Safety evaluation method for analyzing fungus strain producing no mycotoxin based on whole genome sequence
A technology for safety evaluation and mycotoxins, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial determination/inspection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
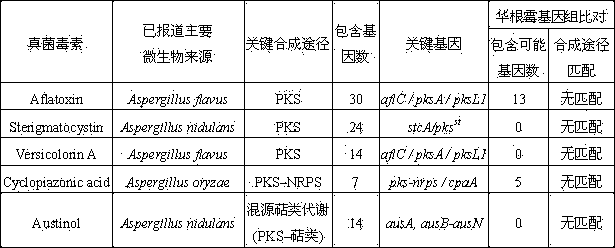
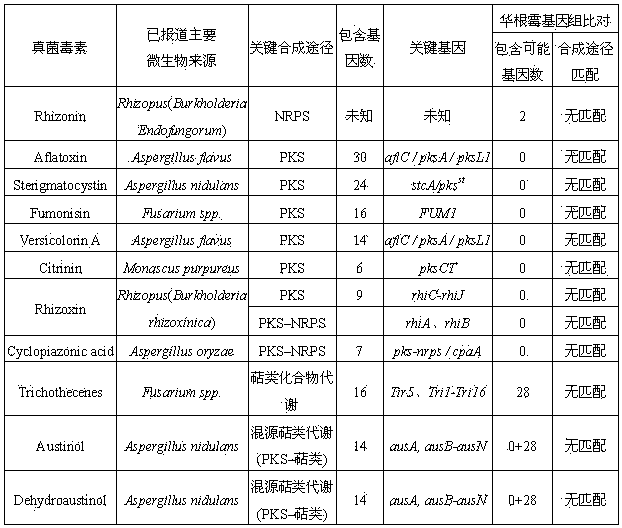
[0017] Embodiment 1: filamentous fungus Rhizopus sinensis ( Rhizopus chinensis ) Safety evaluation of whether CCTCC M 201021 produces mycotoxin:
[0018] Rhizopus chinensis Rhizopus chinensis It is an important functional microorganism in my country's traditional brewing industry. Rhizopus sinensis strain CCTCC M 201021 is a filamentous fungus isolated from Chinese liquor brewing Daqu (Xu Y, Wang D, Mu XQ, et al.. Biosynthesis of ethyl esters of short-chain fatty acids using whole- cell lipase from Rhizopus chinensis CCTCC M201021 in non-aqueous phase. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2002, 18:29 –37), according to the whole genome sequence data of the strain (GenBank number ANKS00000000), it was analyzed and judged whether Rhizopus sinensis has the ability to produce mycotoxins. potentially harmful. Focus on the main metabolic pathways and related genes of rhizopus, microsporin and typical filamentous mycotoxins, including PKS, NRPS and PKS-NRPS mixed metabolic pathways, terpen...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2: Aspergillus oryzae ( Aspergillus oryzae ) Safety evaluation of whether RIB326 produces mycotoxin:
[0022]The filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae ( Aspergillus oryzae ) RIB326 is a production strain isolated in the Japanese traditional brewing industry (Umemura, M, Koike, H, Yamane, N, et al. Comparative Genome Analysis Between Aspergillus oryzae Strains Reveals Close Relationship Between Sites of Mutation Localization and Regions of Highly Divergent Genes among Aspergillus Species. DNA RESEARCH, 2012, 19, 375–382). According to Aspergillus oryzae ( Aspergillus oryzae ) RIB326 whole genome sequence data (GenBank number BAEZ00000000), analyze and judge whether the strain has the potential hazard of producing mycotoxin. Focus on the possible mycotoxins derived from Aspergillus, such as the main pathways and related genes of typical mycotoxin metabolism such as aflatoxin and cyclopiazonic acid. Genome analysis showed that about half of the aflatox...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Embodiment 3: Aspergillus niger ( Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88) safety evaluation of mycotoxin production:
[0026] Aspergillus niger ( Aspergillus niger ) is an important fermentation industry production bacteria. In the whole genome data of Aspergillus niger strain CBS 513.88 (GenBank number GCA_000002855.1), after analysis, it was found that this strain has a relatively complete PKS pathway and a complete gene cluster of fumonisin synthesis pathway, and has the ability to produce this toxin, indicating that There is a potential safety risk of producing mycotoxins when the strain is used in industries such as food and medicine. In industrial production applications, the detection of the fermentation products of Aspergillus niger strains found that there are indeed mycotoxins such as fumonisins and ochratoxins. The production of fumonisin by fermentation of Aspergillus niger strain CBS 513.88 has been confirmed by literature reports (Frisvad JC, Larsen TO, Thrane ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com