Cation functional polymers with natural amino acid as side group, preparation method and application of polymer
A functional polymer and natural amino acid technology, applied in the application field of biological functional carrier materials, can solve the problems of low preparation efficiency, narrow molecular weight distribution, unsuitable for large-scale preparation and application, etc., and achieve simple and convenient synthesis operation and regular polymer structure , Conducive to the effect of controlled release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
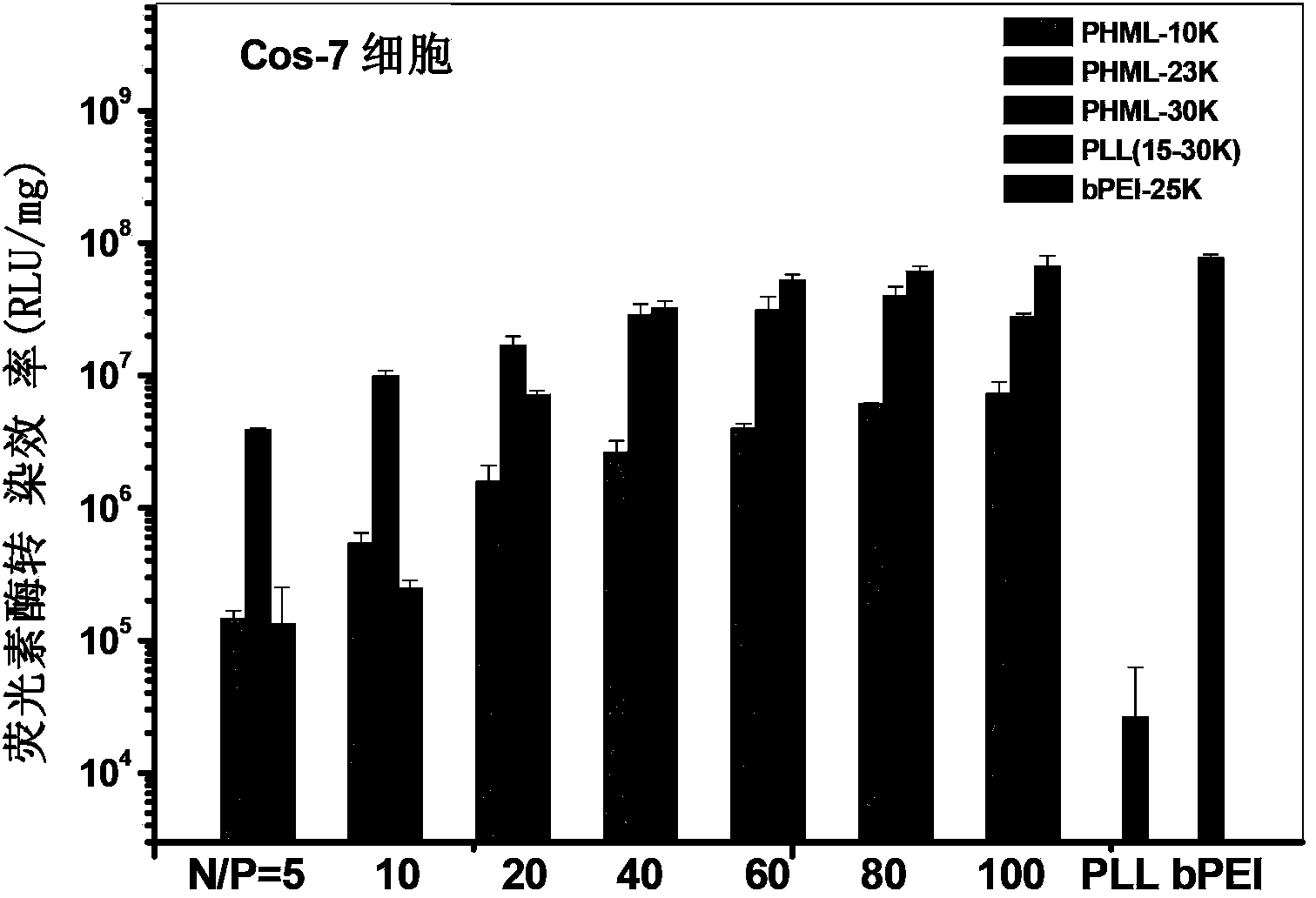
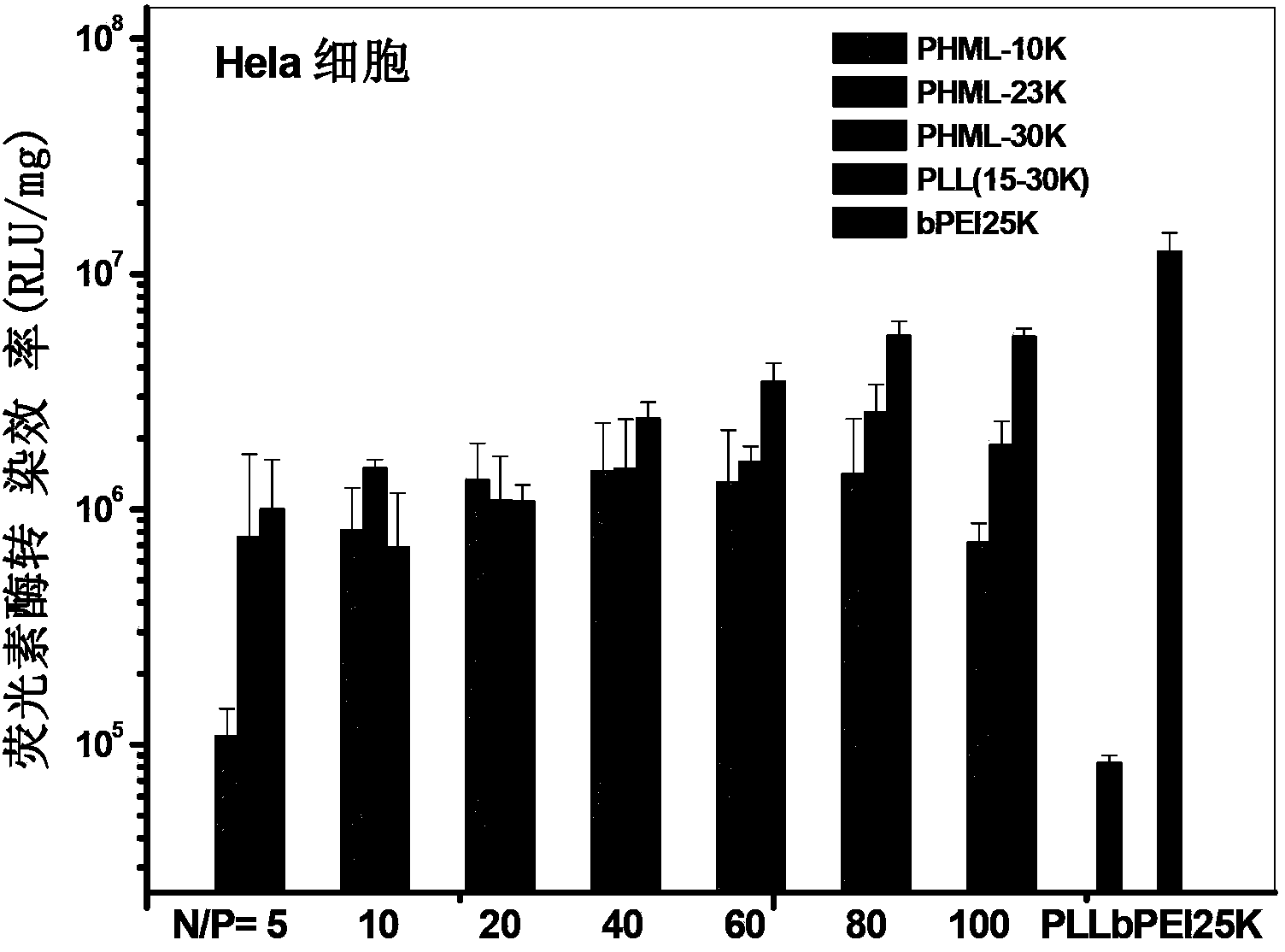
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Place lysine (5.58g, 38.2mmol), sodium hydroxide (1.4g, 35mmol), and 150ml of water in a 500ml reaction flask, and add di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (25.0g , 114.5mmol). After reacting at room temperature for 20 h, add 10% KHSO 4 The pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to less than 3 with aqueous solution. Then it was extracted 3 times with ethyl acetate, the organic phases were combined, washed with water and saturated brine successively, and the obtained organic phase was washed with anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 Drying and concentration under reduced pressure finally gave 8.8 g of Boc-lysine product as white solid, with a yield of 67%. The main structural features of the product are as follows:
[0046] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , δin ppm): 1.44 (CH 3 , 18H, s), 1.49-1.96 (CH 2 , 6H, brm), 2.99-3.19 (CH 2 N, 2H, br), 4.22-4.38 (COCH(R)NH, 1H, m)
[0047] ESI-MS: [M+Na + ]=369.2m / z
Embodiment 2
[0049] The first step: Boc-lysine (2.76g, 8mmol) and hydroxyethyl methacrylate (1.3g, 10mmol) obtained in Example 1 were dissolved in 50ml of dichloromethane, and then slowly added dropwise to the A small amount of DMAP was added to a solution of 20ml of dichloromethane in DCC (1.65g, 8mmol), and the reaction was stirred at 50°C for 5h. Thereafter, part of the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, separated and purified by column chromatography (dichloromethane / petroleum ether=2:1) to obtain a colorless oily Boc-lysine functionalized methacrylate monomer with a yield of 70 %. The main chemical structural features are as follows:
[0050] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , δin ppm): 6.13, 5.61 (C=CH 2 , 2H, s), 5.12, 4.62 (NHCOO, 2H, s), 14.48-4.26 (OCH 2 CH 2 O, COCH(R)NH, 5H, m), 3.17-3.03(CH 2 N, 2H, q), 1.94 (C=CCH 3 , 3H, s), 1.96-1.49 (CH 2 , 6H, brm), 1.44 (C (CH 3 ) 3 ,9H,s)
[0051] ESI-MS: [M+Na + ]=481.4m / z
[0052] The second step: the Boc-lysine function...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Boc-lysine functionalized methacrylate monomer (1.56g, 3.36mmol), 4-cyanomethylpentanoic acid dithiobenzoate (8mg, 0.031 mmol), azobisisobutyronitrile (6mg, 0.0372mmol), and 10ml of dry THF were added to a dry Schlenk tube, and the residual oxygen in the reaction solution was removed through three freeze-vacuum-thaw cycles with nitrogen, 50°C The reaction was stirred for 24 h under the protection of nitrogen. Thereafter, the Schlenk tube was immersed in liquid nitrogen to quench the reaction, and the reactant was precipitated with ether to obtain a pink precipitate. The solvent was further decanted and dried in a vacuum oven for 24 hours to obtain a Boc-lysine functionalized methacrylate polymer with a conversion rate of 59%. Its number average molecular weight Mn is 23.7KD and PDI is 1.38. On this basis, the obtained Boc-lysine functionalized methacrylate polymer was dissolved in 2ml of dichloromethane, and 2ml of trifluoroacetic acid was added, stirred at room tempe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com