Bacterium lactobacillus helveticus having high proteolysis activity
A technology of lactobacillus and lactic acid bacteria, applied in the field of lactic acid bacteria, can solve the problems of unstudied fermented milk, etc., and achieve the effect of good flavor, easy to drink or eat
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0160] [Example 1] Identification of Lactobacillus helveticus CP3232 bacterial strain
[0161] Lactobacillus helveticus CM4 strain (accession number FERM BP-6060) was cultivated. A new Lactobacillus helveticus CP3232 strain showing properties as described in Examples 2 to 5 was obtained from a mutant strain derived from said CM4 strain.
[0162] The Lactobacillus helveticus CP3232 strain was anaerobically cultured in an MRS agar medium at 37° C. for 24 hours, and then the morphologically observed characteristics of the obtained colonies, their physiological characteristics and the like were examined. In addition, the 16S rRNA sequence was determined and confirmed to have 99.9% homology with another Lactobacillus helveticus strain (type strain). Therefore, it was revealed that the strain thus obtained definitely belongs to Lactobacillus helveticus and is a new strain.
Embodiment 2
[0163] [Example 2] Preparation of fermented milk
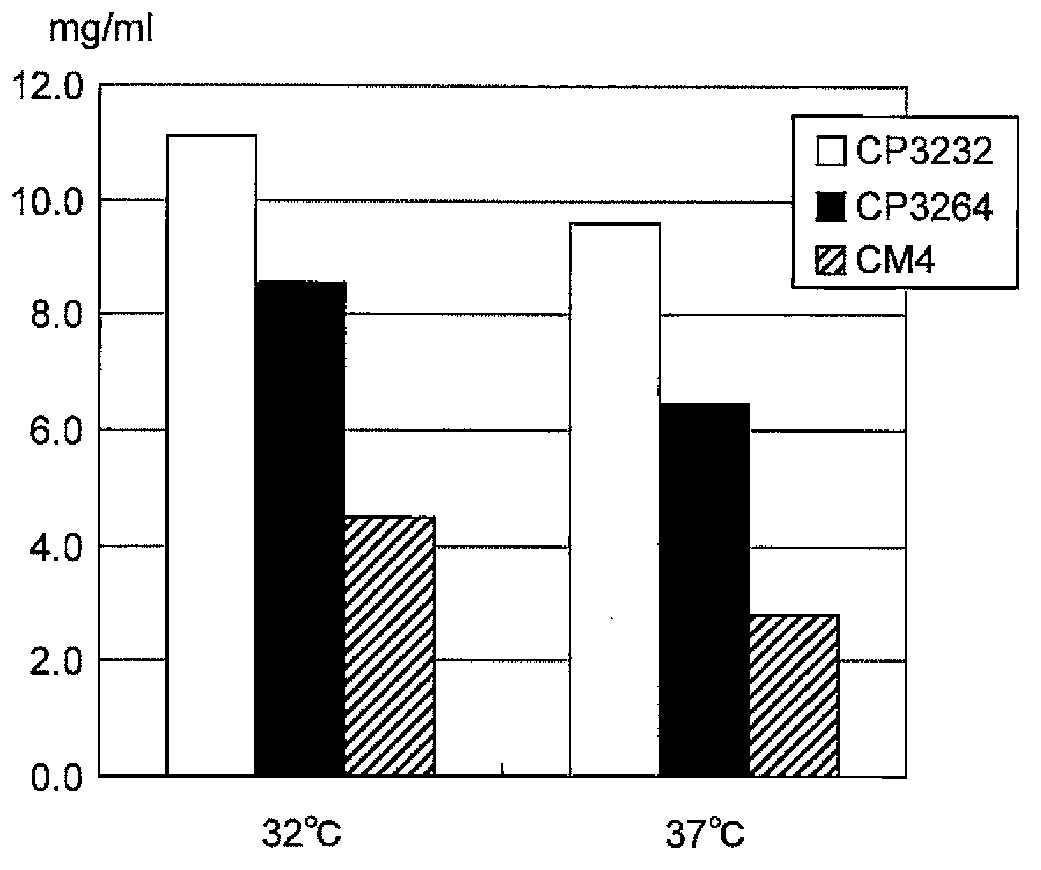
[0164]9.00% (w / w) reconstituted skim milk powder was sterilized by increasing the temperature to 95°C and then cooled to 15°C. The resultant was used as a milk medium. Fermented milk containing lactic acid bacteria (5%) was added to the milk medium (for inoculation), followed by culturing at 37° C. for 24 hours. Repeat this step, and use the fermented milk thus obtained as a starter. This starter (3%) was added to the milk medium, followed by culturing at 32°C or 37°C for 24 hours. The pH and acidity of this fermented milk were measured. Acidity was measured using a Hiranuma automatic titrator COMTITE-450 (Hiranuma Sangyo Co., Ltd.). Lactobacillus helveticus CP3232 strain and Lactobacillus helveticus CP3264 strain (isolated from a commercially available antihypertensive drug), Lactobacillus helveticus CM4 strain (accession number FERM BP-6060), Lactobacillus helveticus CP1092 strain as lactic acid bacteria were used , Lac...
Embodiment 3
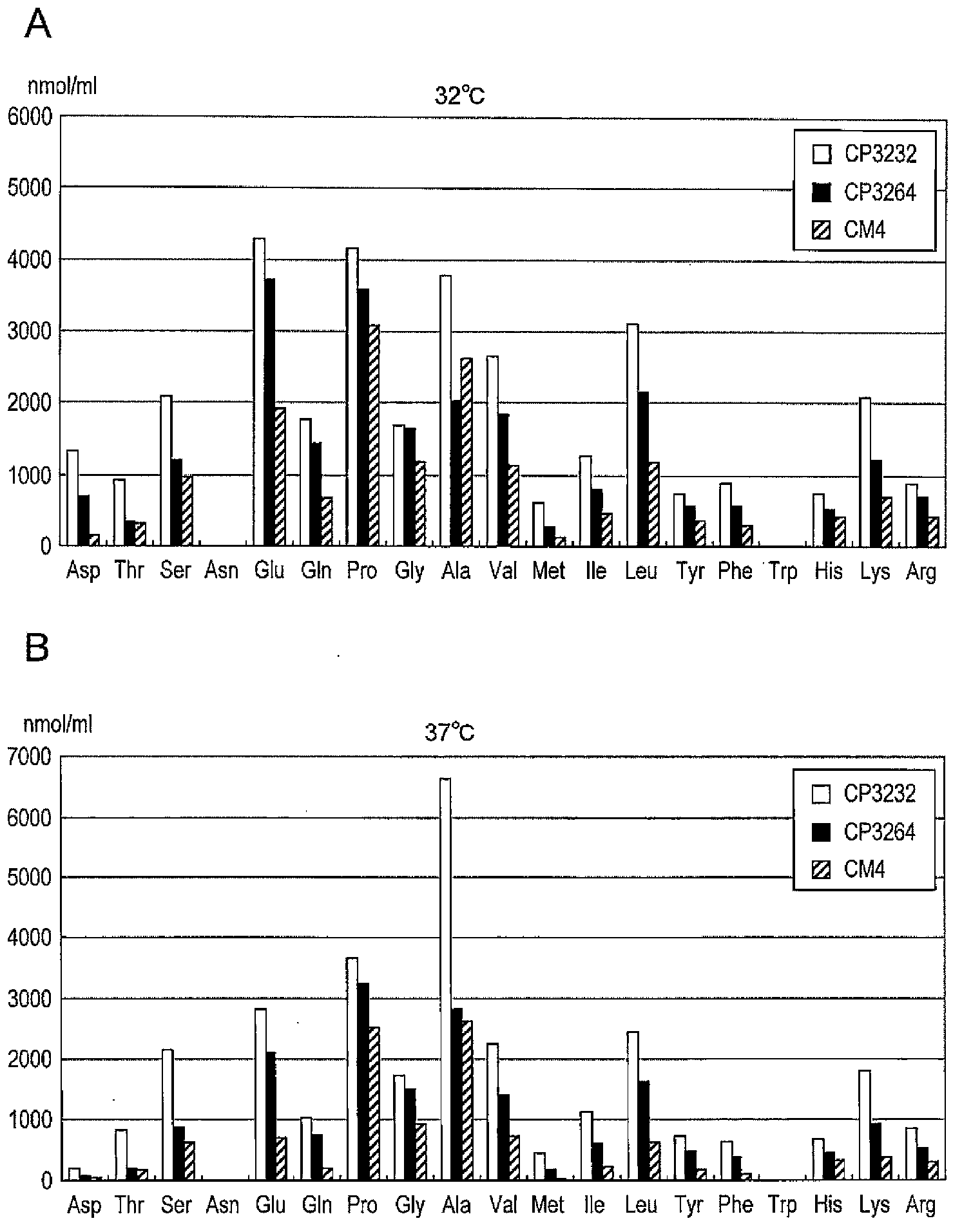
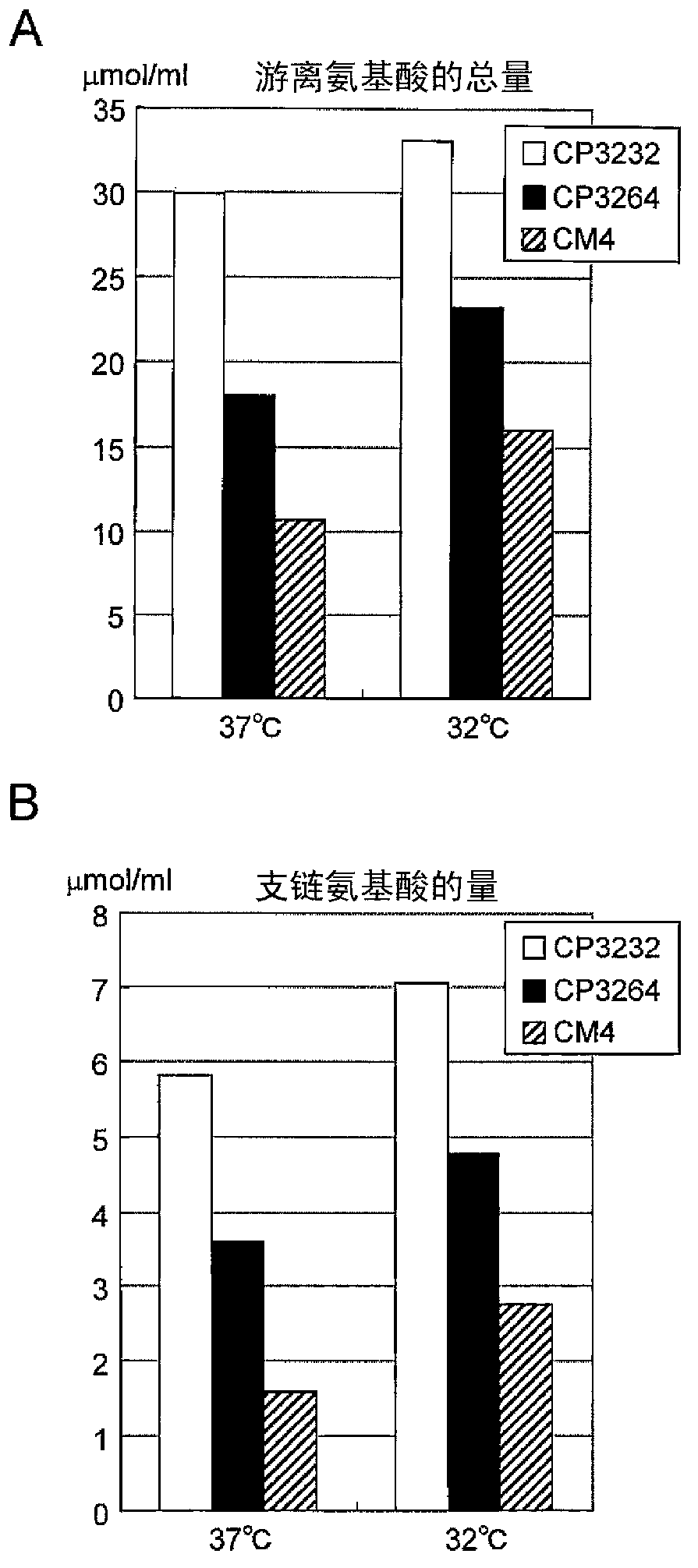
[0171] [Example 3] Determination of free amino acids in fermented milk supernatant
[0172] The fermented milk obtained in Example 2 was centrifuged at 10000 g for 10 minutes. The supernatant was appropriately diluted with distilled water, the solution was filtered with a 0.2 μM membrane filter, and then measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, Shimadzu Corporation) using an amino acid automatic analyzer (C-R7A / LC-10A). Analysis conditions are described below.
[0173] Column: Shim-pack Amino-Li (100mmL×6.0mmI.D.)
[0174] Ammonia trap: Shim-pack ISC-30Li (50mmL×4.0mmI.D.)
[0175] Column temperature: 38°C to 58°C
[0176] Reaction temperature: 65°C
[0177] Mobile phase: Shimadzu mobile phase kit for amino acid analysis, namely, Li type
[0178] Reaction solution: Shimadzu reaction solution kit for amino acid analysis, i.e., OPA reagent
[0179] Flow rate: 0.4ml / min.
[0180] Sodium hypochlorite was added to the reaction solution to detect proline. Fl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com