Method for producing non-woven fabric, non-woven fabric, device for producing non-woven fabric, and support for producing non-woven fabric
A manufacturing method and technology of non-woven fabrics, applied in textiles and papermaking, non-woven fabrics, fabric surface trimming, etc., can solve the problems of poor appearance, poor continuous production, disturbed fiber fabrics, etc., and achieve a firm network structure and shape-forming properties Excellent, high formability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
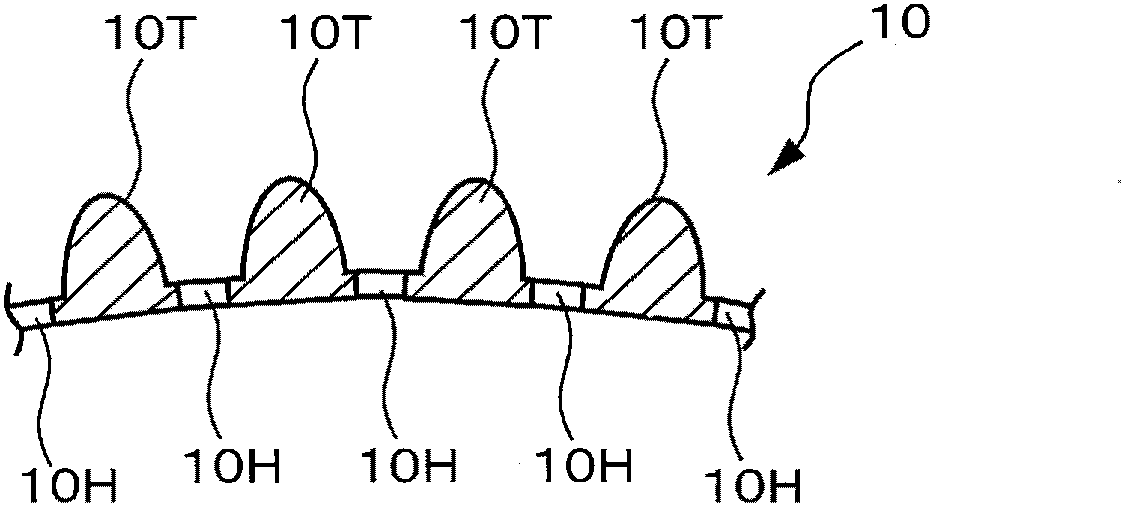
[0101] as mentioned above figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the manufacturing method of the nonwoven fabric of the first embodiment is realized by the aforementioned nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus 1 .
[0102] First, the fabric 60 is fed by the feeding part 21 to the surface of the support body 10 on which the protrusion-shaped part 10T is formed.
[0103] The fiber material that can be used for the fibers of the fabric 60 is not particularly limited. Specifically, the following fibers etc. are mentioned. There are polyolefin fibers such as polyethylene (PE) fibers and polypropylene (PP) fibers, and fibers using thermoplastic resins such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyamide alone. Furthermore, there are conjugated fibers having structures such as core-in-sheath type and side-by-side type. Conjugated fibers are preferably used in the present invention. Here, the composite fiber includes a core-sheath fiber in which a high-melting-point component is a c...
Embodiment 1
[0121] Example 1 was produced by the above-mentioned production method of the first embodiment under the following conditions. That is, the fiber of the fabric 60 used the composite fiber of the core sheath structure whose core part is polyethylene terephthalate (melting point: 255 degreeC), and the sheath part is polyethylene (melting point: 132 degreeC). The fabric 60 is conveyed by the support body 10 and the air conveyor 23 provided only on the blowing side of the first nozzle part 11, and the surface of the support body 10 is shaped into unevenness by blowing the first hot air W1 and the second hot air W2. shape. The temperature of the first hot air W1 is set to 80° C., and the wind speed is set to 25 m / sec. The temperature of the second hot air W2 is set to 145° C., and the wind speed is set to 5.0 m / sec. The processing speed for processing into a concave-convex shape is 50 m / min. Also, the fabric 60 has a basis weight of 27 g / m 2 , the thickness is 3.1mm. A test bod...
Embodiment 2
[0122] In Example 2, a nonwoven fabric test body was produced under the same conditions as in Example 1 above except that the wind speed of the first hot air W1 was set to 50 m / sec and the thickness of the fabric 60 was 3.2 mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com