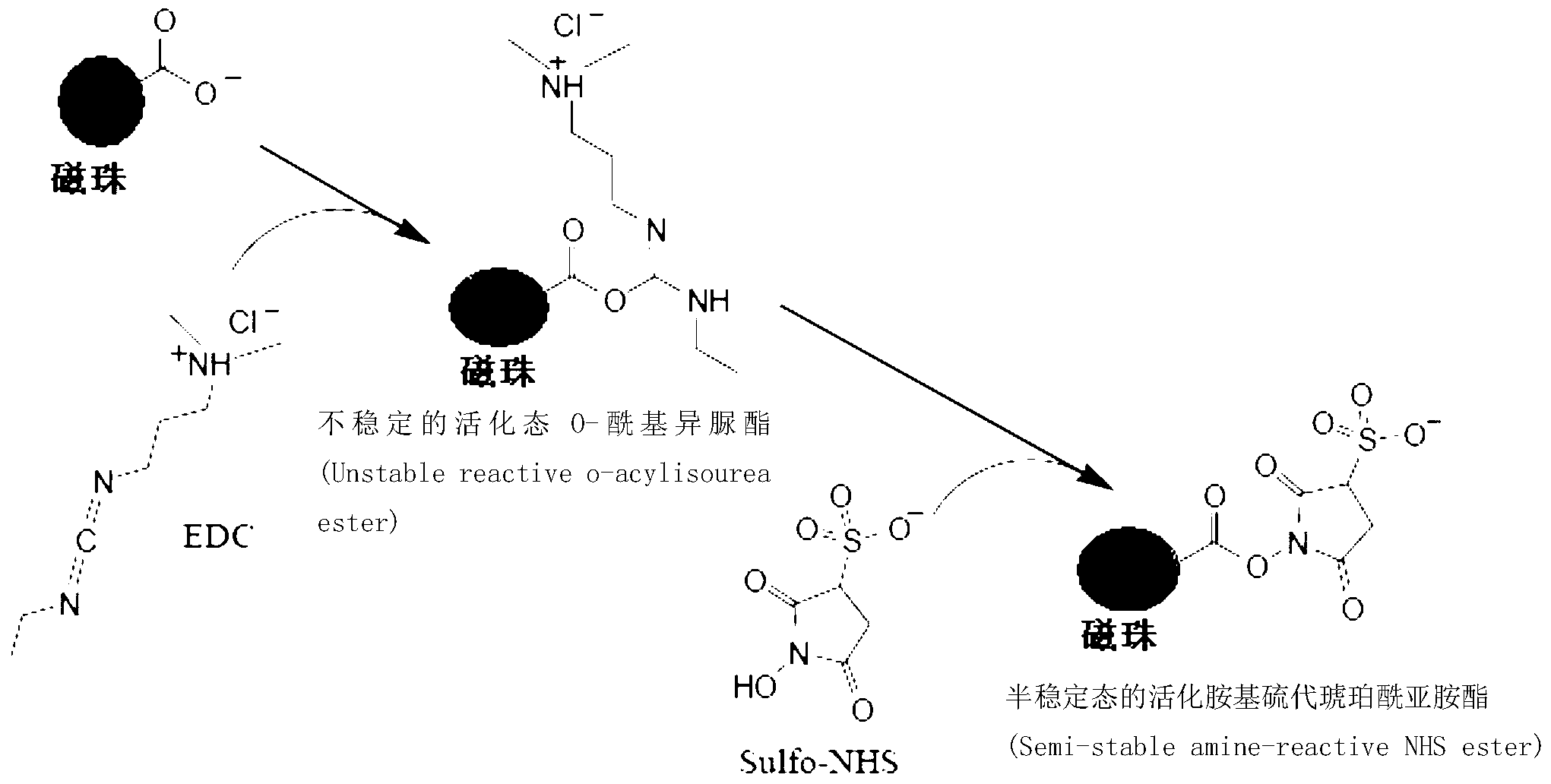
Protein covalent coupling method on surface of magnetic beads
A surface covalent, protein-based technology, applied in the direction of material inspection products, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of self-agglutination of coupled magnetic beads, low coupling efficiency of magnetic beads, non-specific adsorption of magnetic beads, etc., and achieve protein coupling High coupling efficiency, increased coupling efficiency, and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1, carboxyl magnetic beads coupled goat anti-fluorescein isothiocyanate antibody
[0033] 1. Activation of carboxyl magnetic beads
[0034] The purpose of this step is to generate carbodiamine-containing chemical groups on the surface of the magnetic beads.
[0035] 1. Magnetic bead pretreatment
[0036] Take 1000 mg carboxy magnetic bead colloidal solution and settle under the action of magnetic field for 20 minutes, discard the supernatant, and then wash the magnetic beads once with 50 ml pH7.0, 0.01M MES buffer.
[0037] 2. Fully suspend the magnetic beads obtained in step 1 with 20ml pH7.0, 0.01M MES buffer solution, then add EDC and NHS, so that the concentration of EDC is 0.1mM, and the concentration of NHS is 100mM, shake the reaction at room temperature (30 rpm / min) for 240 minutes to obtain an activated magnetic bead solution.
[0038] 2. Goat anti-fluorescein isothiocyanate antibody coupled to carboxyl magnetic beads
[0039] 1. Take 10ml goat ant...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2, carboxyl magnetic beads coupled monoclonal antibody
[0067] 1. Activation of carboxyl magnetic beads
[0068] 1. Magnetic bead pretreatment
[0069] Take 200 mg carboxyl magnetic bead colloidal solution and settle under the action of a magnetic field for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and wash the sedimented magnetic beads with pH 4.0, 0.1 M MES buffer 3 times, 20 ml each time.
[0070] 2. Fully suspend the magnetic beads obtained in step 1 with 20ml pH4.0, 0.1M MES buffer, then add EDC and NHS, make the concentration of EDC 30mM, and the concentration of NHS 0.3mM, shake the reaction at room temperature (20 rpm / min) for 10 minutes, which is the activated magnetic bead solution.
[0071] 2. Carboxyl magnetic beads conjugated monoclonal antibody
[0072] 1. Take thyroxine monoclonal antibody, load it on a Sephadex G25 chromatographic column, elute with pH 4.0, 0.1M MES buffer, and collect 4ml of antibody solution.
[0073] 2. Coupling
[0074] Add...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com