Vertical rotary compressor
A vertical rotary compressor technology, applied in the field of rotary compressors, can solve the problems of increased oil discharge, compressor wear failure, oil viscosity reduction, etc., to improve the noise level, improve reliability and efficiency, and reliability problems Improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
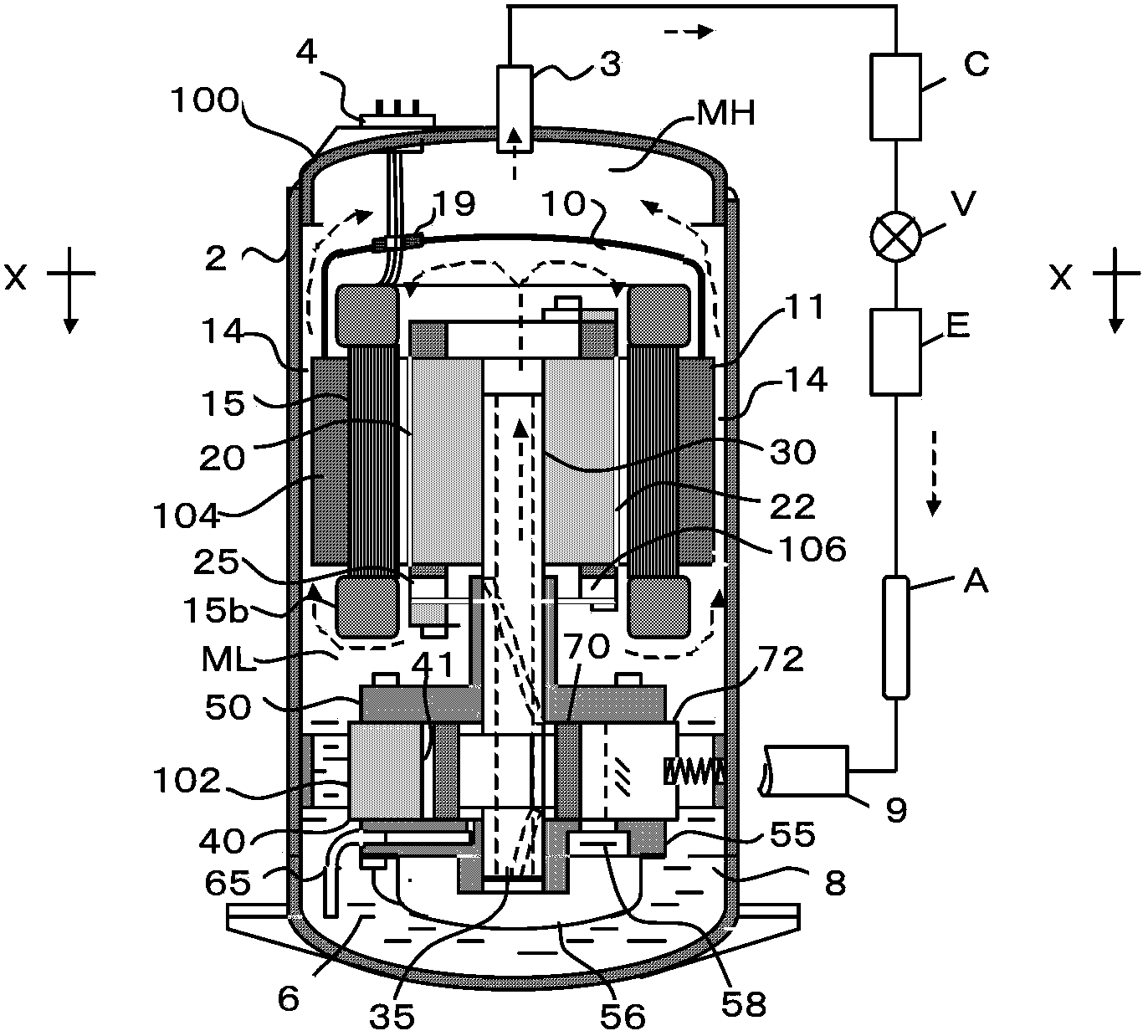
[0047] figure 1 Shown is the basic configuration of the rotary compressor 100 according to the first embodiment and the outline of the refrigeration cycle apparatus connected thereto. The vertical rotary compressor 100 is composed of an electric motor 104 mounted on a hermetic cylindrical casing 2 and a rotary compressor 102 mounted on the lower side thereof, and an oil storage chamber at the bottom of the casing 2 Oil 6 is sealed in 8. The outer peripheries of the motor stator 11 and the compression device 102 are fixed at the inner diameter of the casing 2 . Therefore, the space formed between the motor 104 and the compression device 102 is called an ML cavity.
[0048] The motor 104 is composed of a motor stator 11 equipped with motor windings 15 and a motor rotor 20 fixed to the crankshaft 30 . On the other hand, the compression device 102 is constituted by a piston 70 arranged on the cylinder 40, a vane 72, a crankshaft 30 provided with a shaft through hole, a main bea...
Embodiment 2
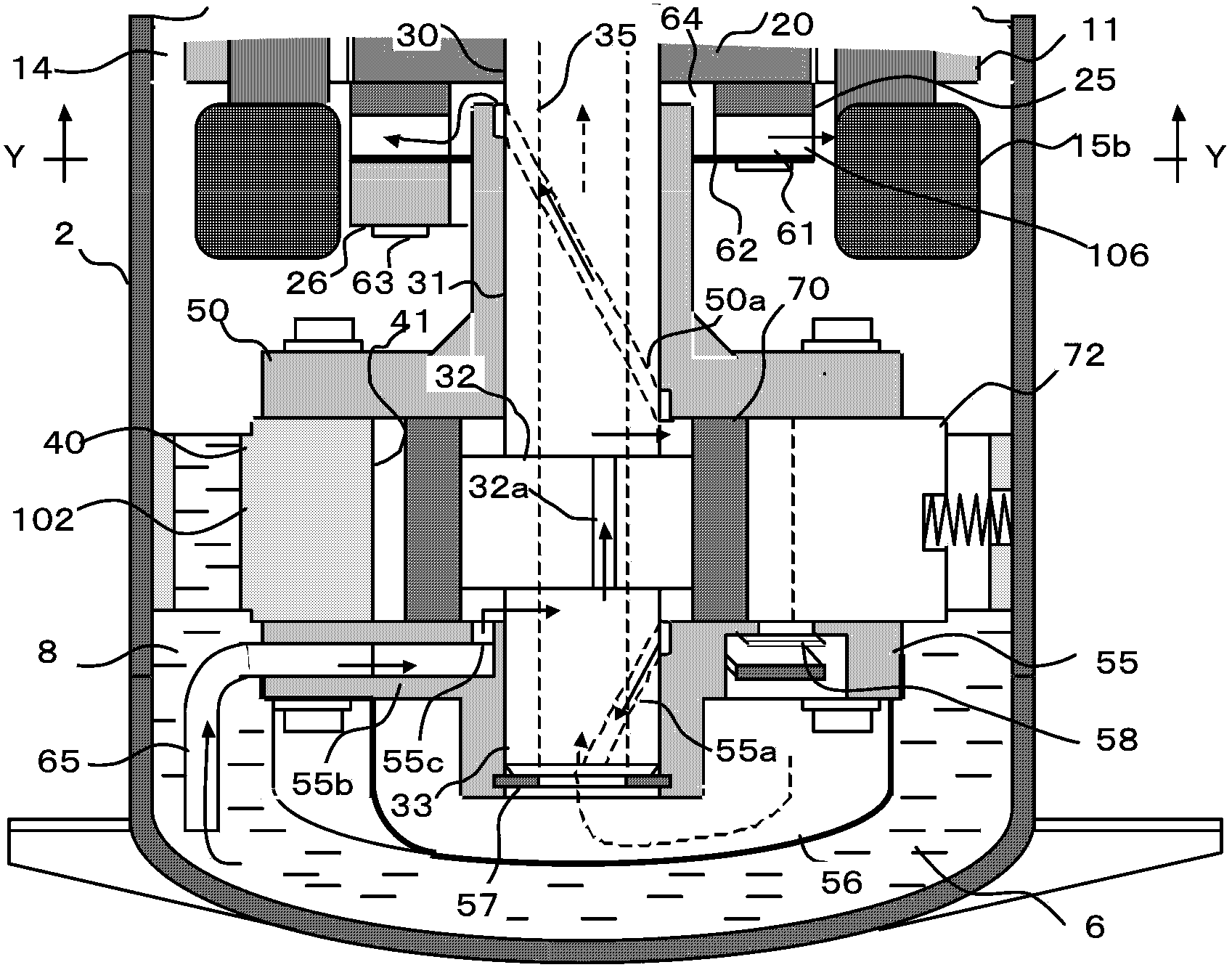
[0072] Since the amount of refrigerant flowing in the shaft through hole 35 is the same as the amount of refrigerant discharged from the discharge pipe 3 , the diameter of the shaft through hole 35 only needs to be the same as the inner diameter of the exhaust pipe 3 . However, the diameter of the shaft through hole 35 is limited by the shaft diameter of the crankshaft 30 . Especially in a rotary compressor with a high-speed variable frequency motor or a rotary compressor with a large displacement, if the amount of refrigerant passing through the shaft through hole 35 increases, the compression loss of the compression chamber 41 may increase. Figure 10 The illustrated embodiment 2 is a countermeasure for such exceptional conditions.
[0073] In the compression device 102 , the sub bearing 55 and the main bearing 50 each include an exhaust device 58 , a lower muffler 56 , and an upper muffler 51 . The upper muffler 51 is provided with a muffler exhaust hole 51 a, and the two ...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Figure 12 In the illustrated embodiment 3, the bearing exhaust pipe 53 is used to replace the shaft through hole 35 of the crankshaft 30, so that the high-pressure refrigerant discharged from the compression chamber 41 flows out to the winding through the outer peripheral hole 18 of the iron core provided on the motor stator 11. Cover 10 places. The mixed refrigerant discharged into the winding cover 10 flows through the interior of the motor stator 11 to the ML cavity as in the first embodiment, then flows from the iron core peripheral gap 14 to the MH cavity, and is discharged from the exhaust pipe 3 . Therefore, the same actions and effects as those of Embodiment 1 can be obtained. In addition, in the third embodiment, since the shaft through hole 35 of the crankshaft 30 is not used, a conventional oil supply device can be installed inside the crankshaft 30 . In addition, the motor 104 used in this design is a concentrated winding type variable frequency motor.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com