Method for detecting benzopyrene in edible oil
A detection method, the technology of benzopyrene, which is applied in the field of food analysis, can solve the problems of low recovery rate of addition, poor stability, complicated pretreatment, etc., and achieve the effect of optimizing saponification time, saponification temperature and accurate detection results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] (1) Repetitive experiment
[0014] The detection method of benzopyrene in edible oil of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0015] (1) Pretreatment method: Weigh 0.3854g, 0.4699g, 0.5300 and 0.5521 of tea seed oil respectively, add 5mL of 1mol / L potassium hydroxide ethanol aqueous solution to shake until clear, continue to shake for 1min, and saponify in a water bath at 50°C 1h, after cooling to room temperature, add 5ml of ultrapure water to the sample centrifuge tube, shake well, then add 15ml of n-hexane, mix well on a vortex mixer, centrifuge, transfer the supernatant into the test tube, and Add 10ml of n-hexane to the sample centrifuge tube, and operate as above, wash the combined two extracts with 5ml ultrapure water twice, place the extract in a nitrogen blower and concentrate to dryness, and use tetrahydrofuran + acetonitrile = 2+ 8. Dilute the mixed solution to 1ml, filter the membrane and measure it on the machine;
[0016] (2) Analyze wit...
Embodiment 2
[0020] (2) Add recovery test
[0021] According to the experimental method of Example 1, after weighing the same sample as in Example 1, add the standard solution of BaP, the specific addition amount is shown in Table 1, the subsequent pretreatment and instrument analysis are the same as in Example 1, and the test results are as follows Table 1 shows.
[0022] The theoretical formula for calculating the standard recovery rate based on the concentration value:
[0023] P=(c2-c1) / c3×100%
[0024] In the formula: P is the recovery rate of standard addition; c1 is the sample concentration, that is, the measured value of the sample, c1=m1 / V1; c2 is the concentration of the spiked sample, that is, the measured value of the spiked sample, c2=m2 / V2; c3 is the added amount, c3=c0×V0 / V2: m=c0×V0; m1 is the substance content in the sample; m2 is the substance content in the spiked sample; m is the substance content in the spiked volume; V1 is the sample volume; V2 is the volume of the...
Embodiment 3
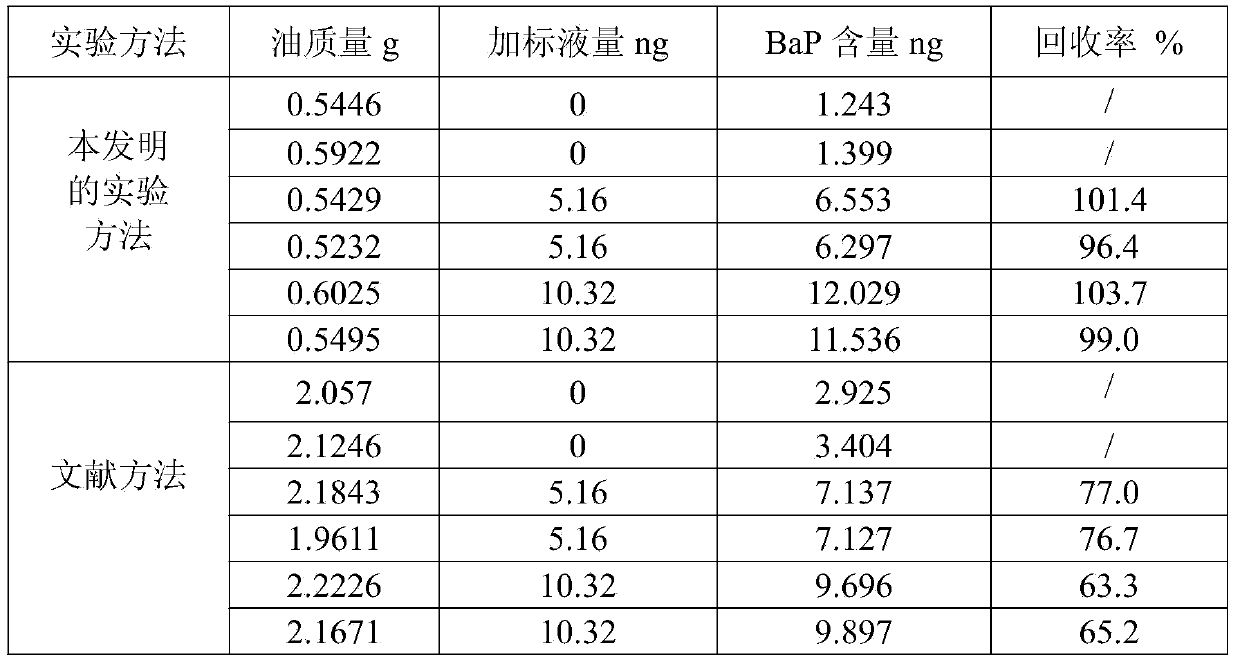
[0028] The present invention is compared with the experimental method in "Measurement and Safety Evaluation of Benzo(a)pyrene in Fried Foods in Guiyang" published by Yang Zhannan et al. in "Food Science". Saponification in a water bath for 1 h, while the above-mentioned literature used reflux saponification in a water bath at 80° C. for 1 h. The sample blank experiment and the addition recovery experiment were carried out respectively. The experimental results are shown in Table 2. The addition recovery rate of the present invention is between 96.4~103.7%, and the addition recovery rate adopting above-mentioned document method is between 65.2~77.0%, illustrates that saponification temperature and time in the pretreatment of the present invention are obviously better than comparative literature, Improved data accuracy and shortened experiment time.
[0029] The comparative test of the present invention and comparative literature of table 2
[0030]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com