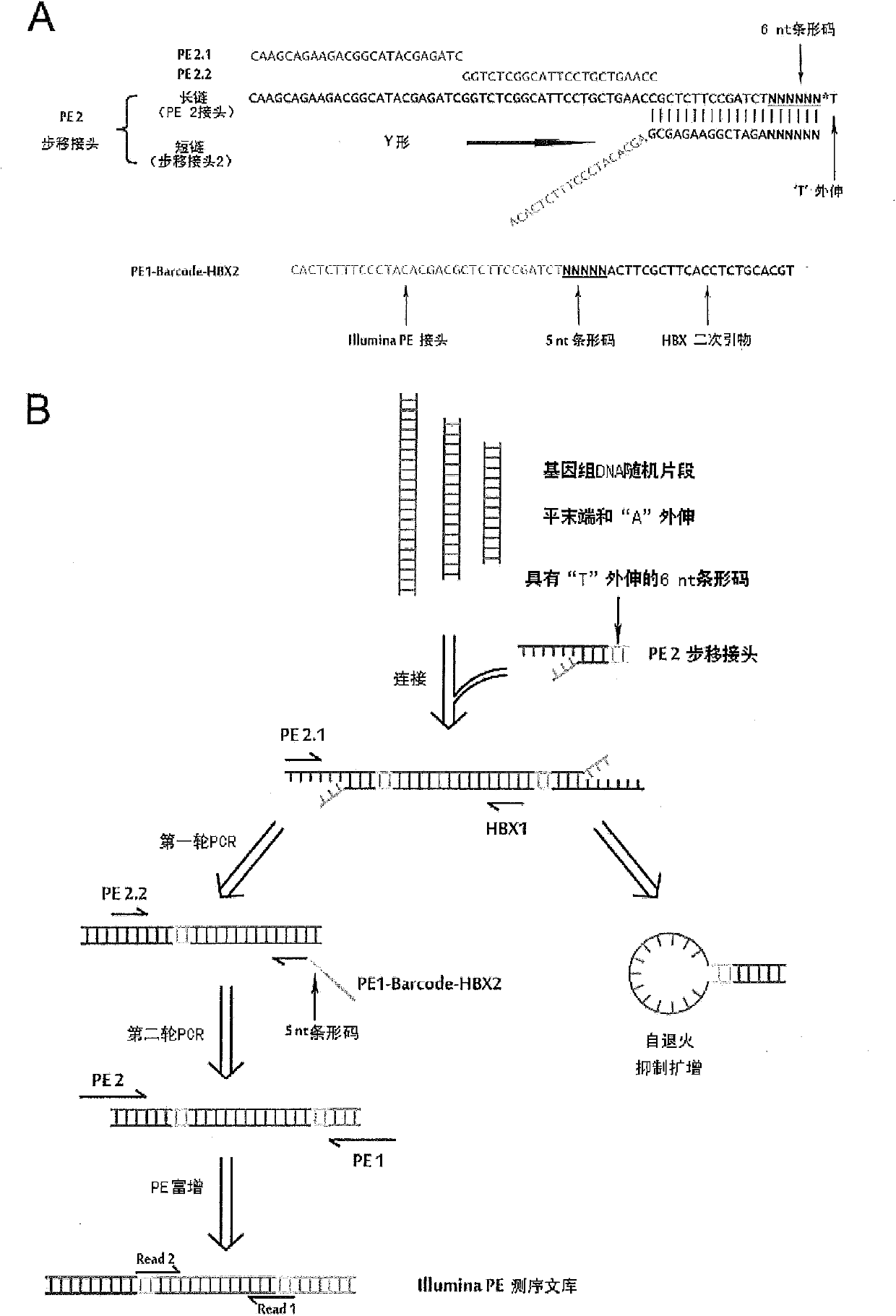
[0225] In order to be consistent with the amplification reaction when isolating the integration site, the verification reaction also used nested PCR. On the human gene sequence of the integrant, two primers (for the first round of PCR primers and nested primers in Table 5) were designed towards the integration site to correspond to the nested primers of the HBX gene. The final PCR product was controlled within 1kb. The integration sites and their validation primers are listed in Table 5, and the integration sites used in the validation experiments are represented by the codes N9+chr1-1 to N13-chrX-1 in the "Information" column, a total of 28.
[0226] Table 5. Primers and results of integration site nested PCR validation
[0227]
[0228]
[0229] 2) Nested PCR validation ...
Embodiment 3
[0242] This embodiment further examines the reliability and relative quantitative possibility of the MAPS identification results of Example 1.
[0243] 1. Semi-quantitative PCR
[0244] 1) Genomic DNA template dilution
[0245]Take 10 μL of HCC genomic DNA (60ng / μL) and add it to tube 1 of the PCR eight-tube strip. Add 15 μL of double distilled water to tubes 2-8 respectively. Take 5 μL of DNA from tube 1 to tube 2; mix well and pipette 5 μL of the mixture from tube 2 to tube 3; mix well and then pipette into the next tube to dilute, and then dilute to tube 7. Finally, the concentration of DNA in the eight tubes was approximately: 60ng, 15ng, 3.75ng, 0.94ng, 0.23ng, 0.06ng and 0ng (pure water, blank control).
[0246] 2) Nested PCR
[0247] For the 28 integration sites in Table 5, according to the method of "2) nested PCR verification" in the step "9. PCR verification and Sanger sequencing verification" of Example 1, basically the same PCR reaction system and cycle conditi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com