Bacteriophage with environment disinfection capability and applications thereof
A bacteriophage and environmental technology, applied in the field of bacteriophage, can solve the problems of animal body injury, death, disease of livestock and poultry, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Phage Screening and Purification
[0052] (1) Collection of samples
[0053] The chicken manure sample in the present invention is collected from a commercial chicken farm in Gaomi, Weifang City, Shandong Province.
[0054] (2) Specific amplification of coliphage in the sample
[0055] Take 2 g of the sample and add it to the pre-amplified Escherichia coli (the ratio of host bacteria added is 1:10), and place it on a constant temperature shaker at 37° C. and culture it at 200 r / min for 6-8 hours.
[0056] (3) Double-layer plate assay to detect the presence of specific phages
[0057] Autoclave the nutrient agar solid medium with 2% agar content, place it at room temperature to about 40-60°C, pour 10-15ml into a petri dish, spread it evenly on the bottom of the dish, leave it at room temperature for 30 minutes to solidify, and use this nutrient The agar plate serves as the bottom agar plate. Take 1 ml of the amplified phage sample amplified by Escherichia coli, centr...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Observation of Phage Morphology
[0064] After centrifuging at 5000rpm for 10min at high speed, 5ml of phage proliferation solution was put into a dialysis bag for PEG concentration to about 0.5-1ml. Finally, 2 times the volume of 2.5% glutaraldehyde was added to fix the sample. The sample was observed by transmission electron microscope.
[0065] The results show that phage Bp7 has a polyhedral stereosymmetric head, which wraps the nucleic acid, with a diameter of about 93nm; a tail with a length of about 106nm and a tail sheath; the neck connects the head and the tail.
Embodiment 3
[0067] Detection of phage stability
[0068] 1. Phage counting method (titer)
[0069] Dilute the obtained phage sample by 10 times with sterile physiological saline, take a certain proportion of the sample diluent 10 μL and mix it with 20 μL of Escherichia coli bacteria liquid, and prepare it by the method in step (3) described in Example 1 Two-layer plate, each dilution was made 3 parallel samples. When counting, observe the phage plaques on the plate, and take a plate with 30 to 300 phage plaques to count and measure the titer. Record the number of phage plaques in three parallel samples of this dilution, and then calculate the average number to calculate the number of phages (titer) in the stock solution.
[0070] Phage titer (pfu / mL) = average number of plaques × dilution factor × 100
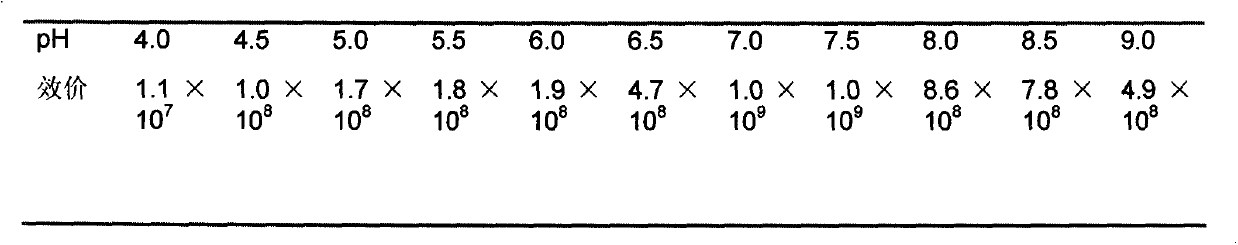
[0071] 2. Detection of phage thermal stability
[0072] Will 1×10 9 pfu / mL bacteriophage Bp7 proliferation solution at 40°C, 50°C, 60°C, 70°C, 80°C, and 90°C, respectively, with two p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com