Rapid detection method for water-soluble azo dyes in foods
A technology of azo dyes and detection methods, which is applied in the direction of analyzing materials through chemical reactions and analyzing materials through observation of the influence of chemical indicators. Problems such as rapid detection and complicated operation can achieve the effects of shortening pre-processing time and detection time, timely and effective rapid screening, and strong anti-interference ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Detection of water-soluble azo dyes in food.
[0041] Take 3.0 g of the sample, add 15 mL of dilute ammonia solution, shake well in a warm water bath, take the supernatant after standing still, add citric acid solution to the supernatant to adjust the pH to 5.8, and obtain the sample extract; extract the sample The liquid was transferred to a polyamide column, the filtrate was separated, and the pigment was enriched on the polyamide column, and the polyamide column was washed 2 to 3 times with a mixture of methanol and acetic acid, 3 mL each time; Elute the polyamide column washed with a mixture of methanol and acetic acid for 2 to 3 times, 2 mL each time, and collect the eluate; divide the eluate into a control group and a detection group in equal amounts, and add Shake 1mL of saturated ammonium acetate solution and 0.1g of zinc powder for 10-20 seconds, filter, and compare with the control group to observe whether the color of the test group fades. If the co...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 Detection limit of water-soluble azo dyes in food.
[0045] Get the flour product sample, add tartrazine standard solution of different volumes respectively and shake up, after detecting by the detection method among the embodiment 1, adjust pH value to neutrality with concentrated acetic acid, distilled water is settled to 10mL, observes the color depth of solution, Filter, and detect the actual concentration of the spiked solution according to GB 5009.35-2003, and make a blank sample control at the same time.
[0046] The detection limit experiments of sunset yellow, carmine, brilliant blue, amaranth, allura red, acid orange II, acid scarlet, and acid golden G are the same as lemon yellow. See Table 2 for the theoretical concentration of the spiked solution and the actual detected concentration after treatment by this method.
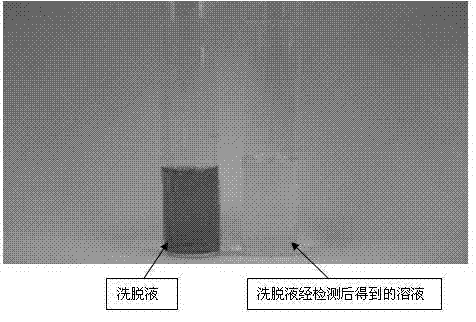
[0047] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the eluent of some spiked samples and their qualitative results, in which 1 is car...
Embodiment 3
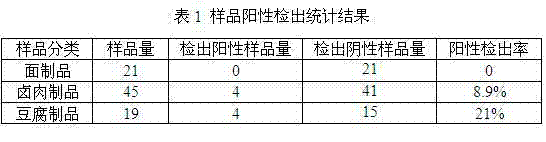
[0050] Example 3 Sample detection positive coincidence rate.
[0051] 85 samples in the embodiment one are detected by GB / T5009.35-2003 "Measurement of Synthetic Colorant in Food", the detection result is compared with the detection result of the inventive method, and the positive coincidence rate is calculated, and the results are as shown in the table 3 shown. As can be seen from Table 3, the method of the present invention has no significant difference with the national standard method in the accuracy of the positive detection rate.
[0052]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com