Lithium salt-graphene derivative composite material and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of composite materials and derivatives, applied in structural parts, electrical components, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable electrode materials, low cycle life, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
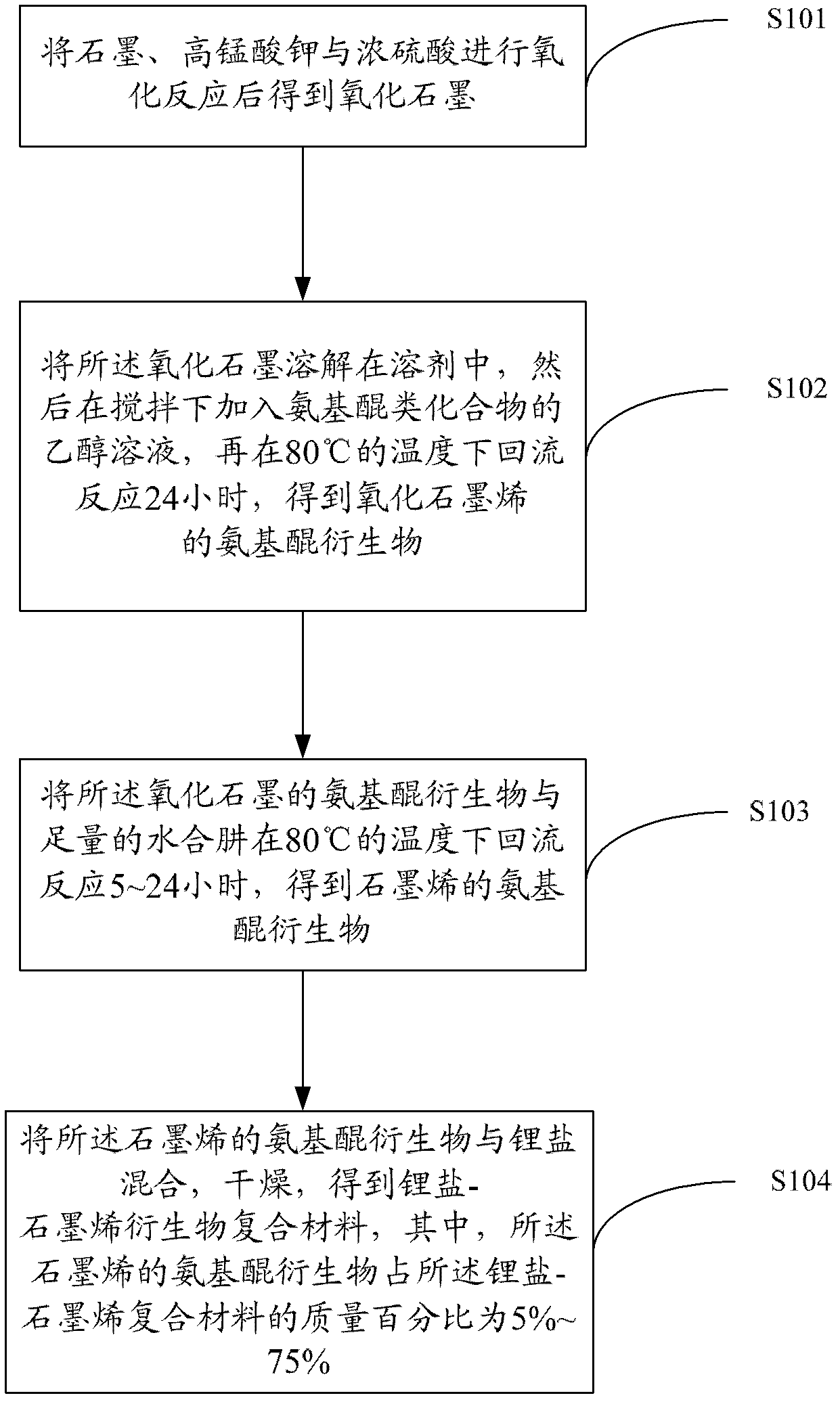
[0026] see figure 1 , the preparation method of the lithium salt-graphene derivative composite material includes the following steps.
[0027] Step S101, oxidizing graphite, potassium permanganate and concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain graphite oxide.
[0028] Graphite oxide can be prepared by a modified Hummers method (Hummers WS, Offeman R E. [J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1958, 80: 1339-1339). The specific steps are: add 20g of 50 mesh graphite powder, 10g of potassium persulfate and 10g of phosphorus pentoxide into concentrated sulfuric acid at 80°C, stir evenly, cool for more than 6h, wash until neutral, and dry. Add the dried sample to 230mL of concentrated sulfuric acid at 0°C, then add 60g of potassium permanganate, keep the temperature of the mixture below 20°C, then keep it in an oil bath at 35°C for 2h, then slowly add 920mL of deionized water . After 15 minutes, add 2.8L of deionized water (which contains 50mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide), after which the color of the mixtu...
Embodiment 1
[0048] Present embodiment prepares the technological process of graphite oxide as follows:
[0049] Graphite → Graphite Oxide → Graphene Oxide Derivatization → Graphene Derivatives → Lithium Salt Graphene Derivatives
[0050] (1) Graphite: 99.5% purity.
[0051] (2) Graphite oxide: Add 20g of 50 mesh graphite powder, 10g of potassium persulfate and 10g of phosphorus pentoxide into concentrated sulfuric acid at 80°C, stir evenly, cool for more than 6h, wash until neutral, and dry. Add the dried sample to 230mL of concentrated sulfuric acid at 0°C, then add 60g of potassium permanganate, keep the temperature of the mixture below 20°C, then keep it in an oil bath at 35°C for 2h, then slowly add 920mL of deionized water . After 15 minutes, add 2.8L of deionized water (which contains 50mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide), after which the color of the mixture turns bright yellow. Suction filtration while hot, and then wash with 5L of 10% hydrochloric acid, suction filtration, Graphite o...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The technical process that the present invention prepares graphite oxide is as follows:
[0057] Graphite → Graphite Oxide → Graphene Oxide Derivatization → Graphene Derivatives → Lithium Salt Graphene Derivatives
[0058] (1) Graphite: 99.5% purity.
[0059] (2) Graphite oxide: the preparation method is the same as in Example 1.
[0060] (3) Graphite oxide derivatization: 30mL 1g / L graphite oxide was ultrasonically dissolved in DMF solution for 1h, the obtained suspension was added to a three-necked flask, and 50mL 1g / L 5,8-diaminonaphthoquinone was added under vigorous stirring The ethanol solution of the amine was refluxed at 80° C. for 24 hours, and then a catalytic amount of ferric chloride solution was added, and the solution was refluxed at 80° C. for 24 hours to obtain a 5,8-diaminonaphthoquinone amine polymer derivative of graphene oxide.
[0061] (4) Graphene derivatives: the 5,8-diaminonaphthoquinone amine polymer derivatives of graphene oxide obtained in (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com